7 Essential Steps for Fetal Pig Dissection Success
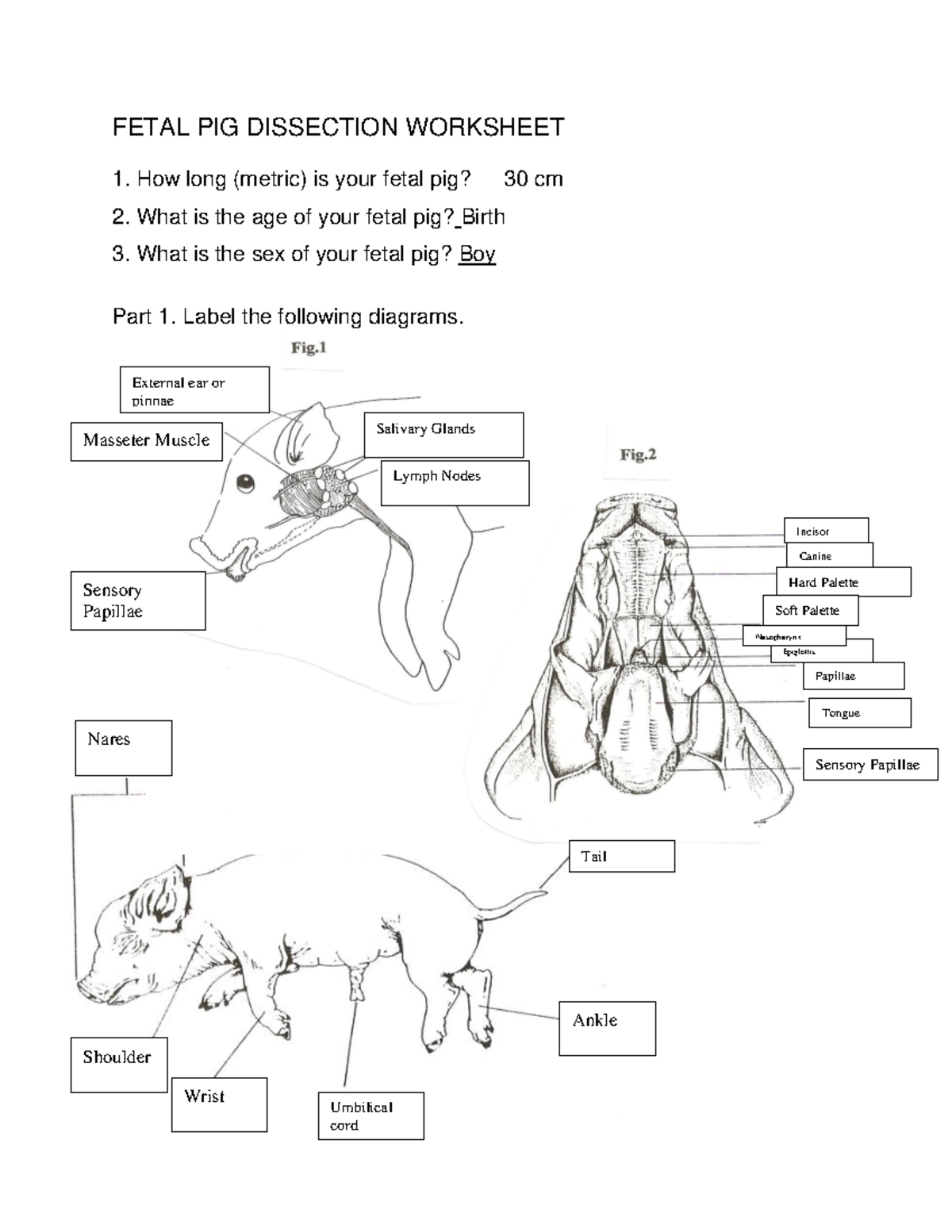
Understanding the Importance of Fetal Pig Dissection
Fetal pig dissection is a crucial part of many anatomy and biology curricula, providing students with hands-on experience and a deeper understanding of mammalian anatomy. This educational tool has been used for decades, offering a unique opportunity for students to explore the internal structures of a mammal in a safe and controlled environment. To ensure a successful and productive dissection experience, it’s essential to follow a structured approach.
Step 1: Preparation is Key
Before starting the dissection, it’s crucial to prepare the necessary materials and tools. This includes:
- A fetal pig specimen, preferably fresh or properly preserved
- A dissection tray or pan to contain the specimen and any debris
- Dissection instruments, such as scissors, forceps, and scalpels
- A magnifying glass or stereo microscope for closer inspection
- A diagram or illustration of the fetal pig’s anatomy
📝 Note: Always handle the fetal pig specimen with care, and follow proper safety protocols when using dissection instruments.
Step 2: External Observation and Measurement
Begin by observing the external features of the fetal pig, taking note of its overall size, shape, and any visible characteristics. Measure the length and weight of the specimen, and record these values for future reference.
- Use a ruler or calipers to measure the length of the fetal pig from the tip of the snout to the base of the tail.
- Weigh the specimen using a balance or scale.
| Measurement | Value |
|---|---|
| Length (cm) | |
| Weight (g) |
Step 3: Initial Incision and Exploration
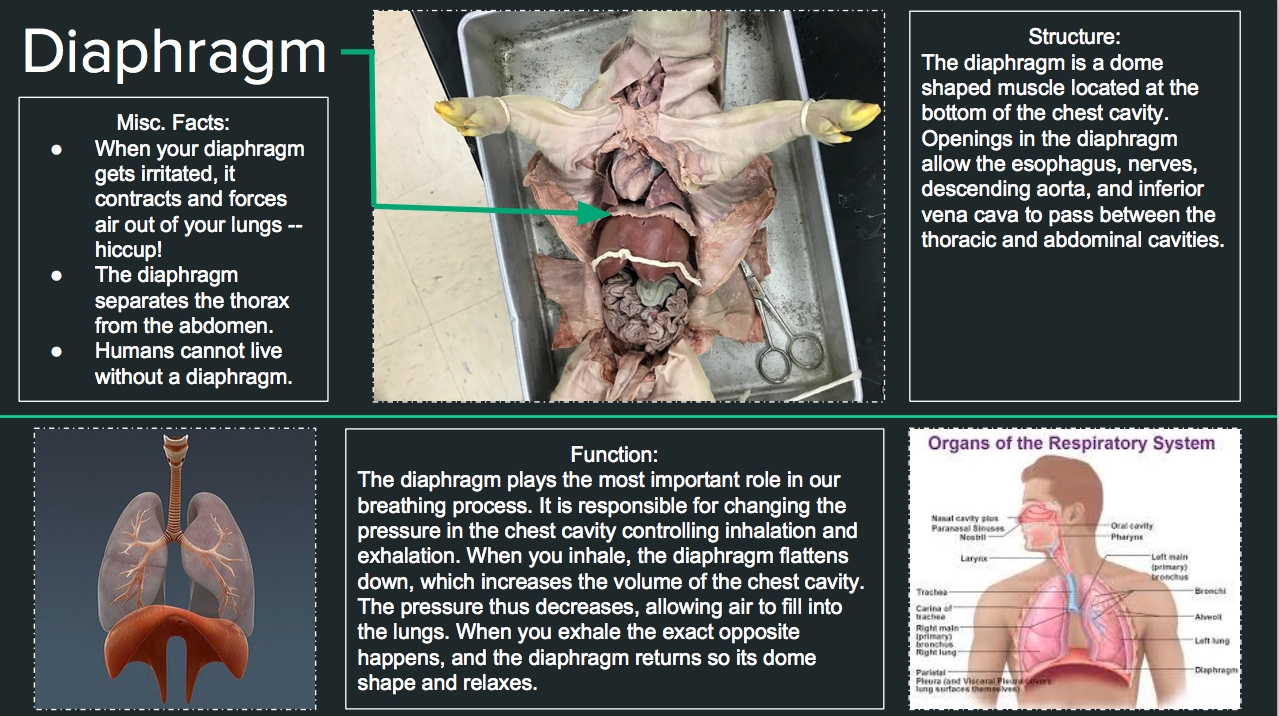
Make an initial incision along the midline of the fetal pig’s abdomen, taking care not to damage any underlying organs. Gently pry open the incision and explore the abdominal cavity, identifying the major organs and structures.
- Use scissors or a scalpel to make a midline incision from the base of the ribcage to the pubic bone.
- Use forceps or a probe to gently move aside any tissue or organs, allowing for a clear view of the abdominal cavity.
Step 4: Organ Identification and Exploration
Systematically identify and explore each of the major organs and systems within the abdominal cavity. This may include:
The digestive system (stomach, small intestine, large intestine)
The circulatory system (heart, arteries, veins)
The respiratory system (lungs, trachea)
The urinary system (kidneys, bladder)
Use a magnifying glass or stereo microscope to examine each organ in greater detail.
Take note of any unusual features or abnormalities.
Step 5: Dissection of Specific Organs and Systems
Select specific organs or systems for more detailed dissection and exploration. This may involve:
Dissecting the stomach and small intestine to examine the digestive system
Exploring the heart and circulatory system to identify major blood vessels and chambers
Examining the lungs and respiratory system to understand gas exchange and respiration
Use specialized dissection instruments, such as a scalpel or scissors, to carefully dissect the selected organs or systems.
Take note of any interesting features or structures.
Step 6: Conclusion and Review
After completing the dissection, take a moment to review the major findings and observations. This is an opportunity to:
Reflect on the anatomy and physiology of the fetal pig
Identify any areas for further study or exploration
Document any interesting features or abnormalities
Use a diagram or illustration to review the major organs and systems.
Record any final observations or notes.
Step 7: Disposal and Cleanup
Finally, properly dispose of the fetal pig specimen and clean the dissection area. This includes:
- Disposing of the specimen according to local regulations and guidelines
- Cleaning and sanitizing all dissection instruments and equipment
- Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water
🚮 Note: Always follow proper safety protocols when disposing of biological specimens and cleaning dissection equipment.
As you conclude the fetal pig dissection, take a moment to reflect on the experience and the knowledge gained. This hands-on activity provides a unique opportunity to explore the internal structures of a mammal, and can be a valuable learning experience for students of anatomy and biology.
What is the purpose of fetal pig dissection in anatomy and biology curricula?
+
Fetal pig dissection provides hands-on experience and a deeper understanding of mammalian anatomy, allowing students to explore the internal structures of a mammal in a safe and controlled environment.
What safety protocols should be followed during fetal pig dissection?
+
Always handle the fetal pig specimen with care, and follow proper safety protocols when using dissection instruments, including wearing gloves and washing hands thoroughly with soap and water.
How can students benefit from fetal pig dissection?
+
Students can benefit from fetal pig dissection by gaining hands-on experience, developing their observation and critical thinking skills, and deepening their understanding of mammalian anatomy and physiology.



