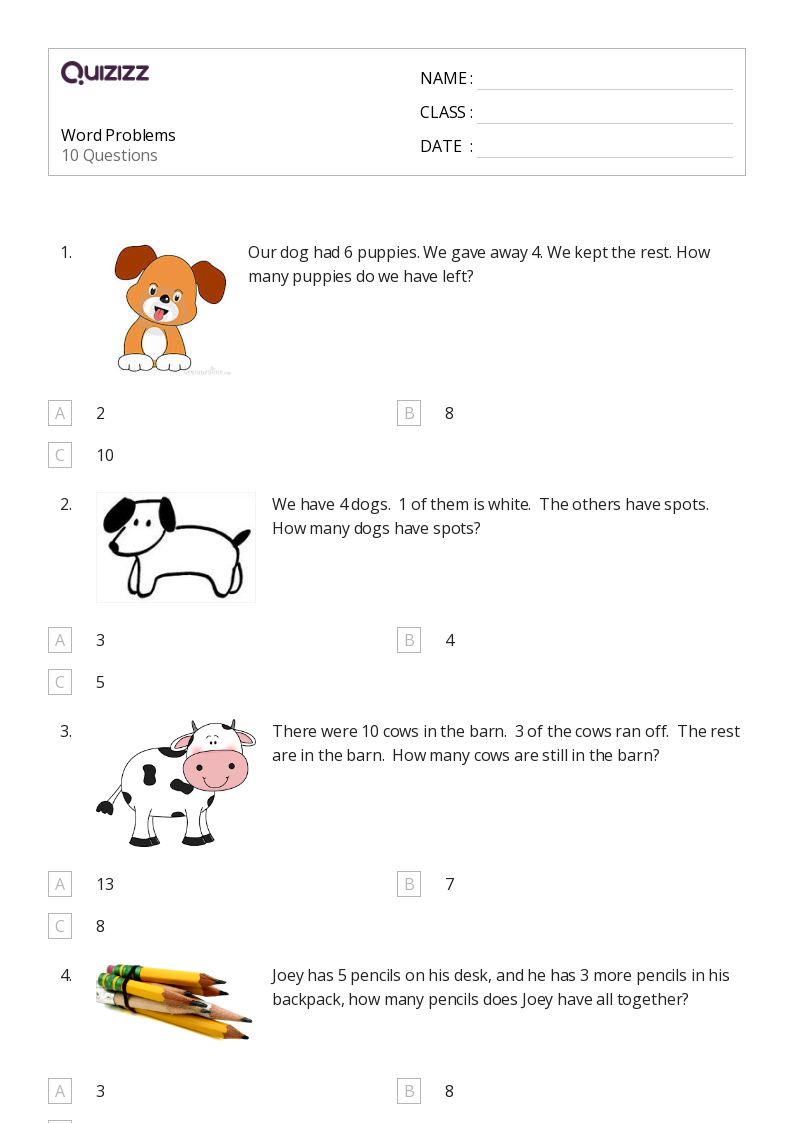
5 Key Enzyme Worksheet Biology Answers
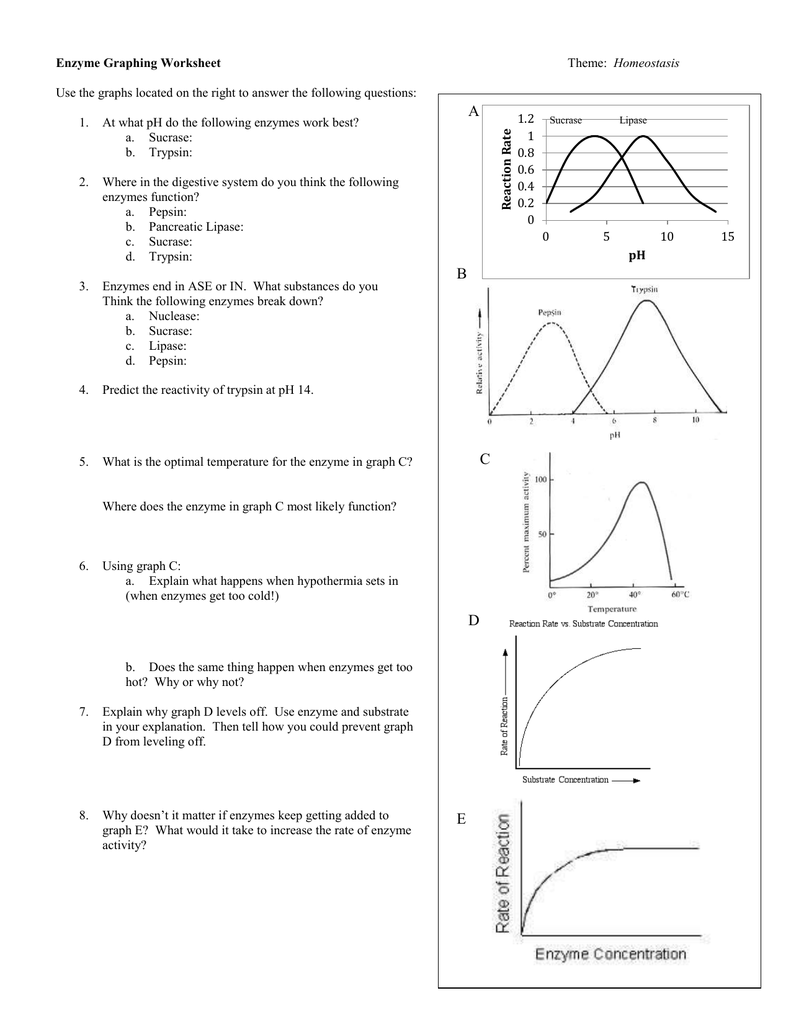
Enzymes: The Biological Catalysts
Enzymes are biological molecules, typically proteins, that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. They are vital for life and serve as catalysts in the body’s various biochemical processes, such as digestion and metabolism. Here, we will explore five key enzymes and their roles in biology, providing answers to common worksheet questions.
1. Amylase
Amylase: The Starch Breaker
Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars. It is produced in the salivary glands and the pancreas.
- Q: Where is amylase produced in the human body?
- A: Amylase is produced in the salivary glands and the pancreas.
- Q: What is the function of amylase in the digestive system?
- A: Amylase breaks down starches into sugars.
2. Lactase
Lactase: The Lactose Breaker
Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk, into glucose and galactose. It is produced in the small intestine.
- Q: What is the primary function of lactase in the digestive system?
- A: Lactase breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk, into glucose and galactose.
- Q: Why do some people have difficulty digesting lactose?
- A: Some people have low levels of lactase, making it difficult for them to digest lactose.
3. Trypsin
Tryptophan: The Protein Breaker
Trypsin is an enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the pancreas.
- Q: Where is trypsin produced in the human body?
- A: Trypsin is produced in the pancreas.
- Q: What is the primary function of trypsin in the digestive system?
- A: Trypsin breaks down proteins into smaller peptides.
4. Pepsin
Pepsin: The Protein Breaker
Pepsin is an enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the stomach.
- Q: Where is pepsin produced in the human body?
- A: Pepsin is produced in the stomach.
- Q: What is the primary function of pepsin in the digestive system?
- A: Pepsin breaks down proteins into smaller peptides.
5. Catalase
Catalase: The Hydrogen Peroxide Breaker
Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. It is found in many cells throughout the body.
- Q: What is the primary function of catalase in the body?
- A: Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
- Q: Why is catalase important for cell health?
- A: Catalase helps protect cells from oxidative damage by breaking down hydrogen peroxide.
Important Notes:
- Enzyme substrate specificity: Enzymes are highly specific to their substrates, meaning they only bind to and act on specific molecules.
- Enzyme inhibitors: Some molecules can inhibit enzyme activity, either by binding to the enzyme or by changing the pH or temperature.
Table: Key Enzymes and Their Functions
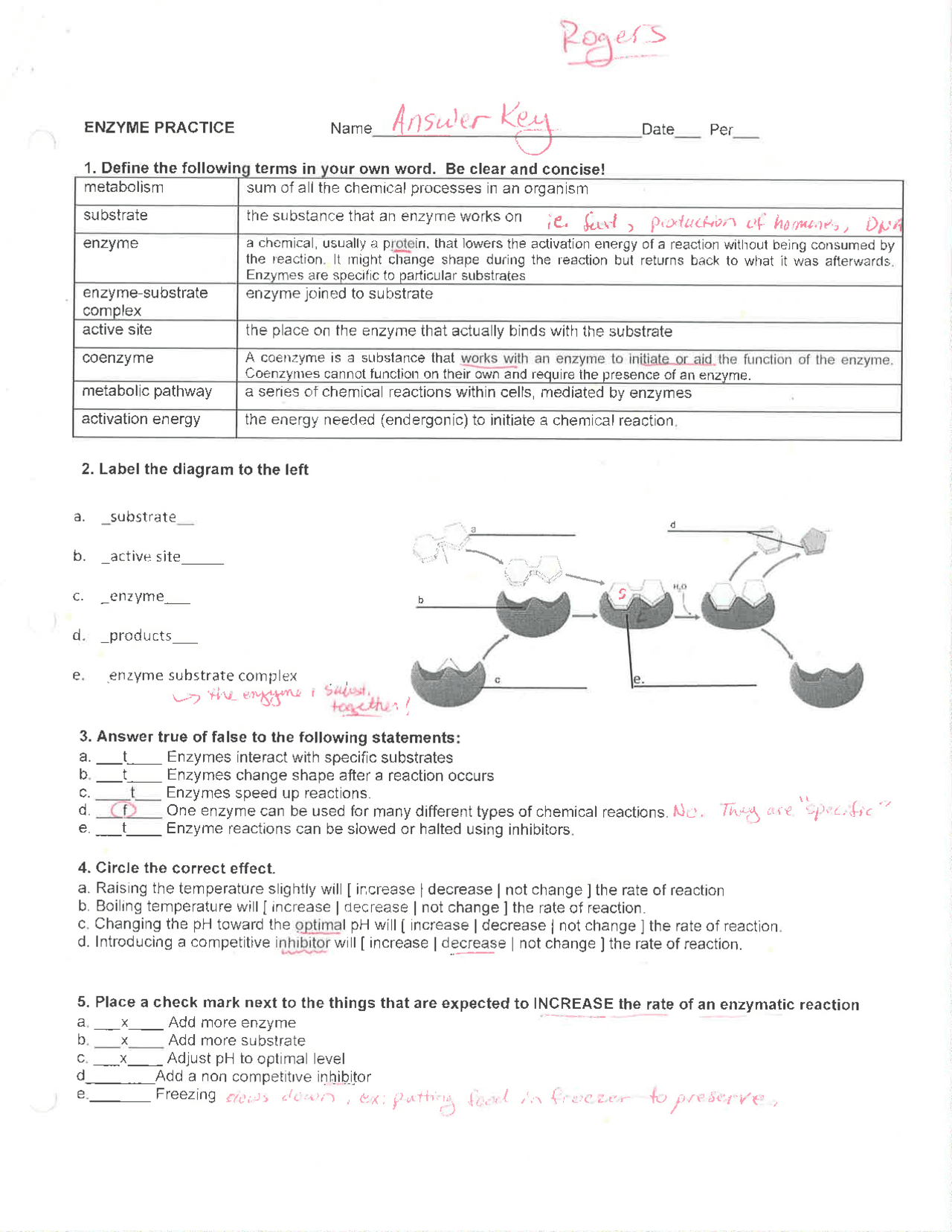
| Enzyme | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Amylase | Breaks down starches into sugars | Salivary glands and pancreas |
| Lactase | Breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose | Small intestine |
| Trypsin | Breaks down proteins into smaller peptides | Pancreas |
| Pepsin | Breaks down proteins into smaller peptides | Stomach |
| Catalase | Breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen | Many cells throughout the body |
Common Questions and Answers:
FAQs
What is the primary function of enzymes in the body?
+Enzymes act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in the body.
What is the difference between lactase and amylase?
+Lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose, while amylase breaks down starches into sugars.
What is the importance of catalase in cell health?
+Catalase helps protect cells from oxidative damage by breaking down hydrogen peroxide.
Key Takeaways:
Enzymes play a crucial role in various biochemical processes in the body. Understanding the functions and locations of key enzymes such as amylase, lactase, trypsin, pepsin, and catalase is essential for appreciating the complexity of biological systems.