Enzymes Worksheet Answers: Unlocking Ch. 6 Section 2 Secrets
Unlocking the Secrets of Enzymes
Enzymes are biological molecules, typically proteins, that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. They are vital for life and serve as catalysts in the body’s various biochemical processes, such as digestion and metabolism. However, understanding enzymes can be a daunting task, especially when delving into the intricacies of their structure, function, and role in the human body.
What are Enzymes?
To grasp the concept of enzymes, it’s essential to understand what they are and how they work. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, meaning they accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed or altered in the process. They have an active site that binds to specific substrates, allowing them to lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. This process enables enzymes to facilitate reactions that would otherwise be too slow or inefficient.
Classification of Enzymes
Enzymes are classified into six main categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze:
- Oxidoreductases: These enzymes facilitate the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another, often resulting in the oxidation or reduction of the substrate.
- Transferases: This class of enzymes catalyzes the transfer of functional groups between molecules.
- Hydrolases: Enzymes that facilitate the hydrolysis of molecules, resulting in the cleavage of chemical bonds using water.
- Lyases: These enzymes catalyze the cleavage of molecules without using water, often resulting in the formation of a double bond or a ring structure.
- Isomerases: Enzymes that facilitate the rearrangement of molecules, resulting in a change in their structure or configuration.
- Ligases: This class of enzymes catalyzes the joining of two molecules, often requiring energy in the form of ATP.
🔍 Note: Understanding the classification of enzymes is crucial in comprehending their role in various biochemical processes.
Enzyme Structure and Function
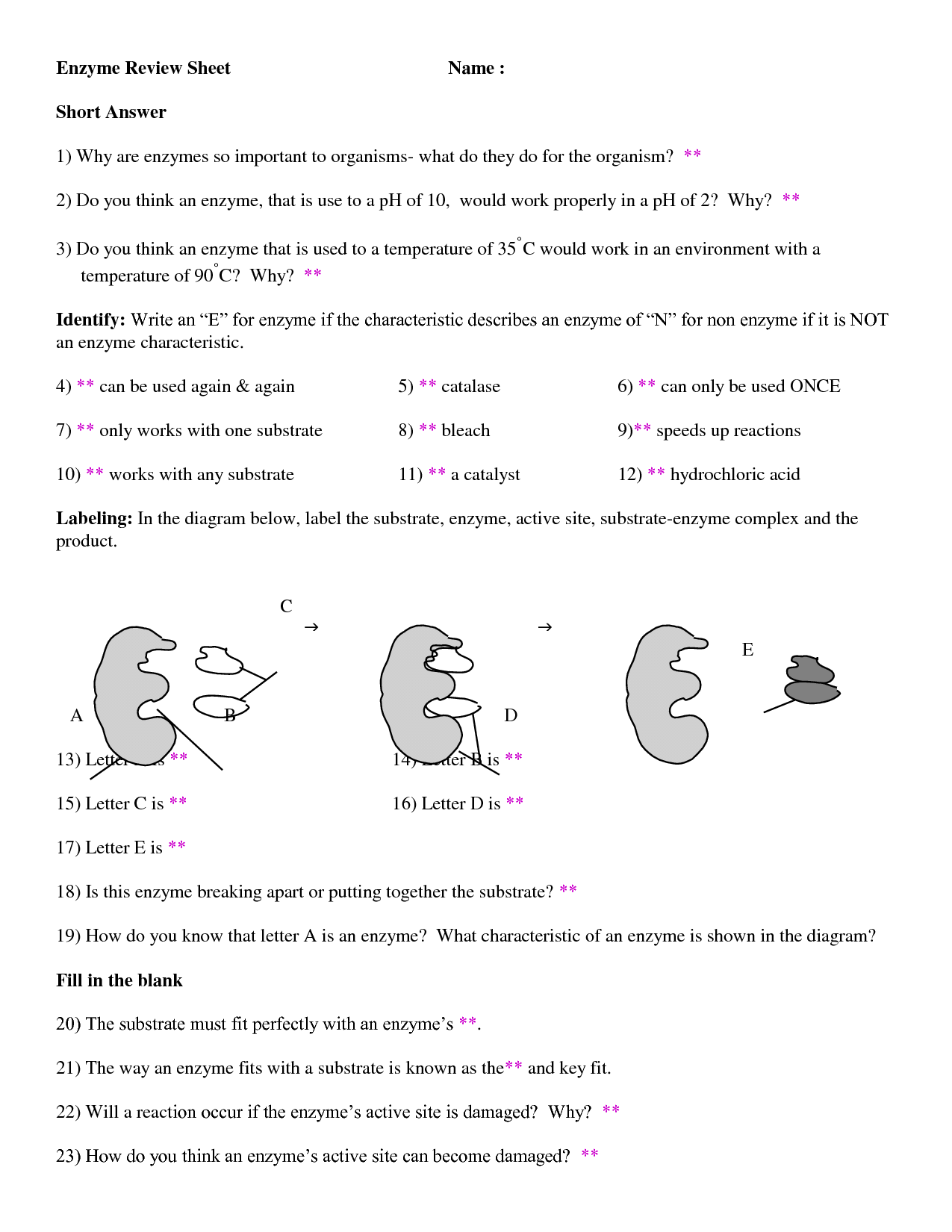
The structure of an enzyme plays a critical role in its function. Enzymes have an active site that binds to specific substrates, allowing them to facilitate chemical reactions. The shape and chemical properties of the active site determine the specificity of the enzyme-substrate interaction.
- Active Site: The region of the enzyme where the substrate binds, allowing the enzyme to catalyze the reaction.
- Substrate: The molecule that binds to the active site of the enzyme, facilitating the chemical reaction.
- Cofactors: Non-protein molecules that assist the enzyme in its catalytic activity.

| Enzyme Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Site | The region of the enzyme where the substrate binds |
| Substrate | The molecule that binds to the active site of the enzyme |
| Cofactors | Non-protein molecules that assist the enzyme in its catalytic activity |
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Several factors can influence enzyme activity, including:
- Temperature: Enzymes have an optimal temperature range in which they are most active.
- pH: Enzymes have an optimal pH range in which they are most active.
- Substrate Concentration: Increasing the substrate concentration can increase enzyme activity.
- Inhibitors: Molecules that bind to the active site of the enzyme, preventing it from catalyzing the reaction.
🔍 Note: Understanding the factors that affect enzyme activity is crucial in comprehending how enzymes function in various biochemical processes.
As we conclude our exploration of enzymes, it’s essential to summarize the key points:
- Enzymes are biological molecules that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed or altered.
- Enzymes are classified into six main categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze.
- The structure of an enzyme plays a critical role in its function, with the active site determining the specificity of the enzyme-substrate interaction.
- Factors such as temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors can influence enzyme activity.
In the next section, we’ll delve into the worksheet answers for Chapter 6, Section 2, providing a comprehensive understanding of enzymes and their role in biochemical processes.
What is the primary function of enzymes?
+Enzymes act as catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions without being consumed or altered in the process.
What are the six main categories of enzymes?
+Oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
What is the role of the active site in enzyme function?
+The active site is the region of the enzyme where the substrate binds, allowing the enzyme to catalyze the reaction.