Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet for Biology Students
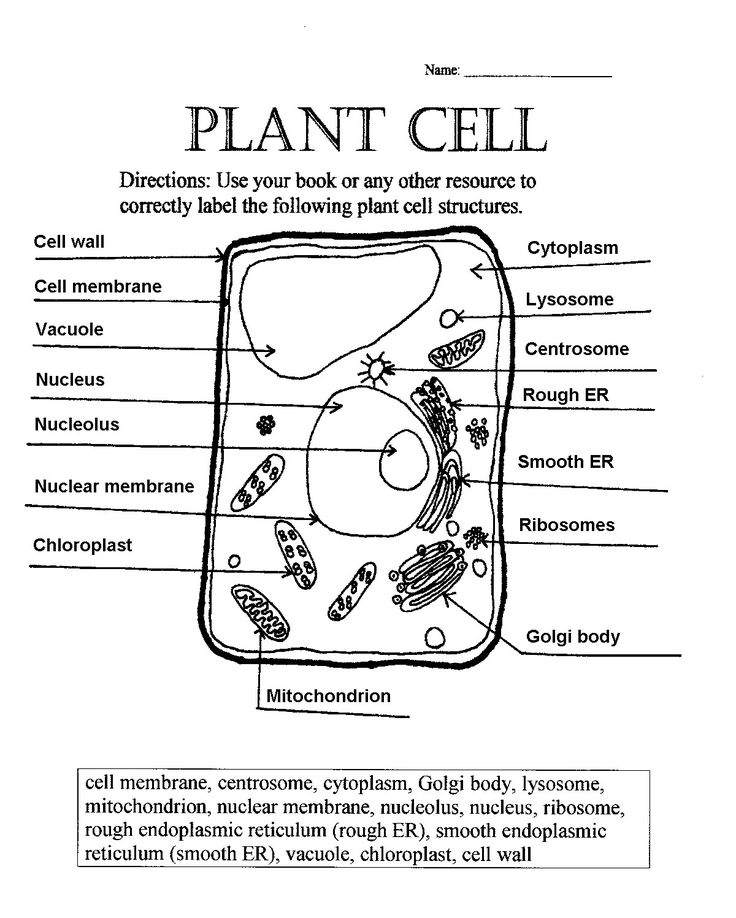
Understanding Plant Cell Structure: A Comprehensive Guide
Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants, responsible for carrying out various biological processes necessary for plant growth and development. The plant cell structure is unique and complex, comprising various organelles that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis. In this article, we will delve into the world of plant cells, exploring their structure, functions, and importance in plant biology.
Plant Cell Diagram: Labeling the Components
A plant cell diagram is a crucial tool for understanding the organization and relationships between different organelles within the cell. The diagram below illustrates the main components of a plant cell:
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Provides structural support and protection to the cell |
| Plasma Membrane | Regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell |
| Cytoplasm | Site of various metabolic reactions, including glycolysis and protein synthesis |
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material (DNA) and controls cell growth and division |
| Chloroplasts | Site of photosynthesis, responsible for producing glucose and oxygen |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy (ATP) for the cell through cellular respiration |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Involved in protein synthesis, transport, and storage |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport |
| Lysosomes | Contains digestive enzymes, responsible for cellular digestion and recycling |
| Vacuoles | Stores water, nutrients, and waste products, maintaining cellular homeostasis |
📝 Note: The plant cell diagram is a simplified representation of the cell's structure. The actual structure may vary depending on the plant species and cell type.
Functions of Plant Cell Organelles
Each organelle within the plant cell has a unique function, working together to maintain cellular homeostasis and support plant growth and development.
- Cell Wall: Provides structural support, protection, and maintains cell shape.
- Plasma Membrane: Regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell, controlling the cell’s interactions with its environment.
- Cytoplasm: Site of various metabolic reactions, including glycolysis and protein synthesis, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Nucleus: Contains genetic material (DNA) and controls cell growth, division, and differentiation.
- Chloroplasts: Responsible for photosynthesis, producing glucose and oxygen essential for plant growth and development.
- Mitochondria: Produces energy (ATP) for the cell through cellular respiration, supporting plant growth and development.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Involved in protein synthesis, transport, and storage, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport, ensuring proper cellular function.
- Lysosomes: Contains digestive enzymes, responsible for cellular digestion and recycling, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Vacuoles: Stores water, nutrients, and waste products, maintaining cellular homeostasis and supporting plant growth and development.
Importance of Plant Cell Structure in Plant Biology
The plant cell structure plays a crucial role in plant biology, supporting various biological processes essential for plant growth and development. Understanding the plant cell structure is essential for:
- Plant Growth and Development: The plant cell structure supports plant growth and development by providing the necessary organelles for photosynthesis, energy production, and cellular homeostasis.
- Cellular Communication: The plant cell structure enables cellular communication, allowing cells to interact with their environment and respond to stimuli.
- Disease Resistance: The plant cell structure plays a crucial role in disease resistance, with organelles such as the cell wall and plasma membrane providing protection against pathogens.
- Crop Improvement: Understanding the plant cell structure is essential for crop improvement, as it allows scientists to develop new crop varieties with improved yields and disease resistance.
What is the main function of the cell wall in plant cells?
+The main function of the cell wall in plant cells is to provide structural support, protection, and maintain cell shape.
What is the role of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, producing glucose and oxygen essential for plant growth and development.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus in plant cells?
+The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport, ensuring proper cellular function.
In conclusion, the plant cell structure is a complex and dynamic entity, comprising various organelles that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis and support plant growth and development. Understanding the plant cell structure is essential for plant biology, crop improvement, and disease resistance. By exploring the world of plant cells, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern plant life.
Related Terms:
- Plant cell worksheet With Answers
- Plant cell Worksheet PDF
- Animal cell diagram
- Animal cell worksheet
- Animal cell labeling worksheet PDF
- Plant cell worksheet Grade 6



