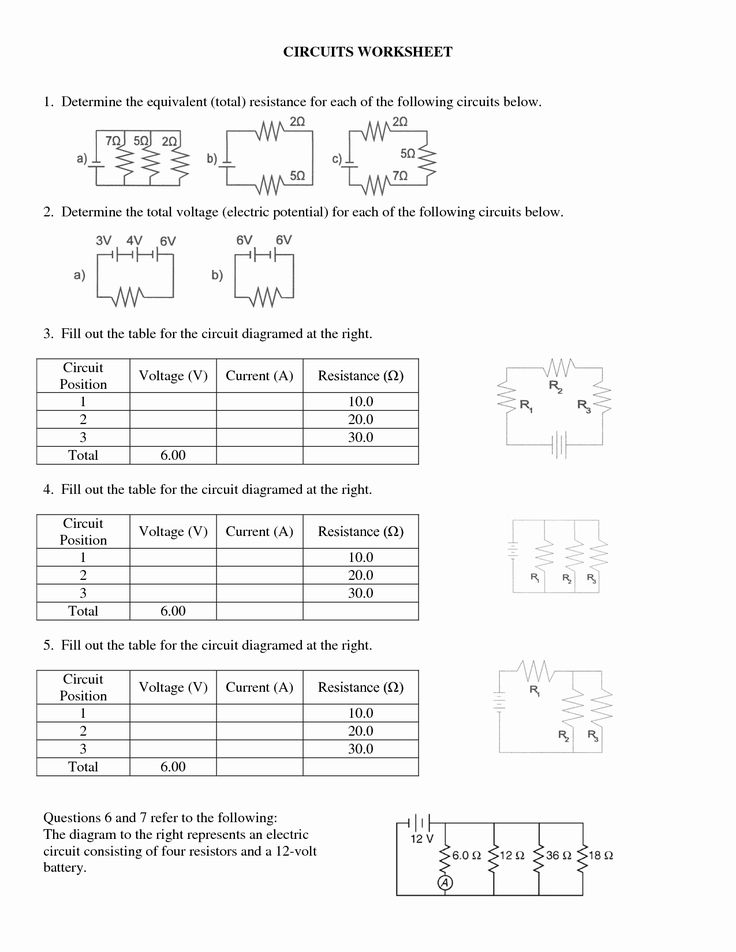
Combination Circuits Worksheet

Understanding Combination Circuits
Combination circuits, also known as complex circuits, are electrical circuits that consist of multiple pathways for electric current to flow. These circuits can be either series, parallel, or a combination of both. Understanding combination circuits is crucial in electronics and electrical engineering, as they are used in a wide range of applications, from simple household appliances to complex industrial systems.
Components of a Combination Circuit
A combination circuit typically consists of the following components:
- Resistors: These are devices that oppose the flow of electric current. In a combination circuit, resistors can be connected in series, parallel, or a combination of both.
- Voltage source: This is the component that provides the voltage needed to drive the current through the circuit.
- Switches: These are devices that can be used to control the flow of current in the circuit.
- Wires: These are the conductors that connect the components of the circuit together.
Types of Combination Circuits
There are several types of combination circuits, including:
- Series-parallel circuits: These circuits consist of a combination of series and parallel connections.
- Parallel-series circuits: These circuits consist of a combination of parallel and series connections.
- Bridge circuits: These circuits consist of four branches, with a voltage source connected across two opposite branches.
Calculating Total Resistance in a Combination Circuit
Calculating the total resistance in a combination circuit can be challenging, but it can be done using the following steps:
- Identify the resistors: Identify the resistors in the circuit and determine their values.
- Determine the connections: Determine how the resistors are connected (series, parallel, or combination).
- Calculate the total resistance: Use the formulas below to calculate the total resistance:
Series connection: RT = R1 + R2 +…
Parallel connection: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +…
Combination connection: Use the formulas above to calculate the total resistance of each section, then combine the results.
📝 Note: When calculating the total resistance of a combination circuit, it's essential to follow the order of operations (PEMDAS) to avoid errors.
Solving Combination Circuit Problems
To solve combination circuit problems, follow these steps:
- Read the problem carefully: Read the problem carefully and identify the given values.
- Draw a diagram: Draw a diagram of the circuit to visualize the connections.
- Calculate the total resistance: Use the formulas above to calculate the total resistance.
- Calculate the total current: Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the total current.
- Calculate the voltage across each resistor: Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the voltage across each resistor.
Example Problems
Here are some example problems to help you practice solving combination circuit problems:
Problem 1
A series-parallel circuit consists of two resistors connected in series, with a third resistor connected in parallel to the series connection. The values of the resistors are R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, and R3 = 30 Ω. The voltage source is 12 V. Calculate the total resistance and the total current.
Solution
RT = R1 + R2 = 10 Ω + 20 Ω = 30 Ω
1/RT = 1/R3 = 1⁄30 Ω
RT = 15 Ω
IT = V/RT = 12 V/15 Ω = 0.8 A
Problem 2
A bridge circuit consists of four resistors connected in a diamond shape, with a voltage source connected across two opposite branches. The values of the resistors are R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, R3 = 30 Ω, and R4 = 40 Ω. The voltage source is 24 V. Calculate the total resistance and the total current.
Solution
RT = (R1 * R3) + (R2 * R4)
RT = (10 Ω * 30 Ω) + (20 Ω * 40 Ω)
RT = 300 Ω + 800 Ω
RT = 1100 Ω
IT = V/RT = 24 V/1100 Ω = 0.022 A
| Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Resistors | R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 20 Ω, R3 = 30 Ω, R4 = 40 Ω |
| Voltage source | 12 V |
| Switches | SPST |
| Wires | Copper |
Now, let’s summarize the key points.
Combination circuits are electrical circuits that consist of multiple pathways for electric current to flow. They can be either series, parallel, or a combination of both. Understanding combination circuits is crucial in electronics and electrical engineering, as they are used in a wide range of applications.
To calculate the total resistance in a combination circuit, identify the resistors and determine their values. Then, use the formulas above to calculate the total resistance.
When solving combination circuit problems, read the problem carefully, draw a diagram, calculate the total resistance, and calculate the total current.
I hope this tutorial has helped you understand combination circuits and how to solve problems related to them.
What is a combination circuit?
+A combination circuit is an electrical circuit that consists of multiple pathways for electric current to flow.
What are the components of a combination circuit?
+A combination circuit typically consists of resistors, a voltage source, switches, and wires.
How do you calculate the total resistance in a combination circuit?
+To calculate the total resistance in a combination circuit, identify the resistors and determine their values. Then, use the formulas above to calculate the total resistance.
Related Terms:
- Combination circuits Worksheet pdf
- Complex Circuits worksheet with answers
- Complex circuit worksheet pdf
- Complex Circuit Practice Worksheet