5 Steps to Master Ecological Succession
Understanding Ecological Succession: A Key to Environmental Balance
Ecological succession is a fundamental concept in environmental science that describes the process of change in the species composition of a biological community over time. It’s a crucial aspect of understanding how ecosystems respond to disturbances, such as natural disasters or human activities. Mastering ecological succession requires a deep understanding of the underlying principles and mechanisms that drive these changes. In this article, we’ll explore the five steps to master ecological succession and provide insights into the key concepts and processes involved.
Step 1: Understand the Types of Ecological Succession
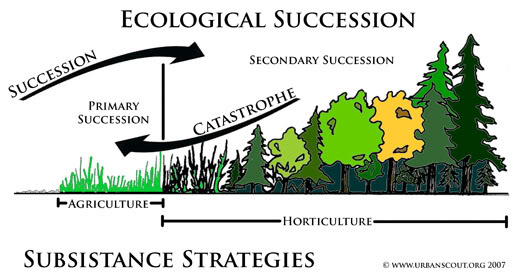
There are two primary types of ecological succession: primary succession and secondary succession. Primary succession occurs in areas where no soil or vegetation existed before, such as after a volcanic eruption or the retreat of a glacier. Secondary succession, on the other hand, takes place in areas where soil and vegetation were previously present but were disturbed or damaged, such as after a forest fire or agricultural activities.
Primary Succession
- Occurs in areas with no previous soil or vegetation
- Begins with the establishment of pioneer species, such as lichens and mosses
- Gradually progresses to more complex communities, such as shrubs and trees
Secondary Succession
- Occurs in areas with previous soil and vegetation
- Begins with the regrowth of vegetation from remaining seeds, roots, or stems
- Progresses rapidly, often with the establishment of a new dominant species
Step 2: Identify the Key Factors Influencing Ecological Succession
Several factors influence the process of ecological succession, including:
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and seasonal patterns affect the types of species that can thrive in an area.
- Soil: The quality and quantity of soil nutrients, as well as the presence of microorganisms, impact the establishment of plant species.
- Topography: The shape and elevation of the land influence the distribution of water, nutrients, and species.
- Disturbance: Natural or human-induced disturbances, such as fires, floods, or deforestation, can reset the succession process.
Step 3: Analyze the Stages of Ecological Succession
Ecological succession involves a series of stages, each characterized by a distinct set of species and community structures. The stages of succession can be broadly categorized into:
- Pioneer Stage: The initial stage, dominated by pioneer species that can tolerate harsh conditions.
- Transition Stage: A stage of rapid growth and diversification, with the establishment of new species and community structures.
- Climax Stage: The final stage, characterized by a stable and complex community, often dominated by a single species.
Step 4: Understand the Role of Keystone Species in Ecological Succession
Keystone species play a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of ecological succession. These species, often predators or herbivores, can:
- Engineer Ecosystems: Create habitat structures that support other species, such as beavers building dams.
- Modify Environmental Conditions: Alter environmental conditions, such as temperature or nutrient availability, to favor certain species.
- Regulate Population Dynamics: Influence population sizes and structures through predation, herbivory, or competition.
Step 5: Apply Ecological Succession Principles to Real-World Scenarios
Mastering ecological succession requires the ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios. This can involve:
- Conservation: Using succession principles to design and implement conservation strategies, such as reforestation or habitat restoration.
- Land Management: Applying succession concepts to manage land use, such as agriculture or forestry, to minimize environmental impacts.
- Ecological Restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems by manipulating succession processes to promote biodiversity and ecosystem function.
📝 Note: Ecological succession is a complex and multifaceted process, and mastering it requires a deep understanding of the underlying principles and mechanisms. By following these five steps, you'll be well on your way to becoming proficient in ecological succession and its applications.
By mastering ecological succession, we can better understand how ecosystems respond to disturbances, design effective conservation strategies, and promote environmental balance.
What is ecological succession?
+
Ecological succession is the process of change in the species composition of a biological community over time.
What are the two primary types of ecological succession?
+
Primary succession and secondary succession.
What is a keystone species?
+
A keystone species is a species that plays a unique and crucial role in shaping the trajectory of ecological succession.