EMS Systems Chapter 1 Answers and Study Guide

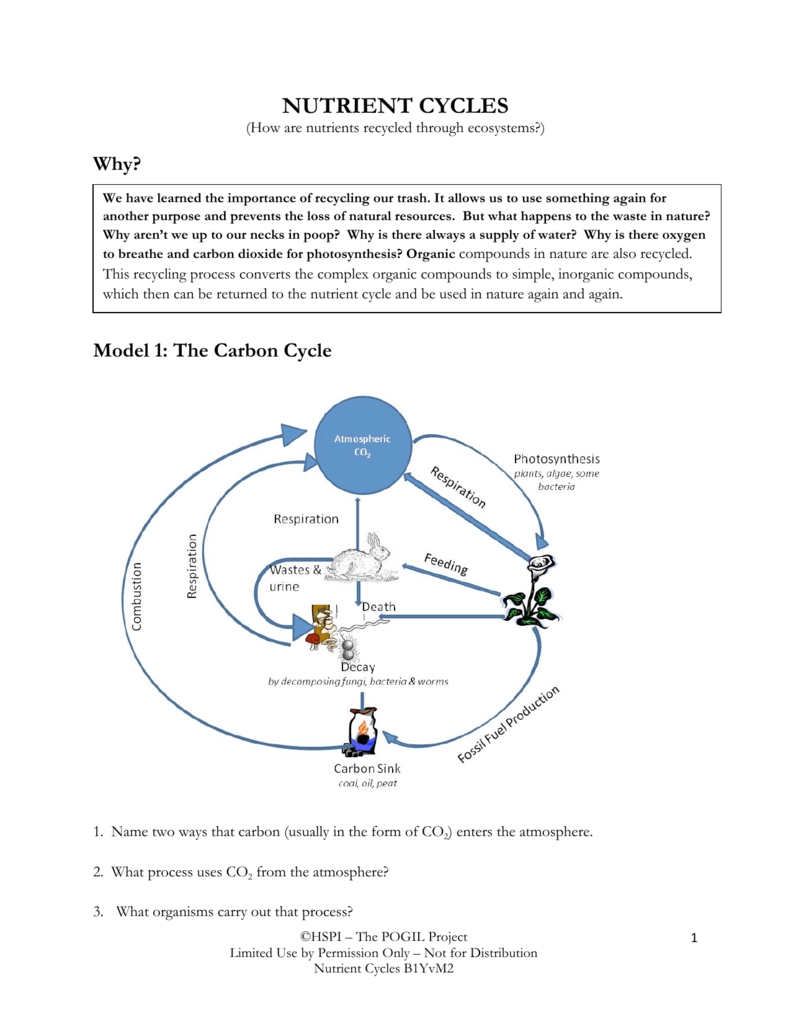
EMS Systems Chapter 1: Overview of EMS Systems
The Emergency Medical Services (EMS) system is a vital component of the healthcare system, providing emergency medical care to those in need. In this chapter, we will explore the history, structure, and components of EMS systems, as well as the roles and responsibilities of EMS personnel.
History of EMS Systems
The concept of EMS dates back to ancient times, with evidence of emergency medical care being provided in ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece. However, the modern EMS system as we know it today began to take shape in the mid-20th century.
Key Milestones in EMS History:
- 1960s: The first ambulance services were established in the United States, with the primary focus on transporting patients to medical facilities.
- 1970s: The EMS Systems Act was passed, providing federal funding for the development of EMS systems across the country.
- 1980s: The first paramedic programs were established, providing advanced life support training for EMS personnel.
- 1990s: The EMS Agenda for the Future was developed, outlining a national vision for EMS systems.
Structure of EMS Systems
EMS systems are typically structured in a hierarchical manner, with multiple levels of care and response.
Components of EMS Systems:
- Emergency Medical Dispatch (EMD): The EMD is responsible for receiving and dispatching emergency calls, as well as providing pre-arrival instructions to callers.
- Ambulance Services: Ambulance services provide transportation and medical care to patients in emergency situations.
- Fire Departments: Fire departments often provide EMS services, including transportation and medical care.
- Hospital Emergency Departments: Hospital emergency departments provide definitive care to patients in emergency situations.
Roles and Responsibilities of EMS Personnel
EMS personnel play a critical role in the delivery of emergency medical care.
Roles and Responsibilities:
- Emergency Medical Technician (EMT): EMTs provide basic life support care, including patient assessment, airway management, and cardiac arrest management.
- Paramedic: Paramedics provide advanced life support care, including patient assessment, medication administration, and cardiac rhythm interpretation.
- EMS Medical Director: The EMS medical director provides medical oversight and direction for EMS personnel.
📝 Note: EMS personnel must possess strong communication and interpersonal skills, as well as the ability to work in high-stress environments.
EMS System Models
There are several models of EMS systems, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages.
Models of EMS Systems:
- Fire-Based EMS: Fire-based EMS systems are integrated with fire departments, providing a seamless response to emergency situations.
- Third-Service EMS: Third-service EMS systems are separate from fire and police departments, providing a dedicated EMS response.
- Private EMS: Private EMS systems are operated by private companies, providing EMS services to specific communities or regions.
Challenges Facing EMS Systems
EMS systems face a number of challenges, including funding constraints, staffing shortages, and increasing demand for services.
Challenges Facing EMS Systems:
- Funding Constraints: EMS systems often struggle to secure adequate funding, leading to limited resources and outdated equipment.
- Staffing Shortages: EMS systems face challenges in recruiting and retaining qualified personnel, particularly in rural areas.
- Increasing Demand: EMS systems are experiencing increasing demand for services, driven by an aging population and growing healthcare needs.
Future Directions for EMS Systems
The future of EMS systems will be shaped by emerging trends and technologies.
Future Directions:
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: EMS systems will increasingly integrate with healthcare systems, providing seamless care transitions and improving patient outcomes.
- Use of Technology: EMS systems will leverage technology, including telemedicine and mobile health applications, to enhance patient care and improve operational efficiency.
- Focus on Prevention: EMS systems will shift towards prevention, providing community-based education and outreach programs to reduce the incidence of emergency situations.
In conclusion, EMS systems play a critical role in the delivery of emergency medical care. Understanding the history, structure, and components of EMS systems, as well as the roles and responsibilities of EMS personnel, is essential for providing high-quality patient care. As EMS systems continue to evolve, they will face challenges and opportunities that will shape the future of emergency medical care.
What is the primary focus of the EMS Systems Act?
+The primary focus of the EMS Systems Act is to provide federal funding for the development of EMS systems across the country.
What is the role of the EMS medical director?
+The EMS medical director provides medical oversight and direction for EMS personnel.
What is the primary challenge facing EMS systems?
+The primary challenge facing EMS systems is funding constraints, leading to limited resources and outdated equipment.