Combination Circuits Worksheet With Answers
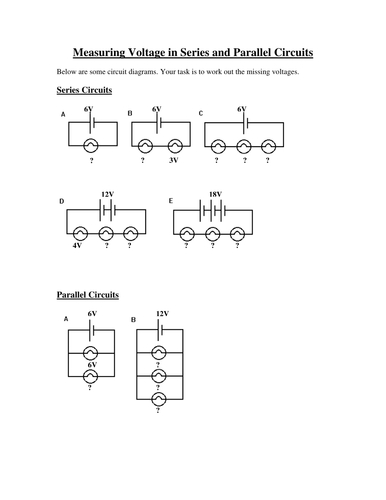
Understanding Combination Circuits
Combination circuits, also known as series-parallel circuits, are a type of electrical circuit that combines both series and parallel connections. These circuits are used to provide multiple paths for electric current to flow, allowing for greater flexibility and reliability in electrical systems. In this worksheet, we will explore the basics of combination circuits and provide answers to common problems.
What is a Combination Circuit?
A combination circuit is a type of electrical circuit that consists of both series and parallel connections. In a series connection, components are connected one after the other, and the current flows through each component in sequence. In a parallel connection, components are connected between the same two points, and the current divides between the components.
Key Components of a Combination Circuit
A combination circuit typically consists of the following key components:
- Voltage Source: A device that provides the electrical energy for the circuit.
- Resistors: Components that resist the flow of electric current.
- Switches: Devices that control the flow of electric current.
- Wires: Conductors that carry electric current between components.
How to Analyze a Combination Circuit
To analyze a combination circuit, follow these steps:
- Identify the components: Identify the voltage source, resistors, switches, and wires in the circuit.
- Determine the connections: Determine how the components are connected (series, parallel, or combination).
- Calculate the total resistance: Calculate the total resistance of the circuit using the formula R_total = R_series + R_parallel.
- Calculate the total current: Calculate the total current flowing through the circuit using the formula I_total = V/R_total.
- Calculate the voltage drop: Calculate the voltage drop across each component using the formula V_drop = I_component x R_component.
Practice Problems
Problem 1
A combination circuit consists of two resistors, R1 and R2, connected in parallel, and a third resistor, R3, connected in series with the parallel combination. The voltage source is 12V. If R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 4Ω, and R3 = 6Ω, calculate the total resistance and total current flowing through the circuit.
Solution
- Calculate the total resistance of the parallel combination: R_parallel = 1 / (1/R1 + 1/R2) = 1 / (1⁄2 + 1⁄4) = 4⁄3 Ω
- Calculate the total resistance of the circuit: R_total = R_parallel + R3 = 4⁄3 + 6 = 22⁄3 Ω
- Calculate the total current flowing through the circuit: I_total = V/R_total = 12 / (22⁄3) = 36⁄11 A
Problem 2
A combination circuit consists of three resistors, R1, R2, and R3, connected in series. The voltage source is 15V. If R1 = 3Ω, R2 = 6Ω, and R3 = 9Ω, calculate the voltage drop across each resistor.
Solution
- Calculate the total resistance of the circuit: R_total = R1 + R2 + R3 = 3 + 6 + 9 = 18Ω
- Calculate the total current flowing through the circuit: I_total = V/R_total = 15 / 18 = 5⁄6 A
- Calculate the voltage drop across each resistor:
- V_drop1 = I_total x R1 = (5⁄6) x 3 = 5⁄2 V
- V_drop2 = I_total x R2 = (5⁄6) x 6 = 5 V
- V_drop3 = I_total x R3 = (5⁄6) x 9 = 15⁄2 V
Notes
- When analyzing a combination circuit, it’s essential to identify the components and connections carefully.
- Use the formulas for total resistance and total current to calculate the values.
- When calculating voltage drop, use the formula V_drop = I_component x R_component.
What is the difference between a series and parallel circuit?
+A series circuit has components connected one after the other, while a parallel circuit has components connected between the same two points.
How do you calculate the total resistance of a combination circuit?
+The total resistance of a combination circuit is calculated by adding the resistances of the series components and the parallel combination.
What is the formula for calculating the voltage drop across a resistor?
+The formula for calculating the voltage drop across a resistor is V_drop = I_component x R_component.
In conclusion, combination circuits are an essential part of electrical systems, and understanding how to analyze them is crucial for designing and troubleshooting circuits. By following the steps outlined in this worksheet, you can calculate the total resistance, total current, and voltage drop across each component in a combination circuit. Remember to identify the components and connections carefully, and use the formulas for total resistance and total current to calculate the values.
Related Terms:
- Combination circuits Worksheet pdf
- Complex Circuits worksheet with answers
- Complex circuit worksheet pdf
- Complex Circuit Practice Worksheet
- Complex circuit problems with answers