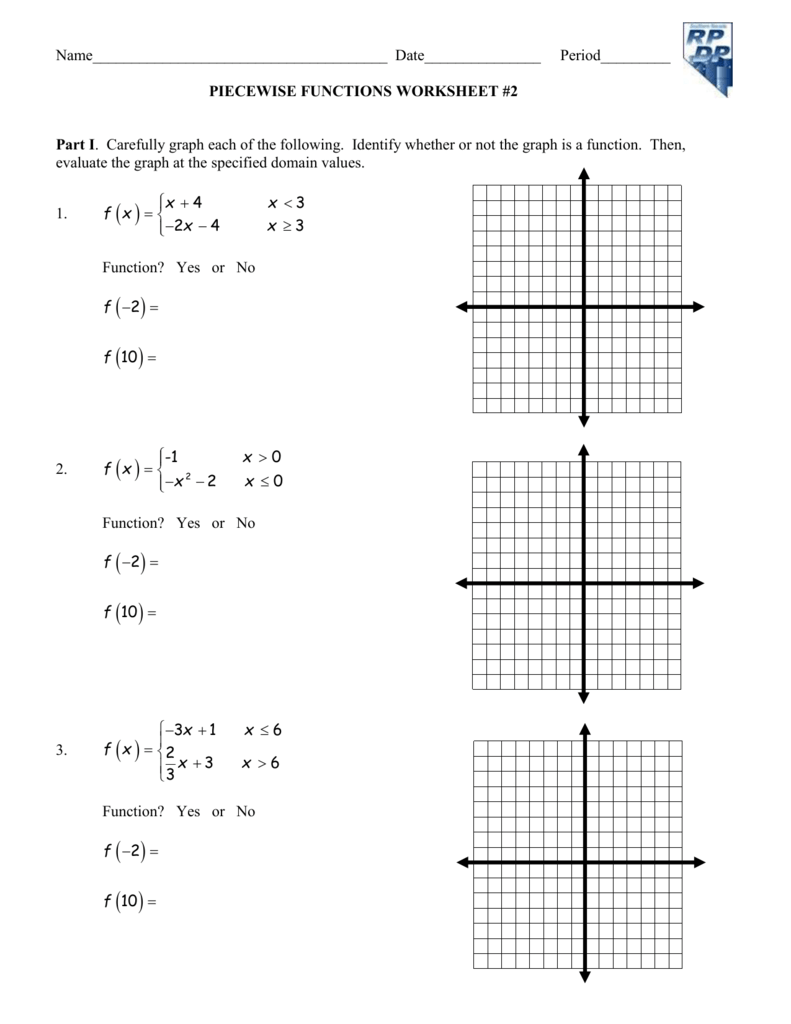
Food Web Worksheet Answer Key
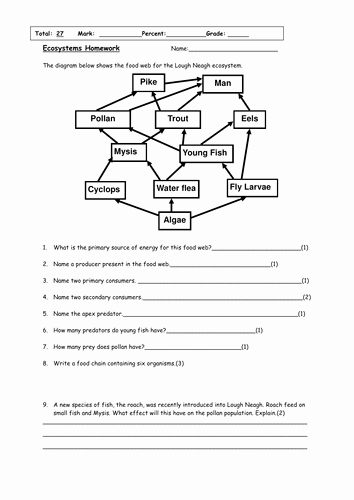
Understanding Food Webs: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Food Webs
A food web is a complex network of food chains that show the feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem. It is a crucial concept in ecology, as it helps us understand the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the world of food webs, exploring their components, types, and importance.
Components of a Food Web
A food web consists of several components, including:
- Producers: These are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants and algae.
- Consumers: These are organisms that consume other organisms for energy, such as animals.
- Decomposers: These are organisms that break down dead organisms into nutrients, such as bacteria and fungi.
- Primary Consumers: These are organisms that consume producers, such as herbivores.
- Secondary Consumers: These are organisms that consume primary consumers, such as carnivores.
- Tertiary Consumers: These are organisms that consume secondary consumers, such as top predators.
Types of Food Webs
There are several types of food webs, including:
- Terrestrial Food Webs: These occur on land and involve organisms such as plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Aquatic Food Webs: These occur in water and involve organisms such as fish, plants, and microorganisms.
- Marine Food Webs: These occur in the ocean and involve organisms such as fish, plants, and microorganisms.
Importance of Food Webs
Food webs play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of an ecosystem. They:
- Show Energy Flow: Food webs demonstrate how energy flows through an ecosystem, from producers to consumers.
- Support Biodiversity: Food webs support a diverse range of species, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem.
- Indicate Ecosystem Health: Food webs can indicate the health of an ecosystem, with changes in the web indicating changes in the ecosystem.
Food Web Worksheet Answer Key
Here is a sample food web worksheet with answers:
Food Web Worksheet
Section 1: Multiple Choice
- What is the primary source of energy for a food web? a) Producers b) Consumers c) Decomposers d) Primary Consumers
Answer: a) Producers
- Which type of consumer eats producers? a) Primary Consumer b) Secondary Consumer c) Tertiary Consumer d) Decomposer
Answer: a) Primary Consumer
- What is the role of decomposers in a food web? a) To consume producers b) To consume primary consumers c) To break down dead organisms d) To produce energy
Answer: c) To break down dead organisms
Section 2: Short Answer
- Describe the difference between a food chain and a food web.
Answer: A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that eat each other, while a food web is a complex network of food chains that show the feeding relationships between different species.
- What is the importance of producers in a food web?
Answer: Producers are the primary source of energy for a food web, producing their own food through photosynthesis.
Section 3: Essay Question
- Explain the concept of a food web and its importance in an ecosystem.
Answer: A food web is a complex network of food chains that show the feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem. It is crucial for maintaining the balance of an ecosystem, demonstrating how energy flows through the ecosystem, supporting biodiversity, and indicating ecosystem health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, food webs are a vital component of ecosystems, demonstrating the complex relationships between different species. Understanding food webs is essential for maintaining the balance of an ecosystem and supporting biodiversity.
What is the primary source of energy for a food web?
+Producers, such as plants and algae, are the primary source of energy for a food web.
What is the role of decomposers in a food web?
+Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead organisms into nutrients, recycling energy and nutrients through the ecosystem.
What is the importance of food webs in an ecosystem?
+Food webs are crucial for maintaining the balance of an ecosystem, demonstrating how energy flows through the ecosystem, supporting biodiversity, and indicating ecosystem health.