Genetics X Linked Genes Worksheet Answers Explained
Understanding X-Linked Genes: A Comprehensive Guide
X-linked genes are a crucial aspect of genetics, and understanding how they work is essential for anyone interested in the field. In this post, we will delve into the world of X-linked genes, explore how they are inherited, and provide answers to common worksheet questions.
What are X-Linked Genes?
X-linked genes are genes that are located on the X chromosome. In humans, females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). X-linked genes can be either dominant or recessive, and their expression is influenced by the sex of the individual.
How are X-Linked Genes Inherited?
The inheritance of X-linked genes follows a specific pattern. Since females have two X chromosomes, they can be either homozygous (having two copies of the same gene) or heterozygous (having one copy of each gene). Males, on the other hand, have only one X chromosome, so they can only be hemizygous (having one copy of the gene).
When it comes to X-linked genes, females can be:
- Homozygous dominant (XX): Having two copies of the dominant gene
- Homozygous recessive (xx): Having two copies of the recessive gene
- Heterozygous (Xx): Having one copy of the dominant gene and one copy of the recessive gene
Males, on the other hand, can only be:
- Hemizygous dominant (X): Having one copy of the dominant gene
- Hemizygous recessive (x): Having one copy of the recessive gene
Types of X-Linked Genes
There are several types of X-linked genes, including:
- Dominant X-linked genes: These genes will be expressed if an individual has just one copy of the gene.
- Recessive X-linked genes: These genes will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the gene.
- X-linked dominant genes: These genes will be expressed if an individual has one copy of the gene, and the other X chromosome has a different gene.
- X-linked recessive genes: These genes will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the gene, and the other X chromosome has the same gene.
Worksheet Answers Explained
Now that we have covered the basics of X-linked genes, let’s move on to some common worksheet questions and answers.
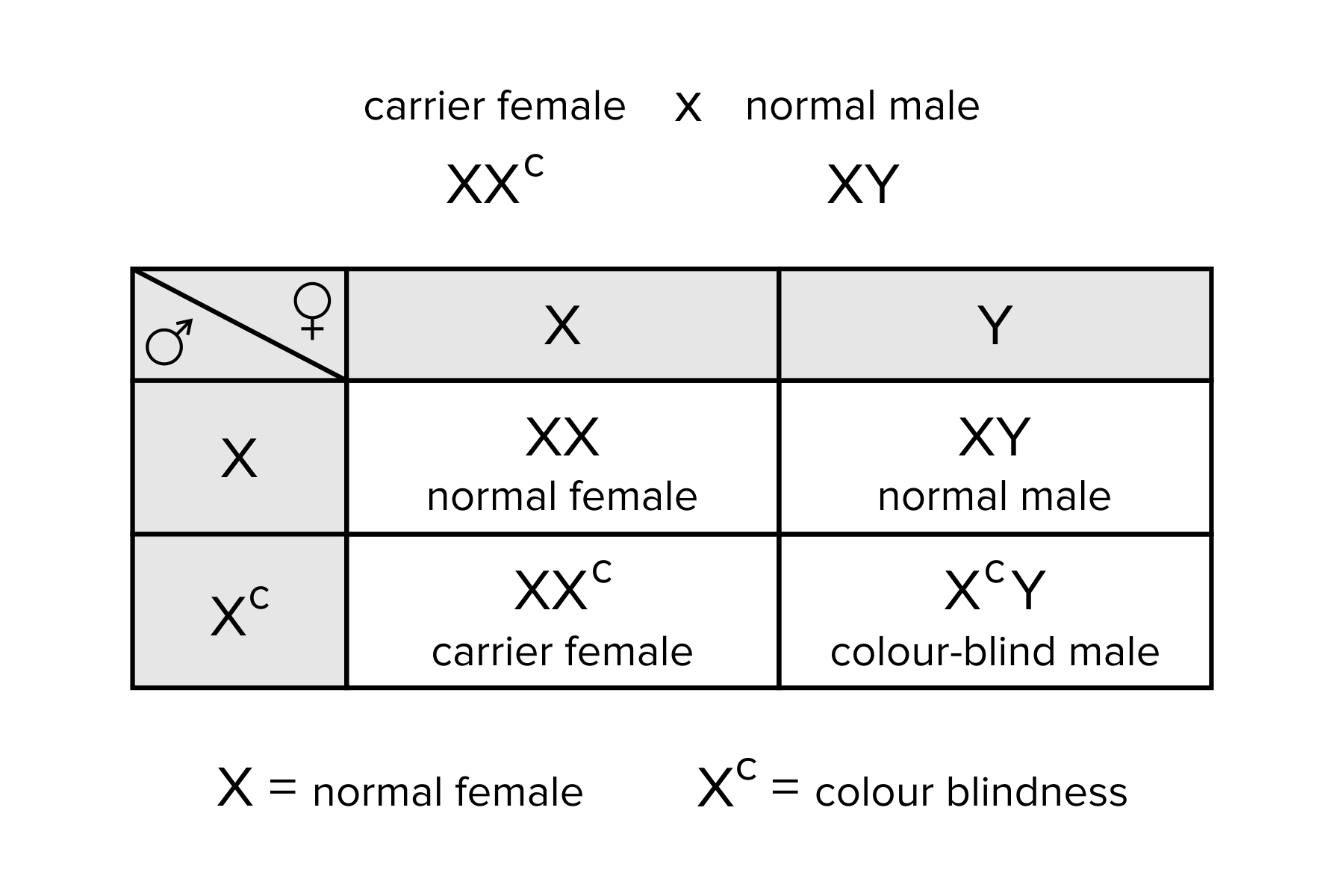
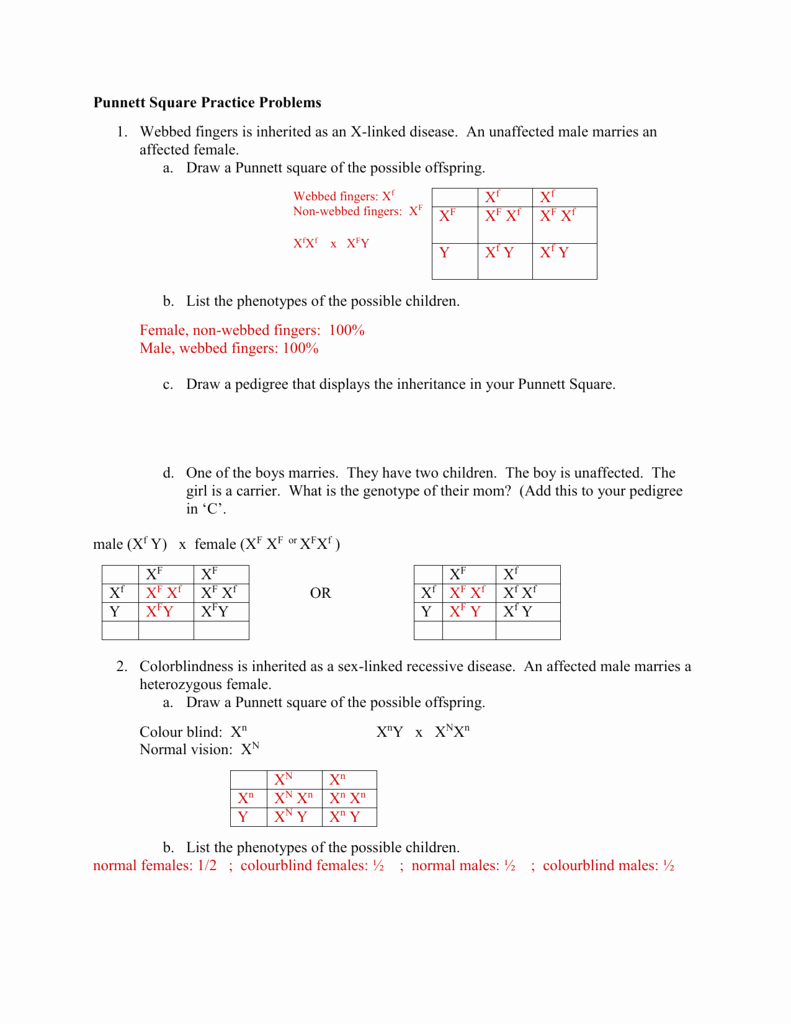
Question 1: What is the probability that a female carrier of an X-linked recessive gene will pass it on to her son?
Answer: 50% (Since the female carrier has one X chromosome with the recessive gene and one X chromosome with the dominant gene, there is a 50% chance she will pass the recessive gene to her son.)
Question 2: What is the probability that a male with an X-linked dominant gene will pass it on to his daughter?
Answer: 100% (Since the male has only one X chromosome with the dominant gene, he will always pass it on to his daughter.)
Question 3: What is the probability that a female with an X-linked recessive gene will express the gene?
Answer: 25% (Since the female has two X chromosomes, she needs to inherit two copies of the recessive gene to express it. The probability of this happening is 25%.)
Important Notes
🔍 Note: X-linked genes can be either dominant or recessive, and their expression is influenced by the sex of the individual.
👩🔬 Note: Females can be homozygous or heterozygous for X-linked genes, while males can only be hemizygous.
Table: X-Linked Gene Inheritance Patterns
| Genotype | Phenotype | Probability |
|---|---|---|
| XX | Normal | 75% |
| Xx | Carrier | 25% |
| xx | Affected | 25% |
| X | Normal | 100% |
| x | Affected | 100% |
X-Linked Genes and Genetic Disorders
X-linked genes are responsible for several genetic disorders, including:
- Hemophilia: A bleeding disorder caused by a recessive X-linked gene.
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A muscle-wasting disorder caused by a recessive X-linked gene.
- Rett syndrome: A neurological disorder caused by a dominant X-linked gene.
In conclusion, X-linked genes play a crucial role in genetics, and understanding their inheritance patterns is essential for predicting the likelihood of genetic disorders.
What is the difference between a dominant and recessive X-linked gene?
+A dominant X-linked gene will be expressed if an individual has just one copy of the gene, while a recessive X-linked gene will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the gene.
Can a male inherit an X-linked gene from his father?
+No, a male can only inherit an X-linked gene from his mother.
What is the probability that a female carrier of an X-linked recessive gene will pass it on to her daughter?
+50%