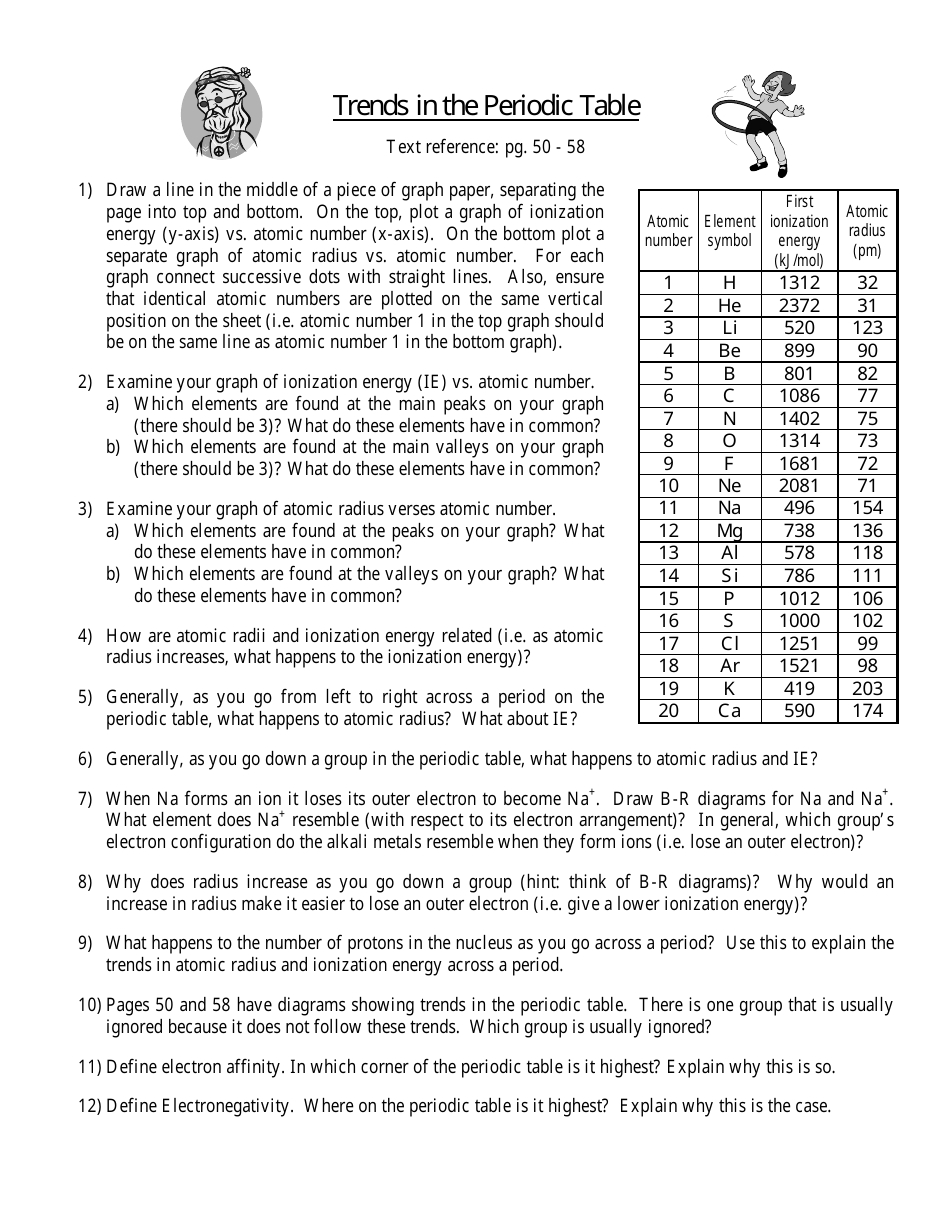
Periodic Trends Worksheet: Mastering Chemistry Made Easy

Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
Periodic trends are a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the behavior of elements and their properties. These trends enable us to predict the characteristics of elements based on their position in the periodic table. In this article, we will delve into the world of periodic trends, exploring the key concepts, factors that influence them, and practical applications.
What are Periodic Trends?
Periodic trends refer to the patterns and relationships that exist between the elements in the periodic table. These trends can be observed in various properties, such as atomic radius, electronegativity, ionization energy, and electron affinity. By analyzing these trends, we can gain insights into the behavior of elements and their compounds.
Key Factors that Influence Periodic Trends
Several factors contribute to the periodic trends observed in the periodic table. Some of the most significant factors include:
- Atomic Radius: The size of an atom, which decreases as you move from left to right across a period and increases as you move down a group.
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons, which increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group.
- Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom, which increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group.
- Electron Affinity: The energy released when an electron is added to an atom, which increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group.
- Shielding Effect: The reduction in the attractive force between the nucleus and electrons due to the presence of inner electrons.
- Effective Nuclear Charge: The net positive charge experienced by an electron due to the presence of inner electrons.
Periodic Trends in Atomic Radius
The atomic radius decreases as you move from left to right across a period due to the increased effective nuclear charge. This is because the additional protons in the nucleus attract the electrons more strongly, pulling them closer to the nucleus.
| Period | Atomic Radius (pm) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 30-50 |
| 2 | 50-70 |
| 3 | 70-100 |
| 4 | 100-150 |
| 5 | 150-200 |
| 6 | 200-250 |
| 7 | 250-300 |
Periodic Trends in Electronegativity
Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right across a period due to the increased effective nuclear charge. This is because the additional protons in the nucleus attract the electrons more strongly, increasing their electronegativity.
| Period | Electronegativity (Pauling Scale) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2.2-3.2 |
| 2 | 3.2-4.2 |
| 3 | 4.2-5.2 |
| 4 | 5.2-6.2 |
| 5 | 6.2-7.2 |
| 6 | 7.2-8.2 |
| 7 | 8.2-9.2 |
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy
Ionization energy increases as you move from left to right across a period due to the increased effective nuclear charge. This is because the additional protons in the nucleus attract the electrons more strongly, making it more difficult to remove an electron.
| Period | Ionization Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 300-500 |
| 2 | 500-700 |
| 3 | 700-900 |
| 4 | 900-1100 |
| 5 | 1100-1300 |
| 6 | 1300-1500 |
| 7 | 1500-1700 |
📝 Note: The values in the tables above are approximate and serve as a general guide to understanding periodic trends.
Practical Applications of Periodic Trends
Periodic trends have numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Materials Science: Understanding periodic trends helps materials scientists design new materials with specific properties.
- Chemical Engineering: Periodic trends are essential in chemical engineering, where they are used to predict the behavior of chemicals and design efficient processes.
- Pharmaceuticals: Periodic trends are used in the development of new medicines, where understanding the properties of elements is crucial.
Mastering Periodic Trends
Mastering periodic trends requires practice and a deep understanding of the underlying concepts. Here are some tips to help you master periodic trends:
- Start with the basics: Ensure you have a solid understanding of atomic structure, electron configuration, and the periodic table.
- Practice, practice, practice: Practice identifying and explaining periodic trends in different properties.
- Use visual aids: Use diagrams and charts to visualize periodic trends and make them more memorable.
- Apply periodic trends to real-world situations: Try to apply periodic trends to real-world situations, such as predicting the properties of elements in a compound.
As you continue to explore the world of periodic trends, remember that practice and patience are key to mastering this fundamental concept in chemistry.
What are periodic trends?
+
Periodic trends refer to the patterns and relationships that exist between the elements in the periodic table.
What factors influence periodic trends?
+
Atomic radius, electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, shielding effect, and effective nuclear charge are some of the key factors that influence periodic trends.
What are some practical applications of periodic trends?
+
Periodic trends have numerous practical applications in materials science, chemical engineering, and pharmaceuticals.