Accurate HVAC Load Calculation Worksheet Made Easy
Accurate HVAC Load Calculation Worksheet Made Easy
Accurate HVAC load calculation is crucial for selecting the right heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) equipment for your building. An oversized or undersized system can lead to wasted energy, reduced comfort, and increased maintenance costs. In this article, we will guide you through a simplified HVAC load calculation worksheet to help you determine the correct size of your HVAC system.
Understanding the Components of HVAC Load Calculation
Before we dive into the worksheet, it’s essential to understand the components that affect HVAC load calculation. These include:
- Sensible heat: The amount of heat that can be felt, typically measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units).
- Latent heat: The amount of heat required to change the state of a substance (e.g., from liquid to gas), also measured in BTUs.
- Conduction: The transfer of heat through a solid material.
- Convection: The transfer of heat through a fluid (e.g., air or water).
- Radiation: The transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
Step 1: Gather Required Data
To perform an accurate HVAC load calculation, you’ll need to gather the following data:
- Building characteristics:
- Location (city, state, zip code)
- Building size (square footage)
- Number of floors
- Insulation type and R-value
- Window size and type
- Door size and type
- Climate data:
- Outdoor design temperature (heating and cooling)
- Outdoor design humidity
- Occupancy and usage:
- Number of occupants
- Occupancy schedule
- Equipment and lighting loads
- HVAC system characteristics:
- System type (e.g., air-source heat pump, gas furnace)
- System size (if existing)
Step 2: Determine the Load Calculation Method
There are two primary methods for HVAC load calculation: the Manual J method and the Manual S method. Manual J is a more detailed and accurate method, while Manual S is a simplified method. For this example, we’ll use the Manual J method.
Step 3: Calculate the Heating Load
Using the Manual J method, calculate the heating load by considering the following factors:
- Conduction: Calculate the heat loss through walls, floors, ceilings, and windows.
- Convection: Calculate the heat loss through air infiltration and ventilation.
- Radiation: Calculate the heat loss through radiation.
Use the following formulas to calculate the heating load:
- Conduction heat loss (Qc): Qc = U * A * ΔT
- U: overall heat transfer coefficient
- A: surface area
- ΔT: temperature difference
- Convection heat loss (Qcv): Qcv = 0.35 * (A * ΔT)
- A: surface area
- ΔT: temperature difference
- Radiation heat loss (Qr): Qr = 0.17 * (A * ΔT)
- A: surface area
- ΔT: temperature difference
Add the conduction, convection, and radiation heat losses to determine the total heating load.
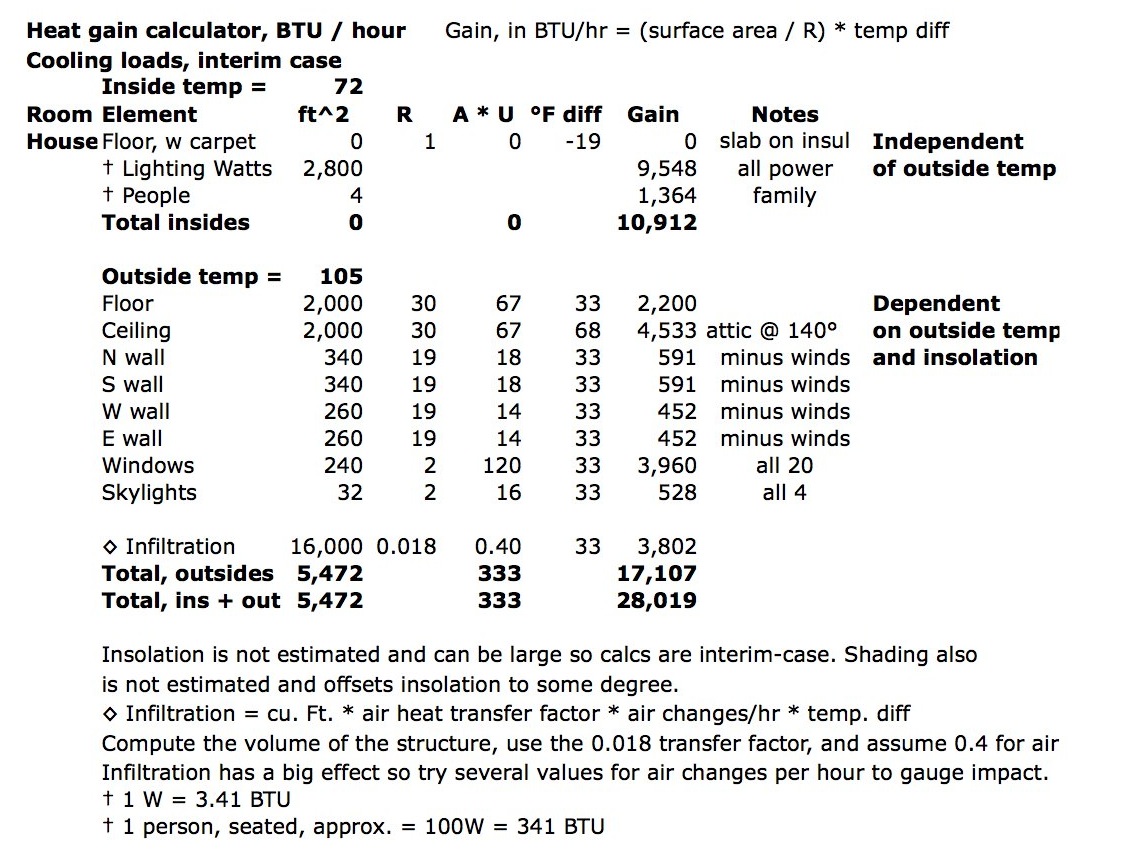
Step 4: Calculate the Cooling Load
Using the Manual J method, calculate the cooling load by considering the following factors:
- Sensible heat: Calculate the heat gain through walls, floors, ceilings, and windows.
- Latent heat: Calculate the heat gain through air infiltration and ventilation.
Use the following formulas to calculate the cooling load:
- Sensible heat gain (Qs): Qs = U * A * ΔT
- U: overall heat transfer coefficient
- A: surface area
- ΔT: temperature difference
- Latent heat gain (Ql): Ql = 0.35 * (A * ΔT)
- A: surface area
- ΔT: temperature difference
Add the sensible and latent heat gains to determine the total cooling load.
Step 5: Determine the HVAC System Size
Using the calculated heating and cooling loads, determine the required HVAC system size. Consider the following factors:
- System type: Choose a system type that meets the calculated loads.
- System size: Select a system size that matches the calculated loads.
📝 Note: Always consult with a professional HVAC engineer or contractor to ensure accurate calculations and proper system sizing.
Conclusion
Accurate HVAC load calculation is crucial for selecting the right HVAC equipment for your building. By following these simplified steps, you can determine the correct size of your HVAC system. Remember to consult with a professional HVAC engineer or contractor to ensure accurate calculations and proper system sizing.
What is the purpose of HVAC load calculation?
+The purpose of HVAC load calculation is to determine the correct size of the HVAC system for a building, ensuring efficient operation, comfort, and energy savings.
What are the two primary methods for HVAC load calculation?
+The two primary methods are the Manual J method and the Manual S method. Manual J is a more detailed and accurate method, while Manual S is a simplified method.
What factors affect HVAC load calculation?
+HVAC load calculation is affected by building characteristics, climate data, occupancy and usage, and HVAC system characteristics.