5 Ways to Cite Textual Evidence Correctly

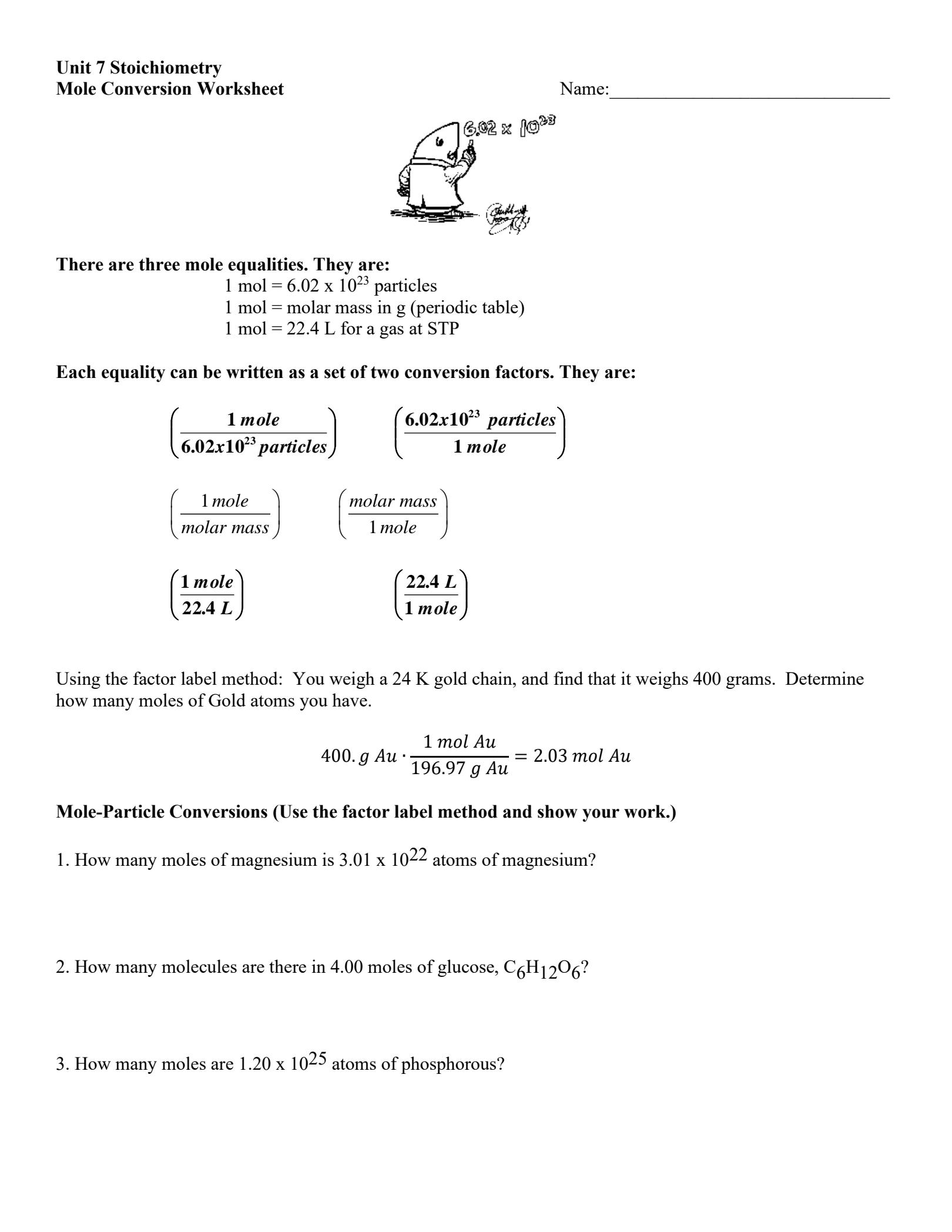
Understanding Textual Evidence and Its Importance in Academic Writing
When writing academic papers, essays, or research papers, it is essential to support your arguments and claims with textual evidence. Textual evidence refers to the use of quotes, passages, or data from credible sources to validate your points and make your writing more convincing. However, citing textual evidence correctly is crucial to avoid plagiarism, give credit to the original authors, and maintain the integrity of your work. In this article, we will explore five ways to cite textual evidence correctly.
Method 1: Direct Quotation
A direct quotation involves copying a phrase or sentence from a source exactly as it appears. When using direct quotations, it is essential to enclose the quoted text in quotation marks and provide a citation. The citation should include the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) where the quoted text can be found.
Example:
“The impact of climate change on global food production is a pressing concern” (Smith, 2020, p. 12).
In this example, “Smith” is the author’s last name, “2020” is the publication year, and “p. 12” indicates the page number where the quoted text can be found.
Method 2: Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing involves restating a passage or idea in your own words. When paraphrasing, it is still necessary to provide a citation to acknowledge the original author’s work. The citation should include the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) where the paraphrased text can be found.
Example:
According to Smith (2020, p. 12), climate change has significant implications for global food production.
In this example, the text has been paraphrased, but the citation still acknowledges the original author’s work.
Method 3: Summarizing
Summarizing involves condensing a longer passage or text into a concise summary. When summarizing, it is essential to provide a citation to acknowledge the original author’s work. The citation should include the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) where the summarized text can be found.
Example:
Smith (2020, pp. 10-15) discusses the impact of climate change on global food production, highlighting the need for sustainable agricultural practices.
In this example, the text has been summarized, and the citation acknowledges the original author’s work.
Method 4: Block Quotation
A block quotation involves copying a longer passage from a source, usually more than four lines. When using block quotations, it is essential to indent the quoted text and provide a citation. The citation should include the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) where the quoted text can be found.
Example:
Smith (2020, p. 12) notes:
“The impact of climate change on global food production is a pressing concern. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are altering the suitability of land for agriculture, leading to reduced crop yields and decreased food security.”
In this example, the block quotation is indented, and the citation acknowledges the original author’s work.
Method 5: In-Text Citation with Multiple Sources
When using multiple sources to support a single argument or point, it is essential to provide an in-text citation that lists all the sources. The citation should include the authors’ last names, publication years, and page number(s) where the relevant information can be found.
Example:
Several studies have highlighted the impact of climate change on global food production (Smith, 2020, p. 12; Johnson, 2019, p. 20; Thompson, 2018, p. 15).
In this example, the in-text citation lists all the sources that support the argument.
📝 Note: When using multiple sources, it is essential to ensure that the citation is formatted correctly to avoid plagiarism and give credit to the original authors.
By following these five methods, you can ensure that you are citing textual evidence correctly and maintaining the integrity of your academic writing.
Now, let’s summarize the key points:
- Direct quotation: Use quotation marks and provide a citation.
- Paraphrasing: Restate the text in your own words and provide a citation.
- Summarizing: Condense the text into a concise summary and provide a citation.
- Block quotation: Indent the quoted text and provide a citation.
- In-text citation with multiple sources: List all the sources that support a single argument or point.
By mastering these methods, you can effectively cite textual evidence and enhance the credibility of your academic writing.
What is textual evidence?
+Textual evidence refers to the use of quotes, passages, or data from credible sources to validate your points and make your writing more convincing.
Why is it essential to cite textual evidence correctly?
+Citing textual evidence correctly is essential to avoid plagiarism, give credit to the original authors, and maintain the integrity of your work.
What are the five methods of citing textual evidence?
+The five methods of citing textual evidence are: direct quotation, paraphrasing, summarizing, block quotation, and in-text citation with multiple sources.