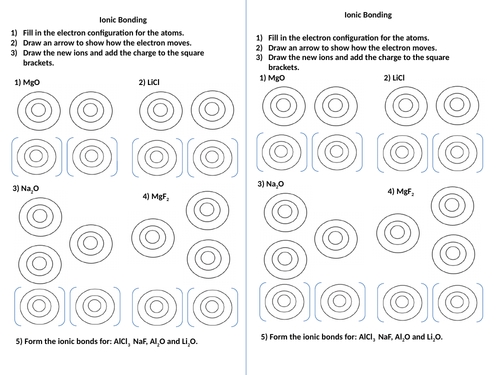
Ionic Bonding Practice Worksheet Answers for Chemistry Students
Understanding Ionic Bonding: A Comprehensive Guide for Chemistry Students
Ionic bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. It is a crucial aspect of understanding the structure and properties of various compounds. In this article, we will delve into the world of ionic bonding, exploring its definition, types, examples, and practice exercises to help chemistry students master this concept.
What is Ionic Bonding?
Ionic bonding occurs when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions holds them together, forming a strong chemical bond. This type of bonding typically occurs between metals and nonmetals.
Types of Ionic Bonds
There are several types of ionic bonds, including:
- Monatomic ions: Formed when a single atom gains or loses electrons to form an ion.
- Polyatomic ions: Composed of multiple atoms that have gained or lost electrons to form an ion.
- Ionic compounds: Formed when a metal ion bonds with a nonmetal ion.
Examples of Ionic Compounds
Some common examples of ionic compounds include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
- Aluminum oxide (Al2O3)
- Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2)
Formation of Ionic Bonds
The formation of ionic bonds involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. This process can be represented by the following steps:
- Electron transfer: One or more electrons are transferred from a metal atom to a nonmetal atom.
- Ion formation: The metal atom loses electrons to form a positively charged ion (cation), while the nonmetal atom gains electrons to form a negatively charged ion (anion).
- Electrostatic attraction: The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other, forming a strong chemical bond.
Practice Exercises
To reinforce your understanding of ionic bonding, try the following practice exercises:
Exercise 1: Write the electron configuration for the following ions:
- Na+ (sodium ion)
- Cl- (chloride ion)
- Ca2+ (calcium ion)
- O2- (oxide ion)
Exercise 2: Identify the type of bond formed between the following atoms:
- Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl)
- Calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O)
- Aluminum (Al) and nitrogen (N)
Exercise 3: Write the chemical formula for the following ionic compounds:
- Sodium and chlorine
- Calcium and oxygen
- Aluminum and nitrogen
📝 Note: Use the periodic table to determine the electron configuration and charges of the ions.
Answers to Practice Exercises
Exercise 1:
- Na+: 1s2 2s2 2p6
- Cl-: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
- Ca2+: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
- O2-: 1s2 2s2 2p6
Exercise 2:
- Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl): Ionic bond
- Calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O): Ionic bond
- Aluminum (Al) and nitrogen (N): Covalent bond
Exercise 3:
- Sodium and chlorine: NaCl
- Calcium and oxygen: CaO
- Aluminum and nitrogen: AlN
Conclusion
Ionic bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the structure and properties of various compounds. By mastering this concept, chemistry students can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of the molecular world. Practice exercises, such as those provided in this article, can help reinforce your understanding of ionic bonding and prepare you for more advanced chemistry topics.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
+Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Can ionic bonds form between two nonmetals?
+No, ionic bonds typically form between metals and nonmetals. When two nonmetals bond, they usually form covalent bonds.
What is the purpose of electron configuration in ionic bonding?
+Electron configuration helps us determine the number of electrons transferred between atoms and the charges of the resulting ions.