DNA Replication Practice Worksheet Answer Key
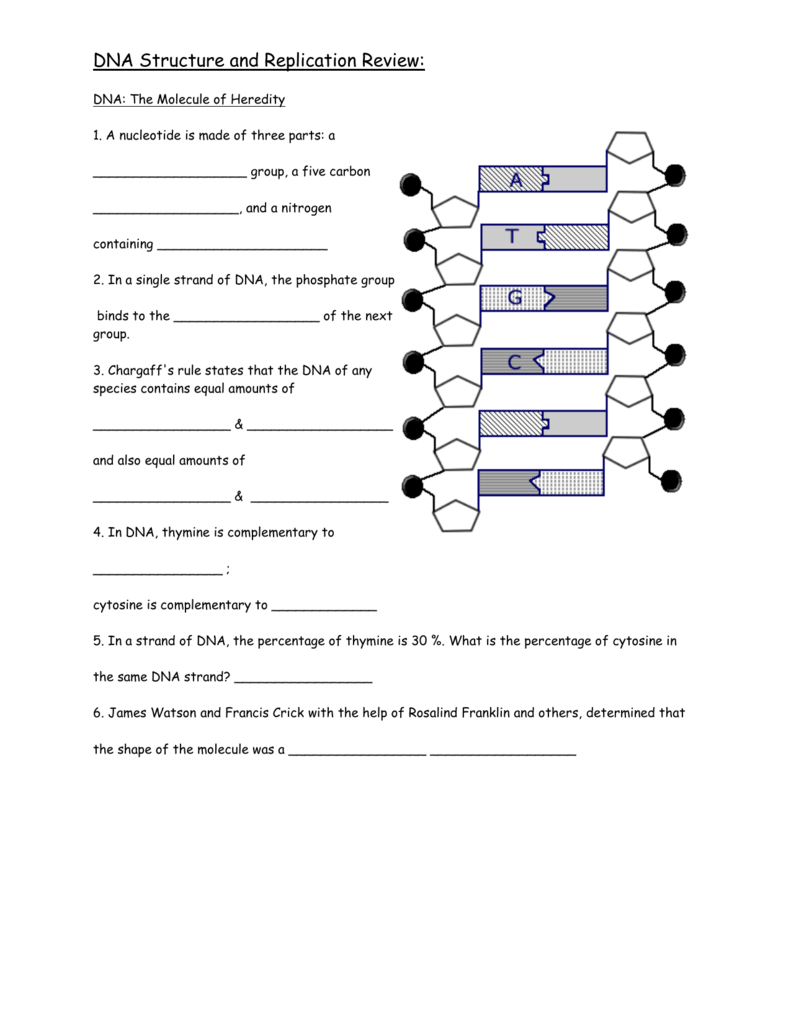
Understanding DNA Replication: A Comprehensive Guide
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. In this guide, we will walk you through the steps of DNA replication, highlighting key concepts and processes.
The DNA Replication Process
The DNA replication process involves several steps, including:
- Initiation: The process of DNA replication begins with the unwinding of the double helix at a specific region called the origin of replication.
- Unwinding: An enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, creating a replication fork.
- Binding of Primers: Short RNA primers are synthesized and bound to the template strands at specific regions called primer binding sites.
- Elongation: DNA polymerase reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C). The nucleotides are then linked together to form a new DNA strand.
- Leading Strand Synthesis: DNA polymerase synthesizes the leading strand continuously, reading the template strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- Lagging Strand Synthesis: The lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments. Each Okazaki fragment is about 1000-2000 nucleotides long and is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- RNA Primer Removal: Once the Okazaki fragments are synthesized, the RNA primers are removed and replaced with DNA nucleotides.
- Ligation: The Okazaki fragments are joined together by an enzyme called DNA ligase, forming a continuous strand.
💡 Note: DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning that the resulting DNA molecule contains one old strand (the template strand) and one new strand.
Key Players in DNA Replication
Several enzymes and proteins play critical roles in the DNA replication process, including:
- Helicase: Unwinds the DNA double helix at the origin of replication.
- Primase: Synthesizes RNA primers, which are necessary for initiating DNA synthesis.
- DNA Polymerase: Reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules.
- DNA Ligase: Joins the Okazaki fragments together, forming a continuous strand.
DNA Replication Practice Worksheet Answer Key
Here are the answers to a sample DNA replication practice worksheet:

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the function of helicase in DNA replication? | Unwinds the DNA double helix at the origin of replication. |
| What is the role of primase in DNA replication? | Synthesizes RNA primers, which are necessary for initiating DNA synthesis. |
| What is the function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication? | Reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules. |
| What is the purpose of the leading strand in DNA replication? | The leading strand is synthesized continuously, reading the template strand in the 5' to 3' direction. |
| What is the function of DNA ligase in DNA replication? | Joins the Okazaki fragments together, forming a continuous strand. |
In summary, DNA replication is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of several enzymes and proteins. Understanding the key concepts and processes of DNA replication is essential for appreciating the intricacies of genetic transmission.
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication?
+The leading strand is synthesized continuously, reading the template strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments.
What is the role of RNA primers in DNA replication?
+RNA primers are necessary for initiating DNA synthesis. They provide a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin synthesizing new DNA strands.
What is the function of DNA ligase in DNA replication?
+DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragments together, forming a continuous strand.