Integumentary System Worksheet: Understanding Skin and Its Functions
Introduction to the Integumentary System
The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body, and it plays a crucial role in protecting us from external factors such as temperature, humidity, and external damage. The system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands. In this worksheet, we will explore the structure and functions of the skin, as well as the other components of the integumentary system.
Functions of the Skin
The skin is the largest organ of the body, covering an area of approximately 22 square feet and weighing around 6 pounds. It performs several vital functions that help maintain our overall health. Some of the main functions of the skin include:
- Protection: The skin acts as a barrier against external factors such as water loss, temperature, and mechanical damage.
- Regulation: The skin helps regulate body temperature through sweating and shivering.
- Sensation: The skin contains nerve endings that allow us to feel sensations such as touch, pressure, and pain.
- Excretion: The skin helps eliminate waste products through sweating.
- Absorption: The skin absorbs certain substances such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide.
Layers of the Skin
The skin consists of several layers, each with its unique structure and function. The main layers of the skin are:
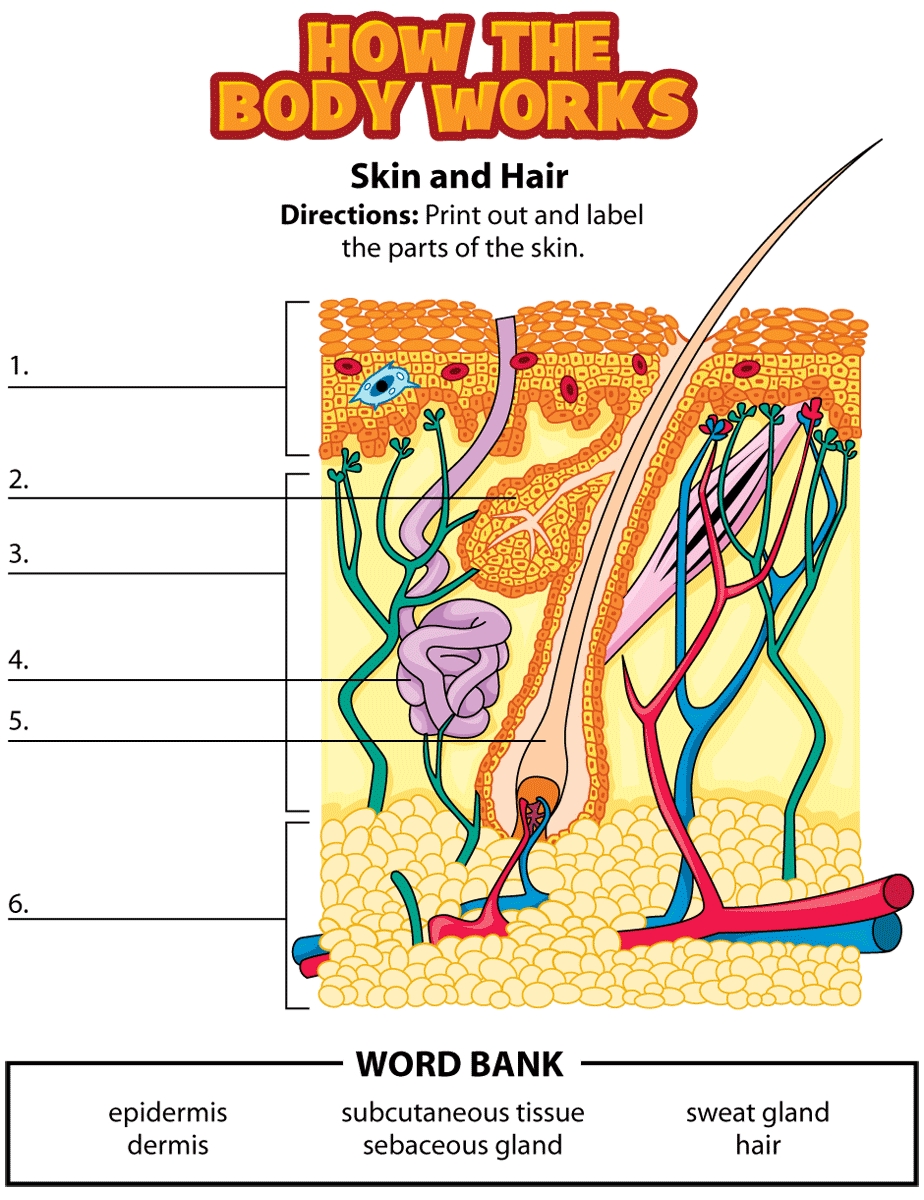
- Epidermis: The outermost layer of the skin, responsible for protecting the body from external damage.
- Dermis: The layer beneath the epidermis, containing blood vessels, nerve endings, and hair follicles.
- Hypodermis: The innermost layer of the skin, attaching the skin to underlying muscles and bones.
Associated Glands and Organs
The integumentary system includes several associated glands and organs that play important roles in maintaining skin health. Some of these include:
- Sweat glands: Produce sweat to regulate body temperature and eliminate waste products.
- Sebaceous glands: Produce sebum to lubricate and protect the skin.
- Hair follicles: Produce hair to provide insulation and protection.
- Nails: Made of keratin, nails protect the tips of fingers and toes.
🔍 Note: The integumentary system also includes other structures such as the eyelids, eyelashes, and lips, which help protect the eyes, nose, and mouth.
Common Disorders and Diseases
The integumentary system is susceptible to various disorders and diseases, some of which include:
- Acne: A skin condition characterized by inflammation and bacterial growth.
- Eczema: A skin condition characterized by dryness, redness, and inflammation.
- Psoriasis: A skin condition characterized by thickening and scaling of the skin.
- Skin cancer: A type of cancer that affects the skin, including melanoma and non-melanoma.
🔍 Note: It's essential to seek medical attention if you experience any unusual skin symptoms or changes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integumentary system plays a vital role in protecting our body and maintaining overall health. Understanding the structure and functions of the skin, as well as the associated glands and organs, can help us appreciate the importance of skin care and maintenance. By taking care of our skin, we can prevent various disorders and diseases, and maintain a healthy and vibrant appearance.
What is the main function of the integumentary system?
+The main function of the integumentary system is to protect the body from external factors such as temperature, humidity, and external damage.
What are the three main layers of the skin?
+The three main layers of the skin are the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
What is the function of sweat glands?
+The function of sweat glands is to produce sweat to regulate body temperature and eliminate waste products.