6 EKG Practice Worksheets to Boost Your Skills
Sharpen Your EKG Interpretation Skills with These 6 Practice Worksheets
Interpreting electrocardiograms (EKGs) is a vital skill for any healthcare professional, particularly those in the fields of cardiology, emergency medicine, and critical care. EKGs provide a graphical representation of the heart’s electrical activity, allowing practitioners to diagnose a range of cardiac conditions, from arrhythmias to myocardial infarctions. However, mastering EKG interpretation requires extensive practice and dedication.
In this article, we will provide you with six EKG practice worksheets to help you improve your skills in interpreting these crucial diagnostic tests. Each worksheet includes a sample EKG tracing, along with a series of questions designed to test your knowledge and ability to analyze the data.
EKG Practice Worksheet 1: Normal Sinus Rhythm
| Lead | P Wave | QRS Complex | T Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Upright | 0.08 sec | Upright |
| II | Upright | 0.10 sec | Upright |
| III | Inverted | 0.08 sec | Inverted |
Questions:
- What is the heart rate in beats per minute (bpm)?
- Is the P wave upright or inverted in lead I?
- What is the duration of the QRS complex in lead II?
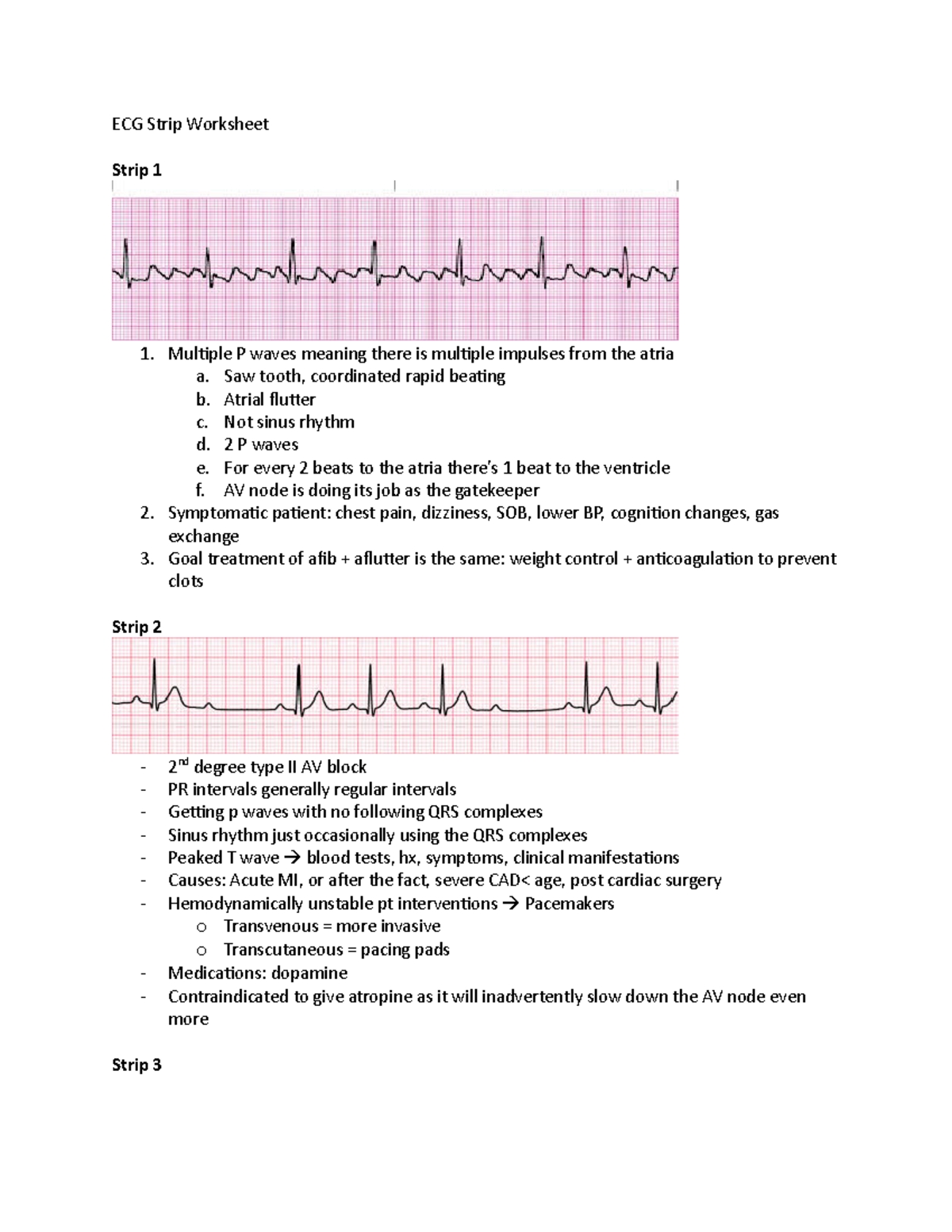
EKG Practice Worksheet 2: Atrial Fibrillation
| Lead | P Wave | QRS Complex | T Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Irregular | 0.10 sec | Variable |
| II | Irregular | 0.12 sec | Variable |
| III | Irregular | 0.10 sec | Variable |
Questions:
- What is the heart rate in bpm?
- Is the rhythm regular or irregular?
- What is the most likely diagnosis based on the EKG tracing?
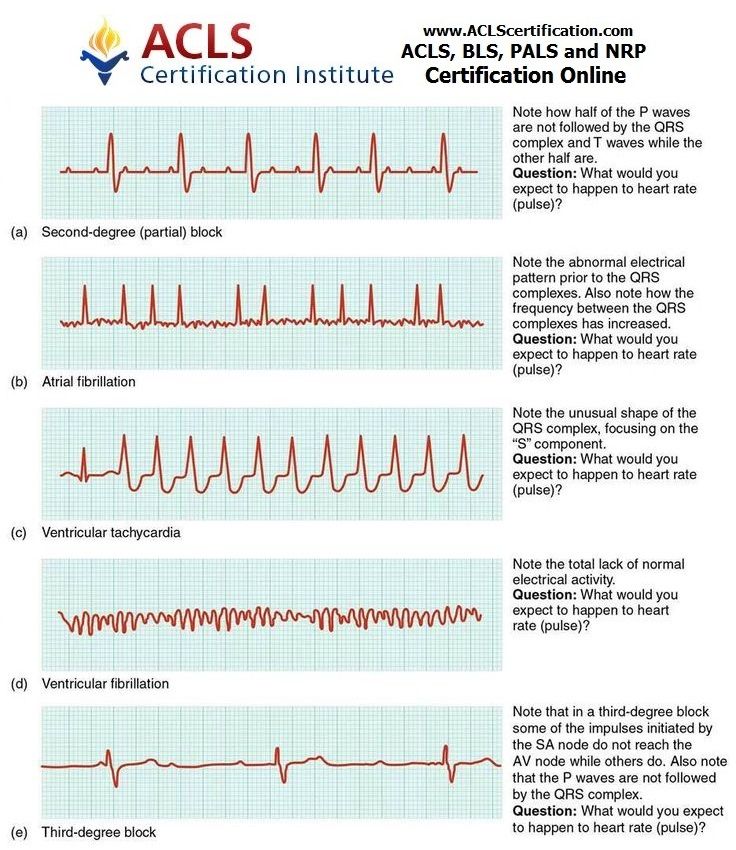
EKG Practice Worksheet 3: Ventricular Tachycardia
| Lead | P Wave | QRS Complex | T Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Absent | 0.14 sec | Inverted |
| II | Absent | 0.16 sec | Inverted |
| III | Absent | 0.14 sec | Inverted |
Questions:
- What is the heart rate in bpm?
- Is the QRS complex narrow or wide?
- What is the most likely diagnosis based on the EKG tracing?
EKG Practice Worksheet 4: Myocardial Infarction
| Lead | P Wave | QRS Complex | T Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Upright | 0.10 sec | Inverted |
| II | Upright | 0.12 sec | Inverted |
| III | Inverted | 0.10 sec | Inverted |
Questions:
- What is the most likely location of the myocardial infarction?
- Is the ST segment elevated or depressed?
- What is the most likely diagnosis based on the EKG tracing?
EKG Practice Worksheet 5: Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
| Lead | P Wave | QRS Complex | T Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Upright | 0.08 sec | Upright |
| II | Upright | 0.10 sec | Upright |
| III | Inverted | 0.08 sec | Inverted |
Questions:
- What is the characteristic feature of the QRS complex in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
- Is the P wave upright or inverted in lead I?
- What is the most likely diagnosis based on the EKG tracing?
EKG Practice Worksheet 6: Bundle Branch Block
| Lead | P Wave | QRS Complex | T Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Upright | 0.12 sec | Upright |
| II | Upright | 0.14 sec | Upright |
| III | Inverted | 0.12 sec | Inverted |
Questions:
- What is the most likely location of the bundle branch block?
- Is the QRS complex narrow or wide?
- What is the most likely diagnosis based on the EKG tracing?
📝 Note: These practice worksheets are intended to provide a basic understanding of EKG interpretation and should not be used as a substitute for formal education or clinical experience.
By working through these six EKG practice worksheets, you will gain a better understanding of the fundamentals of EKG interpretation and be able to apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios. Remember to always practice interpreting EKGs in a controlled environment, and seek guidance from experienced healthcare professionals if you have any questions or concerns.
What is the normal heart rate range in beats per minute (bpm)?
+The normal heart rate range is between 60-100 bpm.
What is the most common type of atrial fibrillation?
+The most common type of atrial fibrillation is paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, which is characterized by intermittent episodes of atrial fibrillation.
What is the difference between a bundle branch block and a Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
+A bundle branch block is a condition in which the electrical impulse is delayed or blocked in one of the bundle branches, whereas Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a condition in which an accessory electrical pathway connects the atria and ventricles, causing a rapid heart rate.
By mastering the fundamentals of EKG interpretation, you will be better equipped to provide high-quality patient care and improve outcomes in a variety of clinical settings. Remember to always stay up-to-date with the latest developments in EKG interpretation and to seek guidance from experienced healthcare professionals if you have any questions or concerns.