Counting Atoms Worksheet 2 Answer Key
Understanding Atomic Structure and Counting Atoms
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, and understanding their structure and how to count them is crucial in chemistry. In this worksheet, we will review the key concepts related to atomic structure and provide answers to common problems encountered when counting atoms.
Atomic Structure Basics
Atoms are composed of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
- Protons: positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus.
- Neutrons: particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus.
- Electrons: negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas
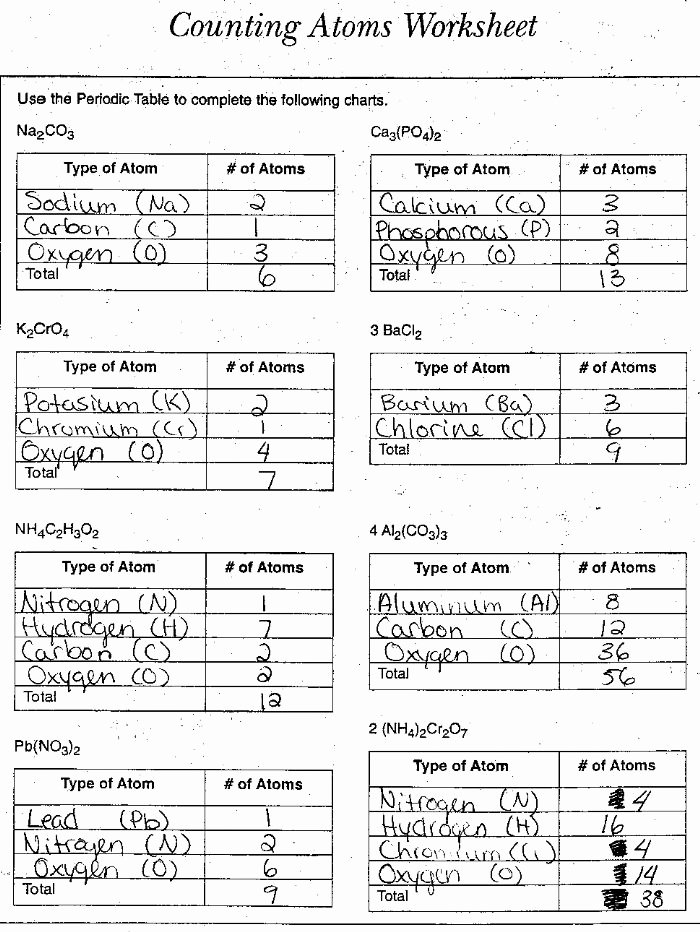
When counting atoms in chemical formulas, it is essential to understand the rules that apply:
- Elements: Count the number of atoms of each element.
- Compounds: Multiply the number of atoms of each element by the subscript number.
- Parentheses: Apply the rules inside the parentheses first, then multiply by the subscript outside.
Counting Atoms Examples
| Chemical Formula | Number of Atoms |
|---|---|
| CO2 | 1 C, 2 O |
| H2O | 2 H, 1 O |
| (NH3)2 | 2 N, 6 H |
Rules for Counting Atoms
- Elements: Count the number of atoms of each element.
- Example: He (1 He)
- Compounds: Multiply the number of atoms of each element by the subscript number.
- Example: CO2 (1 C, 2 O)
- Parentheses: Apply the rules inside the parentheses first, then multiply by the subscript outside.
- Example: (NH3)2 (2 N, 6 H)
[💡] Note: When counting atoms, always follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS).
Practice Exercises
Count the number of atoms of each element in the following chemical formulas:
- CH4
- Ca(OH)2
- (H2O)3
Answers
- CH4: 1 C, 4 H
- Ca(OH)2: 1 Ca, 2 O, 2 H
- (H2O)3: 6 H, 3 O
Common Mistakes and Tips
When counting atoms, be mindful of the following common mistakes:
- Forgetting subscripts: Always check for subscripts and apply the rules accordingly.
- Ignoring parentheses: Parentheses can change the number of atoms significantly; make sure to apply the rules inside and outside the parentheses.
Tips:
- Read the formula carefully: Take your time when reading the chemical formula to avoid missing any subscripts or parentheses.
- Apply the rules step-by-step: Break down the formula into smaller parts to ensure accurate counting.
Atomic Structure and Counting Atoms Review
In this review, we covered the basics of atomic structure and how to count atoms in chemical formulas. Remember to apply the rules carefully and avoid common mistakes.
Summary
- Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Counting atoms in chemical formulas requires understanding the rules for elements, compounds, and parentheses.
- Apply the rules step-by-step to avoid errors.
Image
[Image description: atomic structure illustration]
What is the basic structure of an atom?
+An atom consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
How do you count atoms in a chemical formula?
+Counting atoms in a chemical formula involves applying the rules for elements, compounds, and parentheses. For elements, count the number of atoms of each element. For compounds, multiply the number of atoms of each element by the subscript number. For parentheses, apply the rules inside the parentheses first, then multiply by the subscript outside.
What are common mistakes to avoid when counting atoms?
+
By understanding the basics of atomic structure and how to count atoms in chemical formulas, you will be better equipped to tackle more complex chemistry problems.



