DNA Structure Worksheet Answers for Biology Students
DNA Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Guide for Biology Students
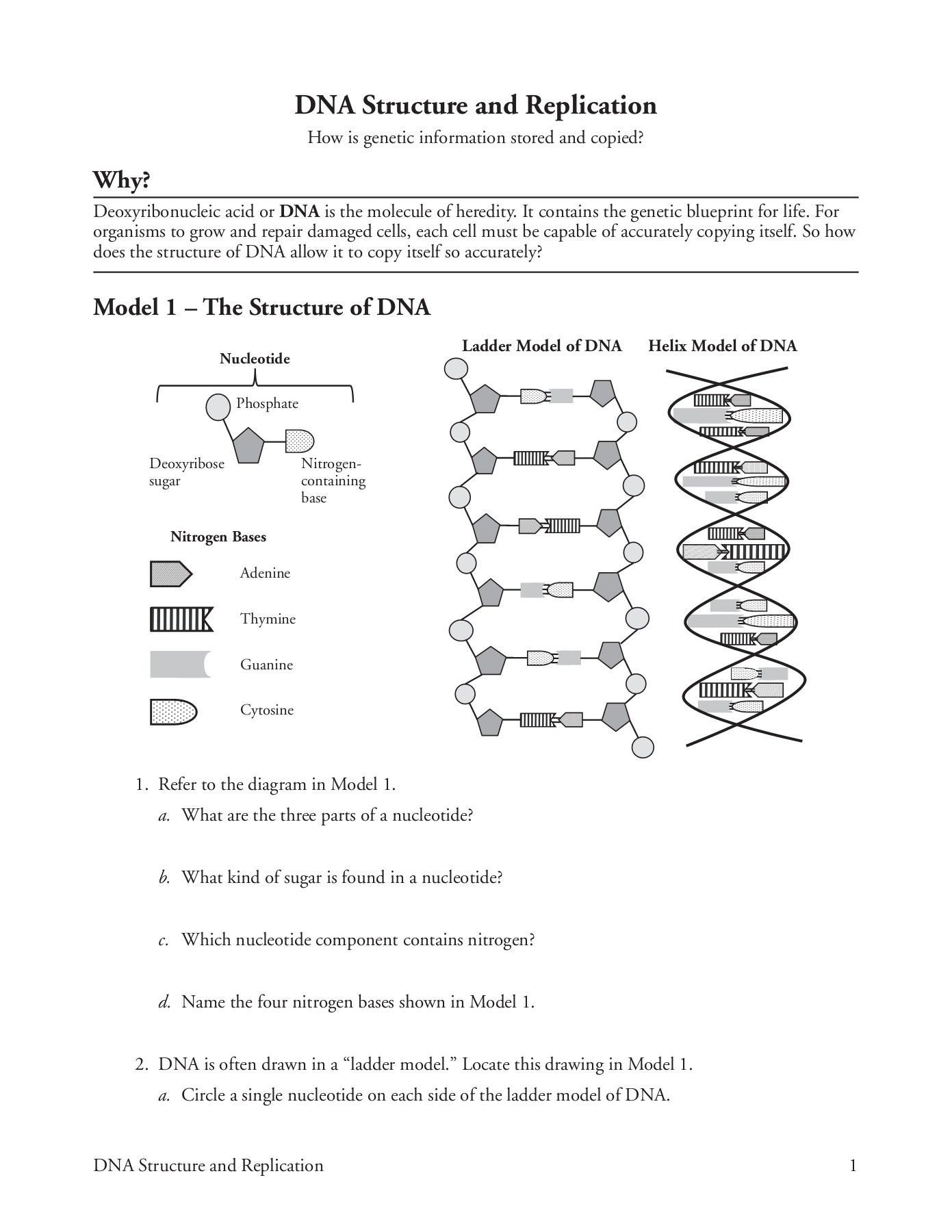
Understanding the structure and function of DNA is crucial for biology students. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNA, exploring its structure, function, and importance in biology.
DNA Structure: The Double Helix Model
The DNA molecule is composed of two strands that are twisted together in a double helix formation. This structure was first discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. The double helix model consists of:
- Sugar and phosphate molecules: These molecules make up the backbone of the DNA molecule.
- Nitrogenous bases: There are four types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T).
- Hydrogen bonds: The nitrogenous bases are paired together through hydrogen bonds. Adenine pairs with thymine, while guanine pairs with cytosine.

| Nitrogenous Base | Pairing Partner |
|---|---|
| Adenine (A) | Thymine (T) |
| Guanine (G) | Cytosine (C) |
DNA Replication: The Process of Creating a New DNA Strand
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process involves:
- Unwinding of the double helix: The double helix is unwound, and the two strands are separated.
- Synthesis of new strands: An enzyme called DNA polymerase matches the nitrogenous bases on the new strands to the bases on the template strands.
- Proofreading and editing: The new strands are proofread and edited to ensure that there are no errors.
🔍 Note: DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning that the new DNA molecule is composed of one old strand and one new strand.
DNA Transcription and Translation: The Central Dogma
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to proteins. This process involves:
- Transcription: The genetic information in DNA is used to create a complementary RNA molecule.
- Translation: The RNA molecule is translated into a protein.
Key Players in DNA Structure and Function
- DNA polymerase: An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands.
- RNA polymerase: An enzyme that synthesizes RNA molecules.
- Ribosomes: Small organelles that translate RNA into proteins.
Importance of DNA in Biology
DNA plays a crucial role in biology, as it:
- Determines genetic traits: DNA determines the characteristics of an organism, such as eye color and height.
- Influences behavior: DNA can influence behavior, such as susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Provides genetic information: DNA provides genetic information for the development and function of all living organisms.
In conclusion, understanding the structure and function of DNA is essential for biology students. The double helix model, DNA replication, transcription, and translation are all critical concepts in molecular biology. DNA plays a vital role in determining genetic traits, influencing behavior, and providing genetic information for the development and function of all living organisms.
What is the function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
+DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by matching the nitrogenous bases on the new strands to the bases on the template strands.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
+The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to proteins, involving transcription and translation.
Why is DNA important in biology?
+DNA plays a crucial role in biology, as it determines genetic traits, influences behavior, and provides genetic information for the development and function of all living organisms.