5 Key Steps in DNA Replication Process
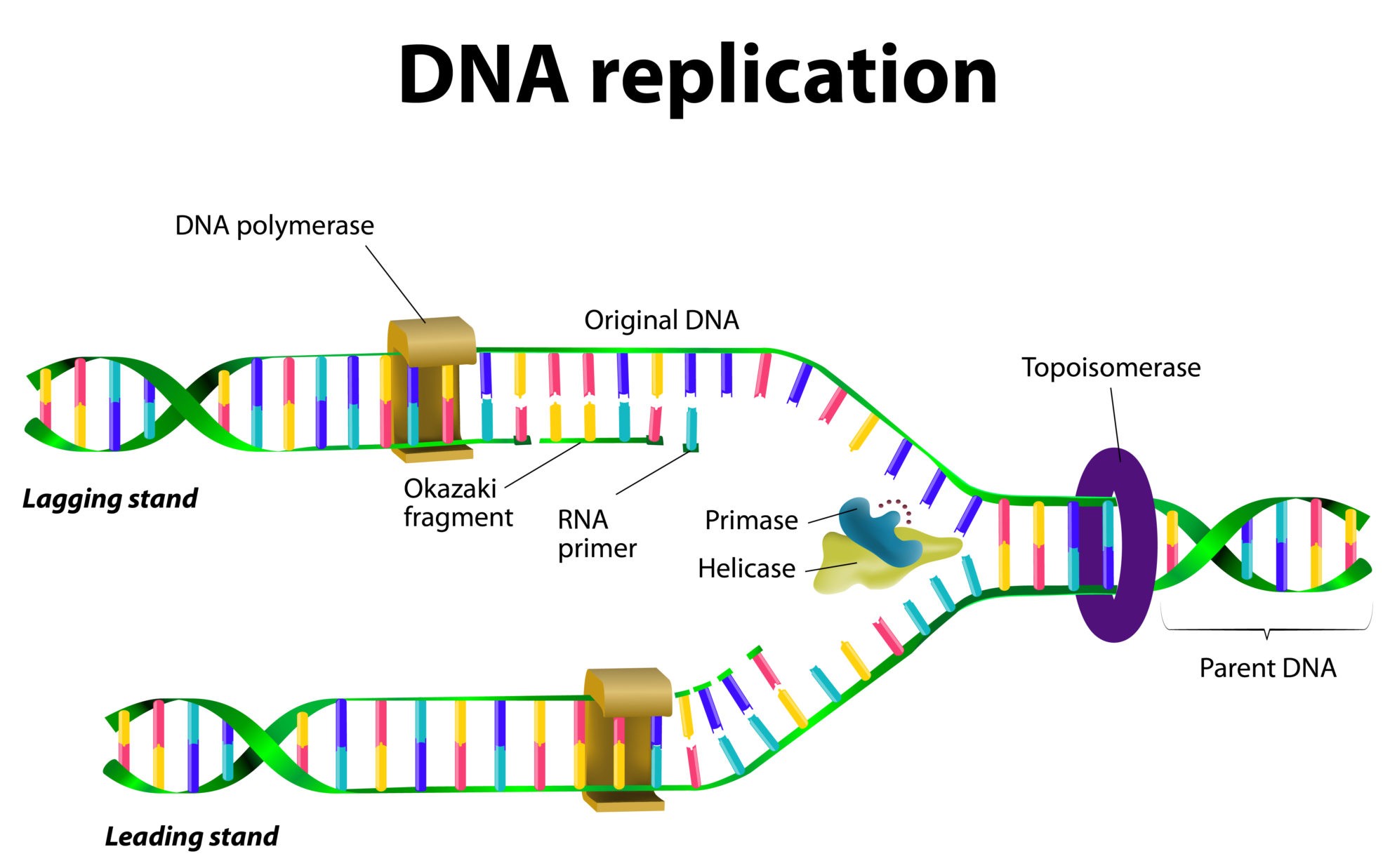
Understanding the DNA Replication Process
The DNA replication process is a complex and crucial mechanism that occurs in all living organisms. It is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. In this article, we will explore the five key steps involved in the DNA replication process.
Step 1: Initiation
The first step in the DNA replication process is initiation. During this stage, the replication machinery is assembled, and the DNA molecule is unwound. The process begins at a specific region of the DNA molecule called the origin of replication. At this site, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the double helix structure of DNA, creating a replication fork.
🔍 Note: The origin of replication is a specific sequence of nucleotides that serves as a binding site for the replication machinery.
Step 2: Unwinding and Binding
As the DNA molecule is unwound, an enzyme called topoisomerase relaxes the supercoiled DNA, allowing the replication machinery to access the template strands. The replication machinery, including enzymes and proteins, binds to the unwound DNA molecule. This complex of enzymes and proteins is known as the replisome.
Key Players in the Replisome
- Helicase: Unwinds the DNA molecule
- Topoisomerase: Relaxes the supercoiled DNA
- Primase: Adds RNA primers to the template strands
- DNA polymerase: Synthesizes new DNA strands
Step 3: Synthesis
During the synthesis stage, the replisome begins to synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the template strands. The process is initiated by the addition of RNA primers to the template strands by the enzyme primase. DNA polymerase then extends the primers by adding nucleotides to the growing DNA strands.
💡 Note: The synthesis stage is a continuous process, with DNA polymerase adding nucleotides to the growing DNA strands in a 5' to 3' direction.
Step 4: Elongation
As the synthesis stage continues, the replisome moves along the DNA molecule, unwinding and synthesizing new DNA strands. This process is known as elongation. During this stage, the replisome encounters various obstacles, including DNA damage and replication forks.
Challenges During Elongation
- DNA damage: Errors in the DNA molecule can occur during replication, leading to mutations
- Replication forks: The replisome must navigate replication forks, where the leading strand and lagging strand meet
Step 5: Termination
The final stage of the DNA replication process is termination. During this stage, the replisome completes the synthesis of the new DNA strands and releases the replicated DNA molecule. The process is completed when the replisome encounters a specific sequence of nucleotides, known as the terminator sequence.
| Stage | Process | Key Players |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Assembly of replication machinery and unwinding of DNA | Helicase, topoisomerase |
| Unwinding and Binding | Unwinding of DNA and binding of replication machinery | Helicase, topoisomerase, primase |
| Synthesis | Synthesis of new DNA strands | Primase, DNA polymerase |
| Elongation | Unwinding and synthesis of new DNA strands | Helicase, topoisomerase, DNA polymerase |
| Termination | Completion of synthesis and release of replicated DNA | Replisome |
In conclusion, the DNA replication process is a complex and highly regulated mechanism that ensures the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. Understanding the five key steps involved in this process is crucial for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern life.
What is the origin of replication?
+The origin of replication is a specific region of the DNA molecule where the replication machinery is assembled and the DNA molecule is unwound.
What is the role of helicase in the DNA replication process?
+Helicase unwinds the DNA molecule, creating a replication fork and allowing the replication machinery to access the template strands.
What is the replisome?
+The replisome is a complex of enzymes and proteins that binds to the unwound DNA molecule and synthesizes new DNA strands.
Related Terms:
- DNA Structure worksheet
- DNA structure and replication pogil
- Dna no rna
- RNA DNA