Isotopes Practice Worksheet for Chemistry Mastery
Understanding Isotopes: A Key to Chemistry Mastery
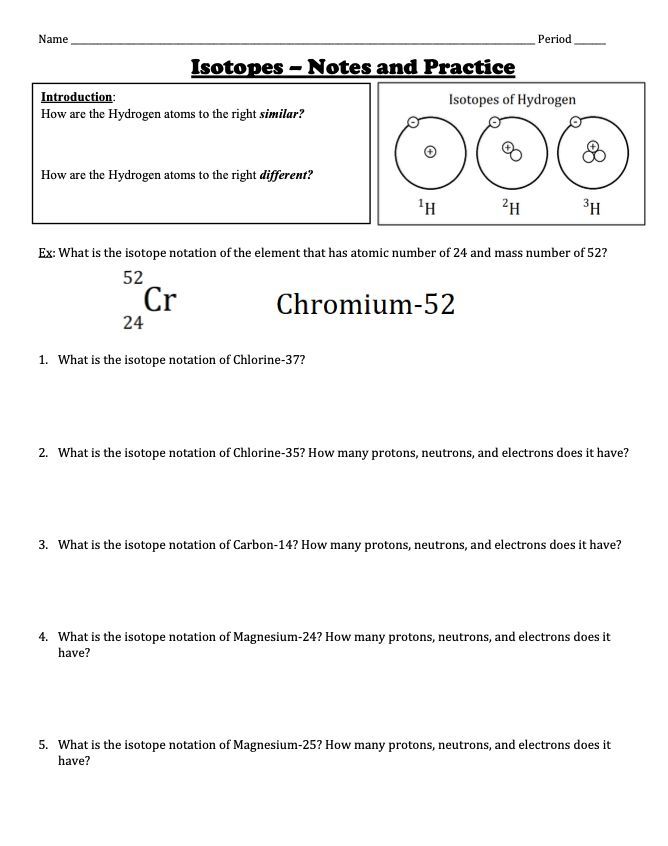
Isotopes are atoms of the same chemical element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. This fundamental concept in chemistry is crucial for understanding various chemical and physical properties of elements. In this worksheet, we will delve into the world of isotopes, exploring their definition, types, and significance in chemistry.
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element that share the same number of protons (atomic number) but have different numbers of neutrons. This variation in neutron number leads to differences in the atomic mass of isotopes. For example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 are isotopes of the element carbon, each having 6 protons but 6, 7, and 8 neutrons, respectively.
Types of Isotopes
There are two main types of isotopes: stable and radioactive.
- Stable Isotopes: These isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay and remain unchanged over time. Examples include carbon-12 and oxygen-16.
- Radioactive Isotopes: These isotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive decay, emitting radiation as they transform into more stable forms. Carbon-14 is a well-known example of a radioactive isotope.
Significance of Isotopes in Chemistry
Isotopes play a vital role in various fields of chemistry, including:
- Chemical Reactions: Isotopes can be used to trace the path of chemical reactions, helping scientists understand reaction mechanisms and kinetics.
- Geochemistry: Isotopes are used to study the Earth’s history, including the formation of rocks and the movement of tectonic plates.
- Medicine: Radioactive isotopes are used in medical applications, such as cancer treatment and imaging.
Key Concepts and Formulas
- Atomic Mass: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Mass Number: The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Isotopic Notation: A way of representing isotopes using the symbol of the element, followed by the mass number (e.g., carbon-12).
📝 Note: Isotopes have the same chemical properties but differ in physical properties, such as mass and radioactivity.
Practice Problems
- What is the main difference between stable and radioactive isotopes?
- Stable isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay, while radioactive isotopes are unstable and undergo decay.
- How are isotopes used in medical applications?
- Radioactive isotopes are used in cancer treatment and imaging.
- What is the significance of isotopes in geochemistry?
- Isotopes are used to study the Earth’s history, including the formation of rocks and the movement of tectonic plates.
Real-World Applications
- Radiocarbon Dating: A method used to determine the age of organic materials by measuring the amount of carbon-14 present.
- Nuclear Power: Radioactive isotopes are used as fuel in nuclear reactors to generate electricity.
Conclusion
Isotopes are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding their properties and applications is crucial for mastering the subject. By recognizing the differences between stable and radioactive isotopes and exploring their significance in various fields, chemists can gain a deeper understanding of the atomic world and its many wonders.
What is the main difference between isotopes and elements?
+
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, while elements are substances consisting of atoms with the same number of protons.
How are isotopes used in environmental science?
+
Isotopes are used to study the movement of water and nutrients in ecosystems, as well as to track the source of pollutants.
What is the most common use of radioactive isotopes?
+
Radioactive isotopes are most commonly used in medical applications, such as cancer treatment and imaging.