7 Tips to Master Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Understanding the Fundamentals of Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic and endothermic reactions are two types of chemical reactions that are essential to understand in the field of chemistry. These reactions are classified based on the direction of energy flow, and mastering them is crucial for any chemistry student or professional. In this article, we will delve into the world of exothermic and endothermic reactions, exploring their definitions, examples, and key differences.
Tip 1: Define Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
To begin with, it’s essential to understand the definitions of exothermic and endothermic reactions.
- Exothermic Reactions: These are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound. In other words, exothermic reactions are those that emit energy into the surroundings.
- Endothermic Reactions: These are chemical reactions that absorb energy from the surroundings in the form of heat, light, or sound. In other words, endothermic reactions are those that take in energy from the surroundings.
Tip 2: Identify Examples of Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Let’s look at some examples to illustrate the concept better:
- Exothermic Reactions:
- Combustion reactions, such as burning gasoline or wood, are exothermic reactions that release heat and light energy.
- The reaction between acid and base to form salt and water is an exothermic reaction that releases heat energy.
- Endothermic Reactions:
- Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, is an endothermic reaction that absorbs light energy.
- The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen is an endothermic reaction that absorbs heat energy.
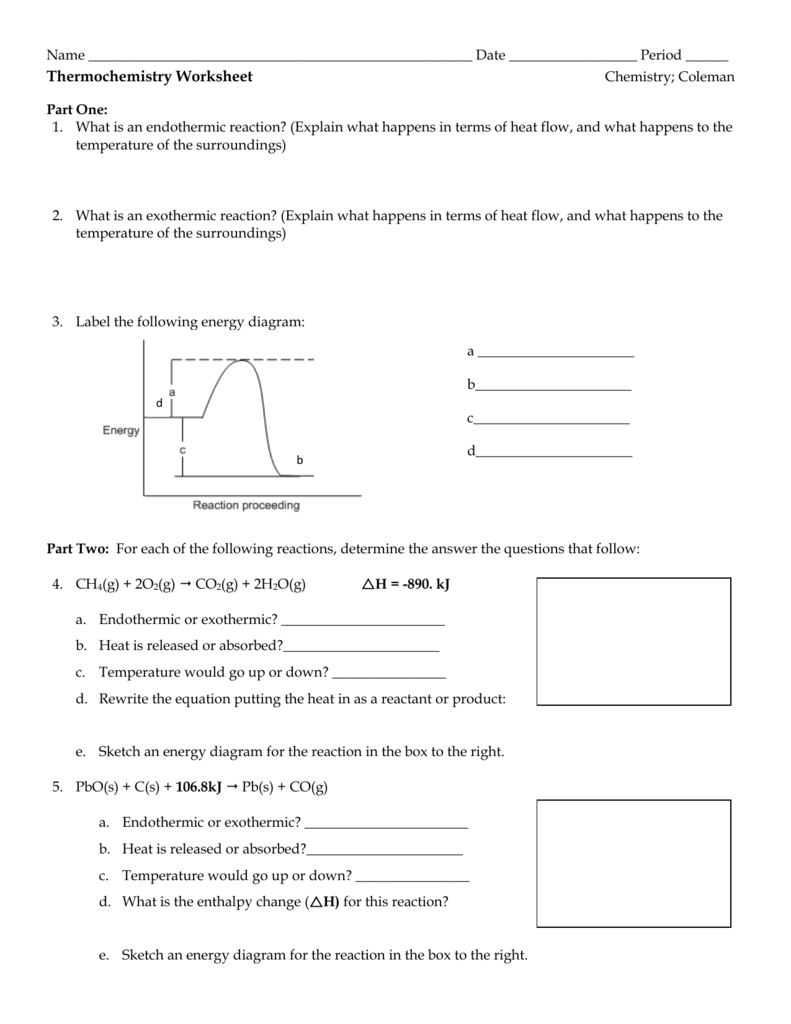
Tip 3: Understand the Energy Profile of Reactions
To master exothermic and endothermic reactions, it’s crucial to understand the energy profile of reactions. The energy profile is a graphical representation of the energy changes that occur during a reaction.
- Exothermic Reactions: The energy profile of an exothermic reaction shows a decrease in energy as the reaction proceeds. This means that the products have lower energy than the reactants.
- Endothermic Reactions: The energy profile of an endothermic reaction shows an increase in energy as the reaction proceeds. This means that the products have higher energy than the reactants.
Tip 4: Recognize the Role of Catalysts in Reactions
Catalysts play a vital role in both exothermic and endothermic reactions. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by it.
- Exothermic Reactions: Catalysts can increase the rate of exothermic reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
- Endothermic Reactions: Catalysts can also increase the rate of endothermic reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
Tip 5: Analyze the Thermodynamics of Reactions
Thermodynamics is the study of the relationships between heat, work, and energy. Understanding the thermodynamics of reactions is crucial to mastering exothermic and endothermic reactions.
- Exothermic Reactions: Exothermic reactions are spontaneous, meaning they occur naturally without external input. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is negative for exothermic reactions.
- Endothermic Reactions: Endothermic reactions are non-spontaneous, meaning they require external input to occur. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is positive for endothermic reactions.
Tip 6: Apply the Laws of Thermodynamics to Reactions
The laws of thermodynamics are fundamental principles that govern the behavior of energy and its interactions with matter.
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: This law states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
- First Law of Thermodynamics: This law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another.
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: This law states that the total entropy of an isolated system always increases over time.
Tip 7: Practice Problems to Reinforce Understanding
To master exothermic and endothermic reactions, it’s essential to practice problems that reinforce understanding.
- Practice Problems: Try solving problems that involve identifying exothermic and endothermic reactions, calculating energy changes, and applying the laws of thermodynamics.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources, such as video lectures and practice exams, to reinforce understanding and improve problem-solving skills.
📝 Note: Mastering exothermic and endothermic reactions requires practice and reinforcement. Try to practice problems regularly and seek help when needed.
Mastering exothermic and endothermic reactions is a crucial aspect of chemistry that requires understanding, practice, and reinforcement. By following these 7 tips, you’ll be well on your way to becoming proficient in identifying and analyzing these types of reactions.
What is the main difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions?
+The main difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions is the direction of energy flow. Exothermic reactions release energy into the surroundings, while endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surroundings.
Can a reaction be both exothermic and endothermic?
+No, a reaction cannot be both exothermic and endothermic. A reaction can either release energy (exothermic) or absorb energy (endothermic), but it cannot do both simultaneously.
What is the role of catalysts in exothermic and endothermic reactions?
+Catalysts can increase the rate of both exothermic and endothermic reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. However, catalysts do not affect the energy change (ΔE) of the reaction.
Related Terms:
- Endothermic and exothermic reactions
- Energy changes worksheet