5 Essential Steps in DNA Replication
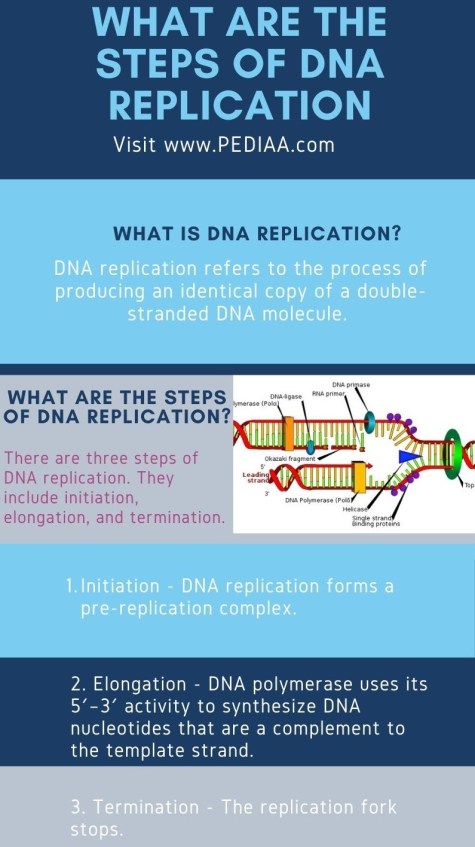
Understanding the Process of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a crucial process that occurs in all living organisms. It involves the creation of an exact copy of the DNA molecule, which is necessary for cell division and the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. The process of DNA replication is complex and involves multiple steps. In this article, we will explore the five essential steps involved in DNA replication.
Step 1: Initiation
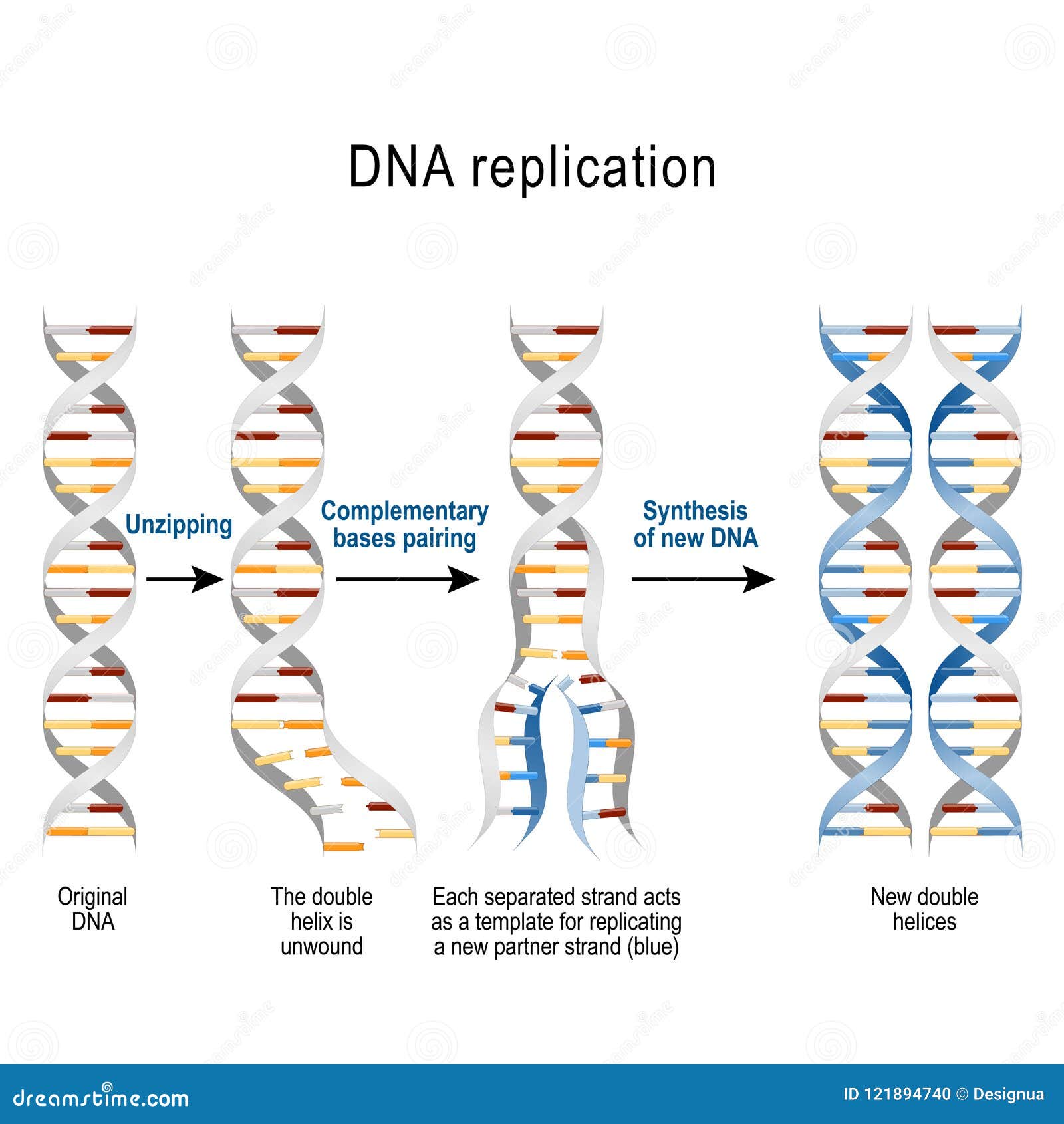
The first step in DNA replication is initiation. During this step, the DNA molecule is unwound, and the replication process is initiated. This is achieved through the binding of proteins to specific regions of the DNA molecule, known as origins of replication. The proteins that bind to these regions are called initiators, and they play a crucial role in unwinding the DNA molecule.
Once the DNA molecule is unwound, an enzyme called helicase is activated. Helicase unwinds the DNA molecule by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases. This creates a replication fork, which is the point at which the DNA molecule is separated into two strands.
🔬 Note: The replication fork is a critical region in the DNA molecule, as it is the site at which the replication process occurs.
Step 2: Unwinding
The second step in DNA replication is unwinding. During this step, the DNA molecule is further unwound, and the replication fork is extended. This is achieved through the action of enzymes called topoisomerases, which relieve the tension in the DNA molecule by cutting and rejoining it.
As the DNA molecule is unwound, the replication fork is extended, and the template strands are exposed. The template strands are the strands of DNA that serve as a template for the synthesis of new DNA molecules.
Step 3: Synthesis
The third step in DNA replication is synthesis. During this step, new DNA molecules are synthesized using the template strands. This is achieved through the action of enzymes called DNA polymerases, which add nucleotides to the growing DNA molecule.
DNA polymerases read the template strands and match the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules. The nucleotides are then linked together to form a new DNA molecule.
🔬 Note: DNA polymerases are highly accurate enzymes that ensure that the new DNA molecule is an exact copy of the template strands.
Step 4: Elongation
The fourth step in DNA replication is elongation. During this step, the new DNA molecule is extended through the addition of nucleotides. This is achieved through the action of DNA polymerases, which continue to read the template strands and add nucleotides to the growing DNA molecule.
As the new DNA molecule is extended, the replication fork is extended, and the template strands are exposed. This process continues until the entire DNA molecule has been replicated.
Step 5: Termination
The fifth and final step in DNA replication is termination. During this step, the replication process is completed, and the new DNA molecule is sealed.
This is achieved through the action of enzymes called DNA ligases, which seal the gaps between the nucleotides. The new DNA molecule is then released, and the replication process is complete.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initiation | The DNA molecule is unwound, and the replication process is initiated. |
| Unwinding | The DNA molecule is further unwound, and the replication fork is extended. |
| Synthesis | New DNA molecules are synthesized using the template strands. |
| Elongation | The new DNA molecule is extended through the addition of nucleotides. |
| Termination | The replication process is completed, and the new DNA molecule is sealed. |
In summary, DNA replication is a complex process that involves multiple steps. The five essential steps involved in DNA replication are initiation, unwinding, synthesis, elongation, and termination. Understanding these steps is crucial for understanding the process of DNA replication and the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
+Helicase unwinds the DNA molecule by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases, creating a replication fork.
What is the role of DNA polymerases in DNA replication?
+DNA polymerases read the template strands and add nucleotides to the growing DNA molecule, ensuring that the new DNA molecule is an exact copy of the template strands.
What is the role of DNA ligases in DNA replication?
+DNA ligases seal the gaps between the nucleotides, completing the replication process and releasing the new DNA molecule.