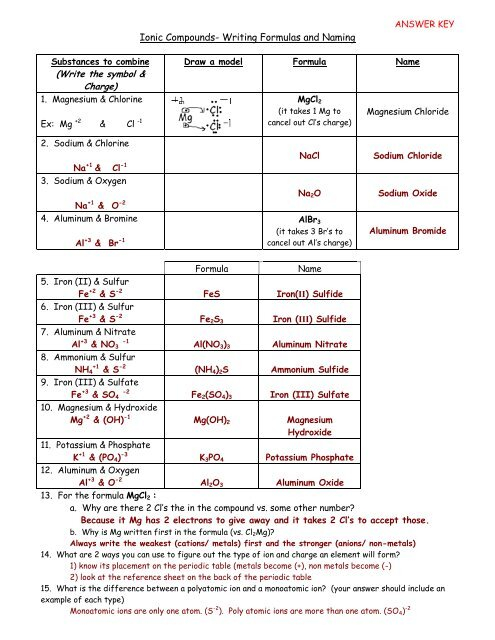
Ionic Compounds Worksheet
Understanding Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. These ions are then attracted to each other and combine to form a compound. In this worksheet, we will explore the basics of ionic compounds, their formation, and their properties.
What are Ionic Compounds?
Ionic compounds are composed of two types of ions: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions, typically formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons. Anions are negatively charged ions, typically formed when a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons. The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together and forms an ionic compound.
💡 Note: Ionic compounds are also known as salts.
Formation of Ionic Compounds
The formation of ionic compounds can be represented by the following general equation:
Metal (M) + Nonmetal (NM) → Ionic Compound (MNM)
For example:
Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) → NaCl (sodium chloride)
In this reaction, the sodium atom loses an electron to form a positively charged sodium ion (Na+), while the chlorine atom gains an electron to form a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-). The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other and form an ionic compound.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have several distinct properties, including:
• High melting and boiling points: Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic attraction between the ions. • Brittleness: Ionic compounds are brittle and can break easily due to the rigid structure of the ions. • Solubility in water: Many ionic compounds are soluble in water, as the polar water molecules can dissolve the ions. • Conductivity: Ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water.
Naming Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are named based on the cation and anion present in the compound. The name of the cation is first, followed by the name of the anion. For example:
NaCl - Sodium chloride CaO - Calcium oxide
👀 Note: When naming ionic compounds, the Roman numerals in parentheses are used to indicate the charge on the ion.
Types of Ionic Compounds
There are several types of ionic compounds, including:
• Binary ionic compounds: Containing only two elements, such as NaCl. • Ternary ionic compounds: Containing three elements, such as CaCO3 (calcium carbonate). • Polyatomic ionic compounds: Containing multiple polyatomic ions, such as NH4NO3 (ammonium nitrate).
Conclusion
Ionic compounds are an essential part of chemistry, and understanding their formation, properties, and naming conventions is crucial for any chemistry student. In this worksheet, we have covered the basics of ionic compounds and provided examples to illustrate key concepts. By mastering the concepts presented here, you will be well on your way to becoming proficient in chemistry.
What is the main difference between ionic compounds and molecular compounds?
+Ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions, while molecular compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
What is the purpose of using Roman numerals in parentheses when naming ionic compounds?
+Roman numerals in parentheses are used to indicate the charge on the ion.
What are some common properties of ionic compounds?
+Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points, are brittle, and are soluble in water.