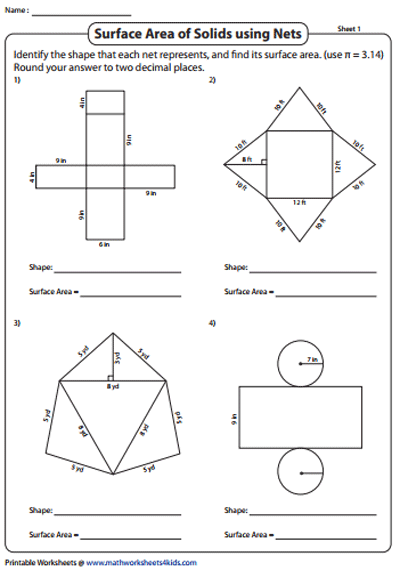
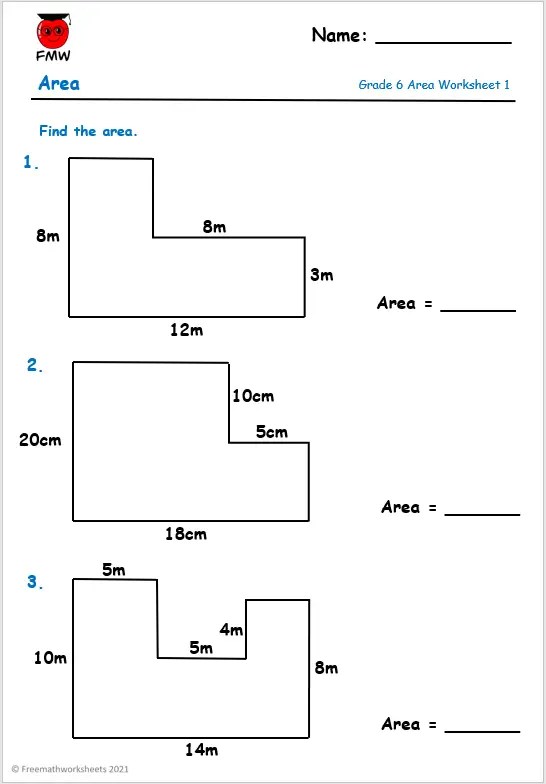
Enzyme Graphing Worksheet Answer Key

Understanding Enzyme Graphing Worksheet Answer Key
Enzyme graphing is an essential concept in biochemistry, allowing us to visualize and analyze the behavior of enzymes. This worksheet answer key provides a comprehensive guide to understanding enzyme graphing, including the different types of graphs, how to interpret them, and what they reveal about enzyme activity.
What is Enzyme Graphing?
Enzyme graphing involves plotting the activity of an enzyme against various parameters, such as substrate concentration, temperature, or pH. This allows us to visualize the relationship between the enzyme's activity and the parameter being varied. By analyzing these graphs, we can gain insights into the enzyme's mechanism of action, its affinity for substrates, and its optimal operating conditions.
Types of Enzyme Graphs
There are several types of enzyme graphs, each providing unique information about the enzyme's behavior. The most common types of enzyme graphs include:
- Velocity-Substrate Concentration Graphs: These graphs plot the enzyme's activity (velocity) against the substrate concentration. They provide information about the enzyme's affinity for the substrate and its maximum velocity (Vmax).
- Velocity-Inhibitor Concentration Graphs: These graphs plot the enzyme's activity against the concentration of an inhibitor. They provide information about the type of inhibition (competitive or non-competitive) and the inhibitor's binding affinity.
- Velocity-pH Graphs: These graphs plot the enzyme's activity against the pH of the solution. They provide information about the enzyme's optimal pH range and its stability at different pH values.
- Velocity-Temperature Graphs: These graphs plot the enzyme's activity against the temperature of the solution. They provide information about the enzyme's optimal temperature range and its thermal stability.
Interpreting Enzyme Graphs
When interpreting enzyme graphs, there are several key features to look for:
- Maximum Velocity (Vmax): The maximum velocity of the enzyme, which represents the highest rate of reaction achievable by the enzyme.
- Michaelis Constant (Km): The substrate concentration at which the enzyme reaches half of its maximum velocity. This value provides information about the enzyme's affinity for the substrate.
- Enzyme Stability: The enzyme's stability at different temperatures, pH values, or inhibitor concentrations. This information is crucial for understanding the enzyme's optimal operating conditions.
Enzyme Graphing Worksheet Answer Key
Now that we've covered the basics of enzyme graphing, let's move on to the worksheet answer key. The following table provides answers to common enzyme graphing questions:
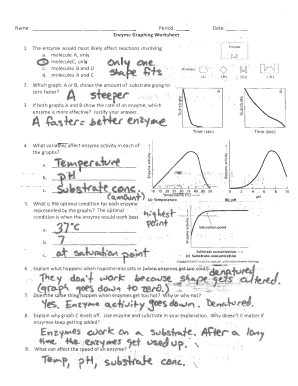
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the enzyme in the given graph? | The maximum velocity (Vmax) of the enzyme is 100 μmol/min. |
| What is the Michaelis constant (Km) of the enzyme in the given graph? | The Michaelis constant (Km) of the enzyme is 5 mM. |
| What type of inhibition is represented by the graph? | The graph represents competitive inhibition, as the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme. |
| What is the optimal pH range of the enzyme? | The optimal pH range of the enzyme is between 7 and 9. |
| What is the thermal stability of the enzyme? | The enzyme is stable up to 40°C, beyond which it starts to denature. |
💡 Note: The answers provided are based on hypothetical enzyme graphs and are intended for illustration purposes only.
Conclusion
Enzyme graphing is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of enzymes. By analyzing these graphs, we can gain insights into the enzyme's mechanism of action, its affinity for substrates, and its optimal operating conditions. The worksheet answer key provided in this article serves as a comprehensive guide for interpreting enzyme graphs and understanding the underlying principles of enzyme kinetics.
What is the purpose of enzyme graphing?
+Enzyme graphing is used to visualize and analyze the behavior of enzymes, allowing us to understand their mechanism of action, affinity for substrates, and optimal operating conditions.
What types of enzyme graphs are commonly used?
+The most common types of enzyme graphs include velocity-substrate concentration graphs, velocity-inhibitor concentration graphs, velocity-pH graphs, and velocity-temperature graphs.
What is the Michaelis constant (Km) and what does it represent?
+The Michaelis constant (Km) is the substrate concentration at which the enzyme reaches half of its maximum velocity. It provides information about the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate.