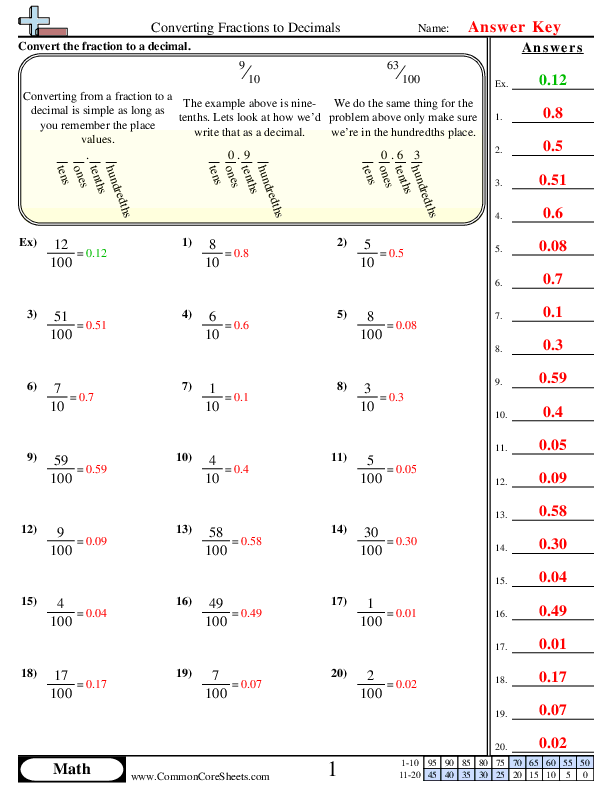
Label Plant Cell Worksheet

Exploring the Structure of Plant Cells: A Comprehensive Worksheet
Plant cells are the basic building blocks of plants, and understanding their structure is crucial for botany, biology, and environmental science. In this worksheet, we will delve into the components of a plant cell, exploring their functions and importance in plant growth and development.
Plant Cell Components
A plant cell is made up of several organelles, each with distinct functions. The main components of a plant cell include:
- Cell Wall: A rigid layer outside the cell membrane, providing support, protection, and maintaining the cell’s shape.
- Cell Membrane: A thin, semi-permeable membrane surrounding the cell, regulating the movement of materials in and out.
- Cytoplasm: A jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane, containing organelles and playing a crucial role in cell signaling and metabolism.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) and regulating cell growth and division.
- Mitochondria: The powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration.
- Chloroplasts: Organelles responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranous tubules and cisternae, involved in protein synthesis, transport, and storage.
- Golgi Apparatus: A complex of flattened sacs and tubules, responsible for protein modification, sorting, and packaging.
- Lysosomes: Membrane-bound sacs containing digestive enzymes, breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances.
- Vacuoles: Storage organelles, containing water, salts, and other substances, helping maintain cell turgor pressure.
Functions of Plant Cell Components
Each component of a plant cell plays a vital role in maintaining the cell’s homeostasis and ensuring proper functioning. Some of the key functions include:
- Cell Wall: Provides structural support, protection from pathogens, and maintains cell shape.
- Cell Membrane: Regulates the movement of materials, communicates with other cells, and responds to environmental stimuli.
- Cytoplasm: Facilitates cell signaling, metabolism, and maintains cellular organization.
- Nucleus: Regulates gene expression, cell growth, and division.
- Mitochondria: Generates energy through cellular respiration, powering cellular activities.
- Chloroplasts: Converts light energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- ER: Synthesizes and transports proteins, lipids, and other molecules.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport or storage.
- Lysosomes: Breaks down and recycles cellular waste and foreign substances.
- Vacuoles: Stores water, salts, and other substances, maintaining cell turgor pressure.
Plant Cell Diagram Labeling
Use the following diagram to label the components of a plant cell:
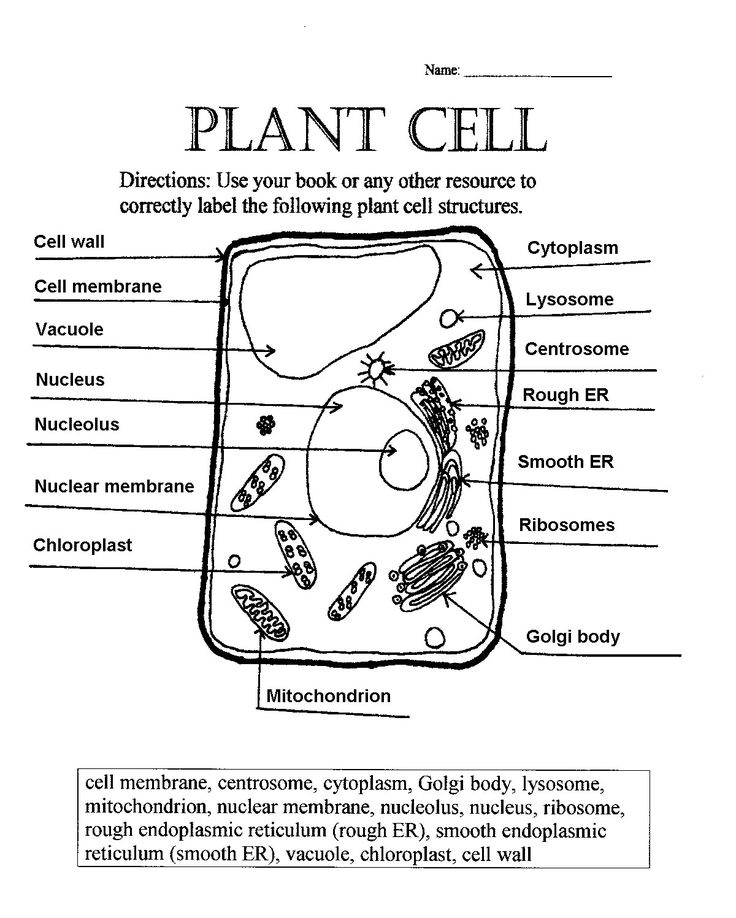
| 1. Cell Wall | _________________________ |
| 2. Cell Membrane | _________________________ |
| 3. Cytoplasm | _________________________ |
| 4. Nucleus | _________________________ |
| 5. Mitochondria | _________________________ |
| 6. Chloroplasts | _________________________ |
| 7. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | _________________________ |
| 8. Golgi Apparatus | _________________________ |
| 9. Lysosomes | _________________________ |
| 10. Vacuoles | _________________________ |
📝 Note: Use the above information to label the components of the plant cell diagram accurately.
By understanding the structure and functions of plant cells, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of plant biology.
The plant cell is a dynamic and highly organized system, with each component working together to maintain cellular homeostasis and ensure proper functioning.
Related Terms:
- Plant cell worksheet With Answers
- Plant cell Worksheet PDF
- Animal cell worksheet
- Plant cell worksheet Grade 6
- Printable plant cell diagram
- Plant cell labeled