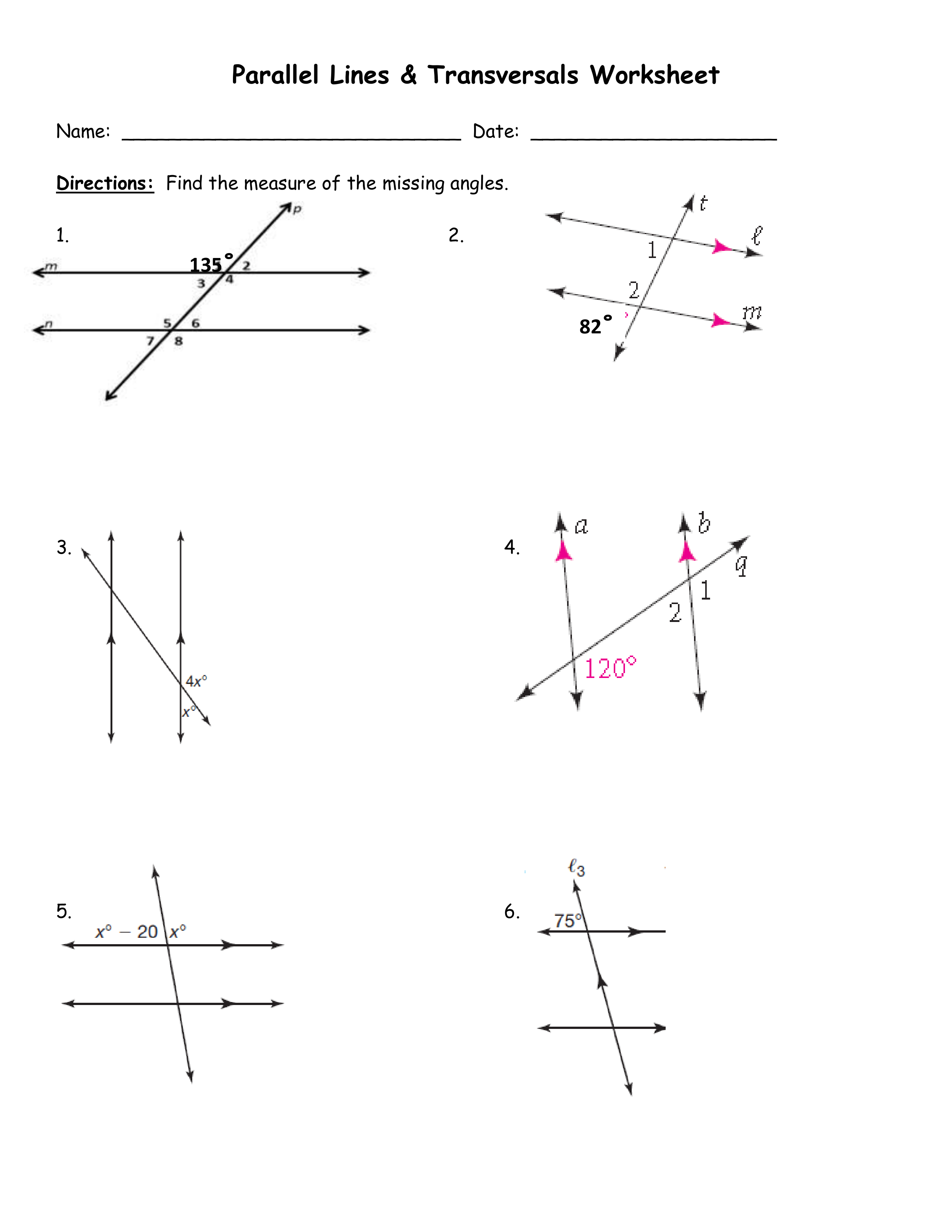
Counting Subatomic Particles Worksheet for Physics Students
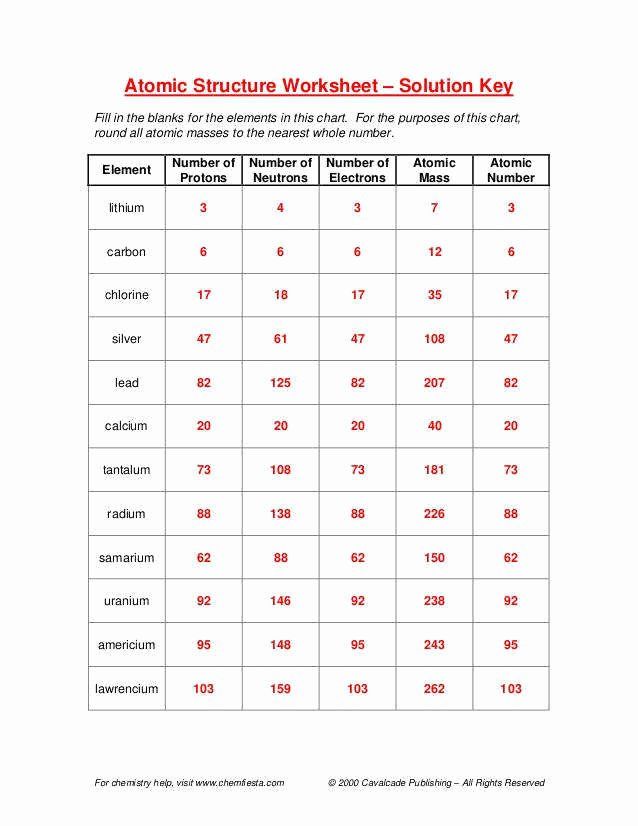
Understanding the World of Subatomic Particles
In the realm of physics, the study of subatomic particles is crucial for understanding the fundamental nature of matter and the universe. As a physics student, it is essential to grasp the concepts of subatomic particles and their interactions. This worksheet is designed to help you count and understand subatomic particles in a fun and interactive way.
What are Subatomic Particles?
Subatomic particles are the building blocks of matter that make up atoms. They are the smallest units of matter that still retain the properties of the element they represent. The three main types of subatomic particles are:
- Protons: positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus of an atom
- Neutrons: particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus of an atom
- Electrons: negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom
Counting Subatomic Particles
Let’s practice counting subatomic particles with a few examples:
- The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. For example, if the atomic number of an element is 6, how many protons does it have?
- The mass number of an element is equal to the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. For example, if the mass number of an element is 14, and it has 7 protons, how many neutrons does it have?
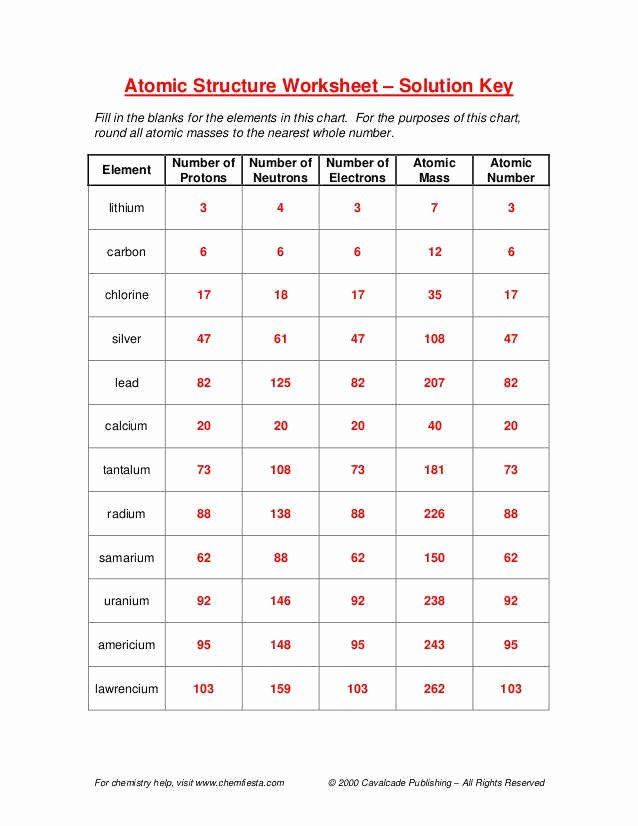
| Element | Atomic Number (Protons) | Mass Number (Protons + Neutrons) | Number of Neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Helium | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 16 | 8 |
Exercises
- If an element has an atomic number of 10, how many protons does it have?
- If an element has a mass number of 20 and 8 protons, how many neutrons does it have?
- If an element has 5 electrons, how many protons does it have?
Notes
💡 Note: The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It is a way of describing the energy levels and orbitals of electrons in an atom. The electron configuration of an atom is determined by the number of electrons it has.
- Energy Levels: the energy levels of an atom are the regions around the nucleus where electrons are found. The energy levels are labeled as 1, 2, 3, etc.
- Orbitals: the orbitals of an atom are the regions within an energy level where electrons are found. The orbitals are labeled as s, p, d, etc.
Electron Configuration Notation
Electron configuration notation is a way of writing the electron configuration of an atom using numbers and letters.
- 1s²: this notation means that there are 2 electrons in the s-orbital of the first energy level
- 2p⁶: this notation means that there are 6 electrons in the p-orbital of the second energy level
Exercises
- Write the electron configuration notation for an atom with 10 electrons.
- Draw the electron configuration diagram for an atom with 8 electrons.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding subatomic particles and their interactions is crucial for physics students. By practicing counting subatomic particles and understanding electron configuration, you will gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental nature of matter and the universe.
What is the difference between protons and neutrons?
+Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. Protons reside in the nucleus of an atom, while neutrons also reside in the nucleus and help determine the mass number of an element.
What is electron configuration notation?
+Electron configuration notation is a way of writing the electron configuration of an atom using numbers and letters. It describes the energy levels and orbitals of electrons in an atom.
How many electrons does a neutral atom have?
+A neutral atom has the same number of electrons as protons. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of the element.
Related Terms:
- Subatomic particles worksheet With answers
- Subatomic particles worksheet PDF answers
- Subatomic particles ions Worksheet
- Atomic Structure Worksheet PDF
- How To get subatomic particles