5 Ways to Master GDP Practice Worksheets

Unlocking the Secrets to Mastering GDP Practice Worksheets
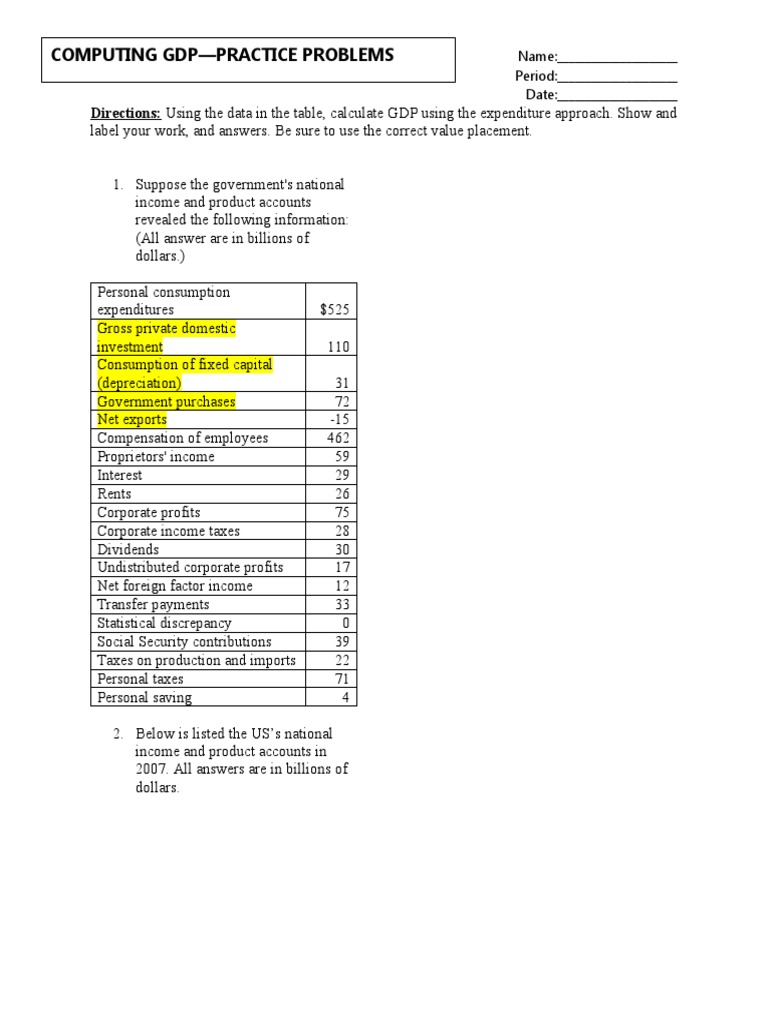
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a crucial concept in economics that measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period. Mastering GDP practice worksheets is essential for students, economists, and professionals to accurately analyze and interpret economic data. In this article, we will delve into five effective ways to master GDP practice worksheets, making you a pro in no time.
1. Understanding the GDP Formula
To begin, it’s essential to grasp the GDP formula, which is:
GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
Where:
- C is consumer spending
- I is investment
- G is government spending
- X is exports
- M is imports
Familiarize yourself with the components of GDP and practice applying the formula to various scenarios. This will help you become more comfortable with the concept and enable you to tackle more complex problems.
📝 Note: Make sure to understand the difference between nominal and real GDP, as well as the various methods of calculating GDP, such as the expenditure approach and the income approach.
2. Breaking Down GDP Components
To master GDP practice worksheets, it’s crucial to understand the individual components that make up the formula. Let’s break down each component:
- Consumer Spending ©: This includes household expenditures on goods and services, such as food, clothing, and entertainment.
- Investment (I): This encompasses business expenditures on capital goods, such as new buildings, equipment, and inventories.
- Government Spending (G): This includes government expenditures on goods and services, such as infrastructure, defense, and education.
- Exports (X): This represents the value of goods and services produced domestically but sold abroad.
- Imports (M): This represents the value of goods and services produced abroad but consumed domestically.
By understanding the individual components, you’ll be better equipped to analyze and calculate GDP.
3. Practicing with Real-World Examples
Practicing with real-world examples is an effective way to master GDP practice worksheets. Use historical data or current events to practice calculating GDP. For instance, you can use the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) website to access real GDP data for the United States.
Try to apply the GDP formula to different scenarios, such as:
- Calculating the GDP of a country with a growing economy
- Analyzing the impact of a recession on a country’s GDP
- Comparing the GDP of different countries
4. Using Visual Aids and Graphs
Visual aids and graphs can help you better understand and analyze GDP data. Use diagrams and charts to illustrate the relationship between GDP components and the overall economy.
Some examples of visual aids include:
- Pie charts: to show the proportion of each component to the overall GDP
- Bar graphs: to compare the GDP of different countries or time periods
- Line graphs: to illustrate the trend of GDP over time
By using visual aids, you’ll be able to identify patterns and trends in GDP data, making it easier to analyze and interpret.
5. Staying Up-to-Date with Economic News
Finally, staying up-to-date with economic news and trends is essential to mastering GDP practice worksheets. Follow reputable sources, such as the BEA, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank, to stay informed about the latest economic developments.
Pay attention to news articles and reports that discuss GDP data, economic indicators, and policy changes. This will help you stay current and apply your knowledge of GDP to real-world scenarios.
| GDP Component | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Spending (C) | C = Household expenditures on goods and services | C = $1,000 (food) + $500 (clothing) = $1,500 |
| Investment (I) | I = Business expenditures on capital goods | I = $10,000 (new building) + $5,000 (equipment) = $15,000 |
| Government Spending (G) | G = Government expenditures on goods and services | G = $50,000 (infrastructure) + $20,000 (defense) = $70,000 |
| Exports (X) | X = Value of goods and services produced domestically but sold abroad | X = $100,000 (exports of goods) + $50,000 (exports of services) = $150,000 |
| Imports (M) | M = Value of goods and services produced abroad but consumed domestically | M = $80,000 (imports of goods) + $30,000 (imports of services) = $110,000 |
By following these five steps, you’ll be well on your way to mastering GDP practice worksheets. Remember to practice regularly, stay up-to-date with economic news, and use visual aids to enhance your understanding of GDP.
By mastering GDP practice worksheets, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the economy and be able to analyze and interpret economic data with confidence.
What is the difference between nominal and real GDP?
+Nominal GDP measures the value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders using current prices, while real GDP measures the value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders using constant prices, adjusted for inflation.
How is GDP used in economic analysis?
+GDP is used as a broad indicator of a country’s economic performance, providing insights into the overall size and growth rate of the economy. It is also used to compare the economic performance of different countries and to analyze the impact of economic policies.
What are some common criticisms of GDP as a measure of economic performance?
+Critics argue that GDP does not account for income inequality, environmental degradation, and unpaid work, such as household chores and caregiving. Additionally, GDP only measures the market value of goods and services, ignoring non-market activities and informal economies.
Related Terms:
- Calculating GDP Practice problems pdf