Eukaryote vs Prokaryote: Key Differences in Cell Structure
Introduction to Cell Structure
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. All living things, from simple bacteria to complex humans, are composed of one or more cells. Cells are incredibly diverse, with different types of cells exhibiting unique characteristics that enable them to perform specific functions. However, despite their diversity, all cells can be broadly classified into two categories: eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In this article, we will explore the key differences in cell structure between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
What are Prokaryotes?
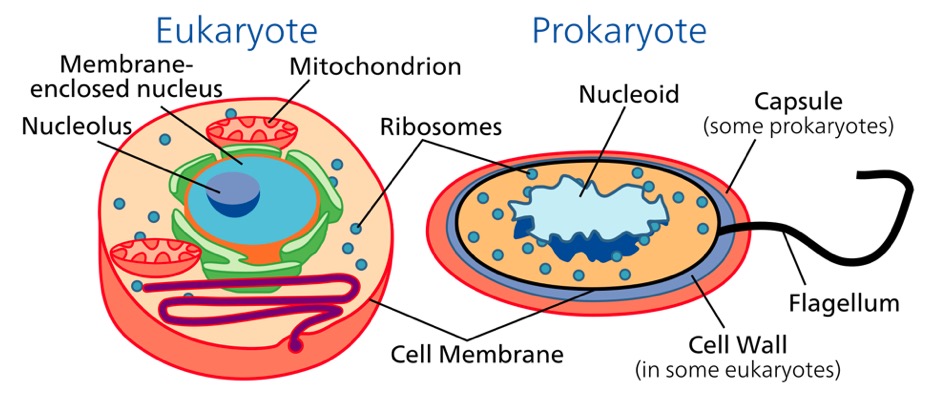
Prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are the most ancient forms of life on Earth, with fossil records dating back over 3.5 billion years. Prokaryotes are typically single-celled and include bacteria and archaea. They are characterized by their simple cell structure, which consists of a cell wall, a cell membrane, and a region called the nucleoid, where the genetic material (DNA) is located.
What are Eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes, on the other hand, are organisms that have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are more complex and evolved than prokaryotes and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Eukaryotic cells have a distinct nucleus, which is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. They also have other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and a golgi apparatus, which perform specific functions within the cell.
Key Differences in Cell Structure
So, what are the key differences in cell structure between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? Here are some of the main differences:
- Nucleus: Eukaryotes have a true nucleus, which is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. Prokaryotes, on the other hand, lack a true nucleus and have a region called the nucleoid, where the genetic material (DNA) is located.
- Membrane-bound organelles: Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and a golgi apparatus, which perform specific functions within the cell. Prokaryotes lack these organelles.
- Cell size: Eukaryotic cells are typically larger than prokaryotic cells.
- Cell wall: Prokaryotes have a cell wall that provides structural support and maintains the cell’s shape. Eukaryotes have a cell wall, but it is not as rigid as that of prokaryotes.
- Cytoskeleton: Eukaryotes have a cytoskeleton, which provides structural support and maintains the cell’s shape. Prokaryotes lack a cytoskeleton.
- Genetic material: Eukaryotes have linear chromosomes, while prokaryotes have circular chromosomes.
| Characteristics | Eukaryotes | Prokaryotes |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | True nucleus with nuclear envelope | No true nucleus (nucleoid) |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Present (e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts) | Absent |
| Cell size | Larger | Smaller |
| Cell wall | Present, but not as rigid as prokaryotes | Present, rigid |
| Cytoskeleton | Present | Absent |
| Genetic material | Linear chromosomes | Circular chromosomes |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the key differences in cell structure between eukaryotes and prokaryotes are significant. Eukaryotes have a true nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and a cytoskeleton, which provide structural support and enable the cell to perform specific functions. Prokaryotes, on the other hand, lack these features and have a simpler cell structure. Understanding these differences is essential for appreciating the diversity of life on Earth and the complexity of cellular biology.
What is the main difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
+The main difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is the presence of a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes, which are absent in prokaryotes.
What is the function of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
+The nucleus in eukaryotic cells contains the genetic material (DNA) and regulates cell growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
What is the difference between linear and circular chromosomes?
+Linear chromosomes are found in eukaryotes and are characterized by their linear shape, while circular chromosomes are found in prokaryotes and are characterized by their circular shape.



