Elements Compounds Mixtures Worksheet Answer Key
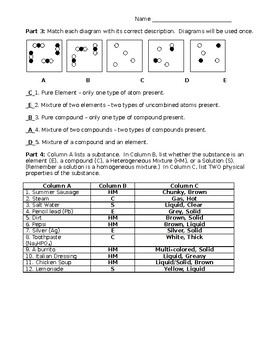
Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures: Understanding the Basics
Chemistry is a vast and fascinating field that studies the building blocks of matter. At its core, chemistry involves understanding the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of chemistry and explore the concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures in detail.
Elements: The Building Blocks of Matter
Elements are the simplest substances in chemistry. They consist of only one type of atom and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks of matter, and they are the foundation of all chemical substances.
There are 118 known elements, each with its unique properties and characteristics. Elements can be classified into different categories based on their properties, such as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
Examples of Elements:
- Hydrogen (H)
- Oxygen (O)
- Carbon ©
- Nitrogen (N)
Compounds: The Combination of Elements
Compounds are formed when two or more different elements are chemically combined. Compounds have properties that are different from those of their individual elements. Compounds can be formed through chemical reactions, such as combustion, synthesis, or decomposition.
Compounds can be classified into different types based on their composition, such as:
- Molecular Compounds: These compounds are formed when two or more different elements are chemically combined and share electrons.
- Ionic Compounds: These compounds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one element to another, resulting in the formation of ions.
Examples of Compounds:
- Water (H2O) - a molecular compound
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) - an ionic compound
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) - a molecular compound
Mixtures: The Physical Combination of Substances
Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are physically combined. Mixtures can be separated into their individual components by physical means, such as filtration, distillation, or chromatography.
Mixtures can be classified into different types based on their composition, such as:
- Homogeneous Mixtures: These mixtures have a uniform composition throughout.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: These mixtures have a non-uniform composition.
Examples of Mixtures:
- Air - a homogeneous mixture of gases
- Soil - a heterogeneous mixture of minerals and organic matter
- Blood - a homogeneous mixture of cells and fluids
Key Differences Between Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
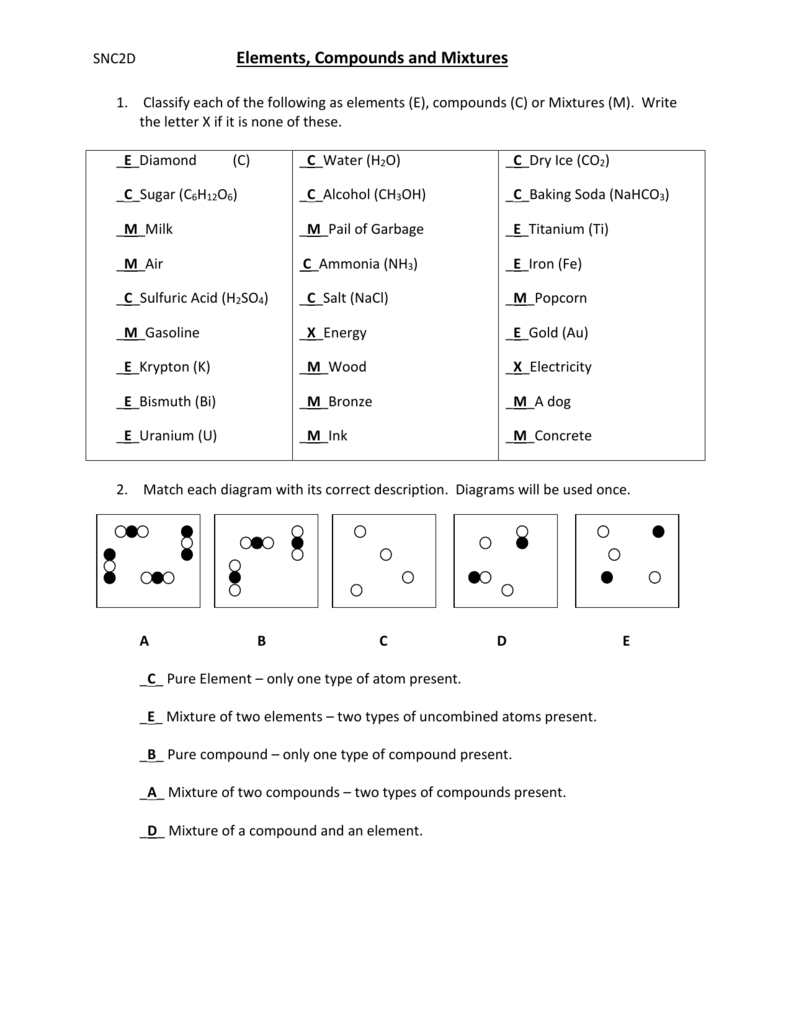
| Property | Elements | Compounds | Mixtures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Only one type of atom | Two or more different elements | Two or more substances |
| Properties | Unique properties | Properties different from individual elements | Properties of individual components |
| Separation | Cannot be broken down | Can be broken down into individual elements | Can be separated into individual components |
📝 Note: The above table highlights the key differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures. Understanding these differences is crucial in chemistry and will help you navigate the world of chemical substances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, elements, compounds, and mixtures are the building blocks of chemistry. Understanding the differences between these three concepts is essential for any aspiring chemist. By recognizing the unique properties and characteristics of elements, compounds, and mixtures, you can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of the chemical world.
What is the main difference between an element and a compound?
+The main difference between an element and a compound is that an element consists of only one type of atom, while a compound consists of two or more different elements chemically combined.
Can a mixture be separated into its individual components?
+Yes, a mixture can be separated into its individual components by physical means, such as filtration, distillation, or chromatography.
What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture?
+A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, while a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition.
Related Terms:
- Element and compound
- Element compound and mixture
- Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures worksheet
- Matter and mixtures
- Quiz element compound mixture
- in a compound the (atoms/molecules)