Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answers Explained
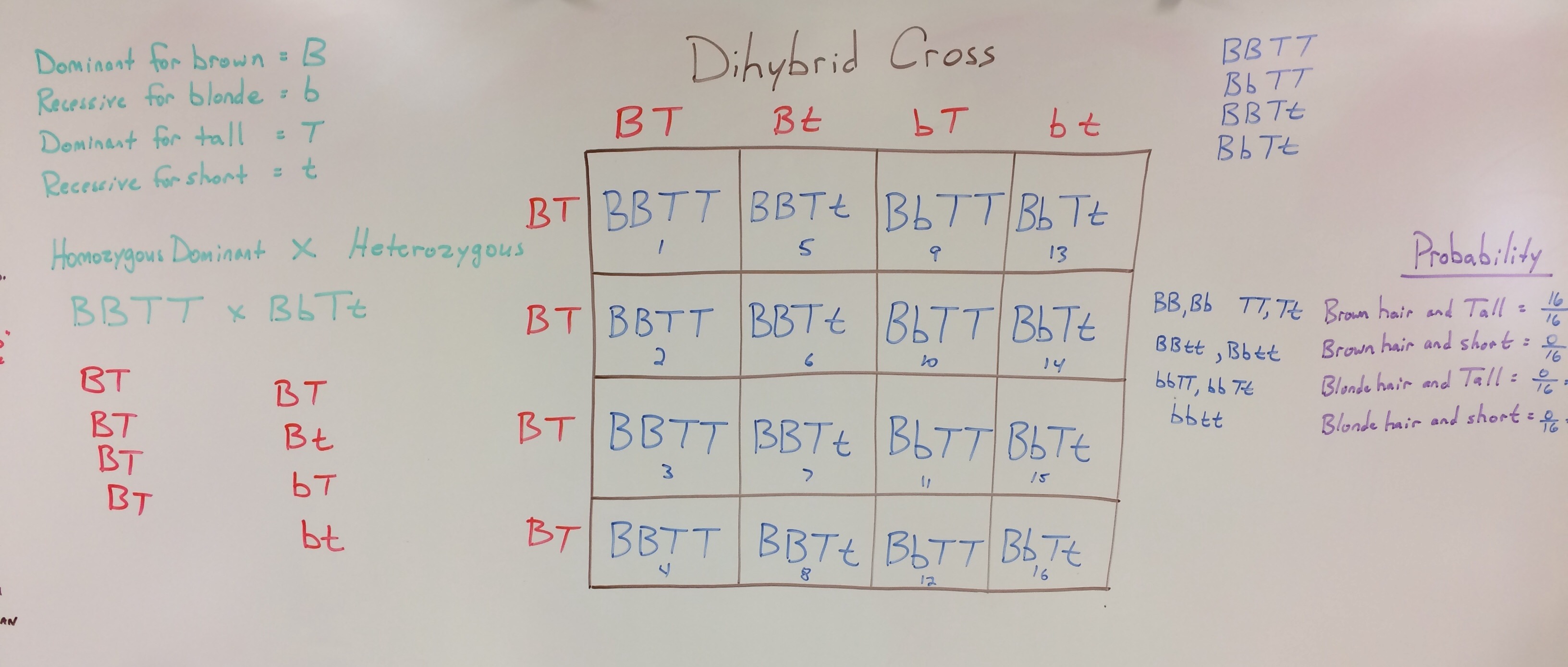
Understanding Dihybrid Crosses: A Comprehensive Guide
In the field of genetics, dihybrid crosses are a fundamental concept used to study the inheritance of traits. A dihybrid cross involves the crossing of two parents that differ in two specific traits, resulting in offspring with a combination of these traits. In this article, we will delve into the world of dihybrid crosses, explaining the concept, the process, and providing a worksheet with answers.
What is a Dihybrid Cross?
A dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves the study of two traits at a time. This type of cross is used to understand the interactions between two genes and how they affect the phenotype of an organism. In a dihybrid cross, the two parents are chosen such that they differ in two specific traits, and the offspring are analyzed to determine the inheritance pattern of these traits.
The Process of a Dihybrid Cross
The process of a dihybrid cross involves several steps:
- Selection of parents: Two parents are selected that differ in two specific traits. For example, let’s say we want to study the inheritance of flower color and plant height in pea plants. We would choose one parent with red flowers and tall stems, and another parent with white flowers and short stems.
- Crossing the parents: The two parents are crossed to produce offspring. This is done by transferring pollen from the anther of one parent to the stigma of the other parent.
- Analysis of offspring: The offspring are analyzed to determine the inheritance pattern of the two traits. This is done by counting the number of offspring with each combination of traits.
- Determination of genotypes and phenotypes: The genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring are determined based on the inheritance pattern. Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype refers to the physical expression of the genotype.
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answers
Here is a sample dihybrid cross worksheet with answers:
Problem 1:
A pea plant with red flowers and tall stems (RrTt) is crossed with a pea plant with white flowers and short stems (rrtt). What is the probability of offspring with red flowers and short stems?
Answer:
To solve this problem, we need to determine the genotype of the offspring. The genotype of the offspring can be determined using a Punnett square.
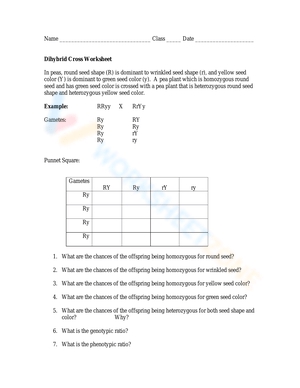
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| T | RT | rT |
| t | Rt | rt |
The probability of offspring with red flowers and short stems (Rrt) is 25%.
Problem 2:
A corn plant with yellow kernels and tall stems (YyTt) is crossed with a corn plant with white kernels and short stems (yytt). What is the probability of offspring with yellow kernels and short stems?
Answer:
To solve this problem, we need to determine the genotype of the offspring. The genotype of the offspring can be determined using a Punnett square.
| Y | y | |
|---|---|---|
| T | YT | yT |
| t | Yt | yt |
The probability of offspring with yellow kernels and short stems (Yytt) is 25%.
Problem 3:
A tomato plant with red fruit and tall stems (RrTt) is crossed with a tomato plant with yellow fruit and short stems (rrtt). What is the probability of offspring with red fruit and short stems?
Answer:
To solve this problem, we need to determine the genotype of the offspring. The genotype of the offspring can be determined using a Punnett square.
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| T | RT | rT |
| t | Rt | rt |
The probability of offspring with red fruit and short stems (Rrt) is 25%.
📝 Note: The answers to these problems assume that the traits are inherited in a simple Mendelian fashion, with no epistasis or other complicating factors.
Conclusion
Dihybrid crosses are an essential tool in genetics, allowing us to study the inheritance of traits and understand the interactions between genes. By analyzing the offspring of a dihybrid cross, we can determine the genotype and phenotype of the offspring and gain insights into the underlying genetics. We hope this article has provided a comprehensive guide to dihybrid crosses and helped you understand the concept and process.
What is the main purpose of a dihybrid cross?
+The main purpose of a dihybrid cross is to study the inheritance of two traits at a time and understand the interactions between two genes.
How is a dihybrid cross different from a monohybrid cross?
+A dihybrid cross involves the study of two traits at a time, while a monohybrid cross involves the study of one trait at a time.
What is the genotype of an organism?
+The genotype of an organism refers to its genetic makeup, including the specific genes and alleles it possesses.
Related Terms:
- Dihybrid cross Worksheet PDF
- Dihybrid practice problems
- Dihybrid cross problems with answers
- Dihybrid cross example