Circle Angle Worksheet for Geometry Mastery
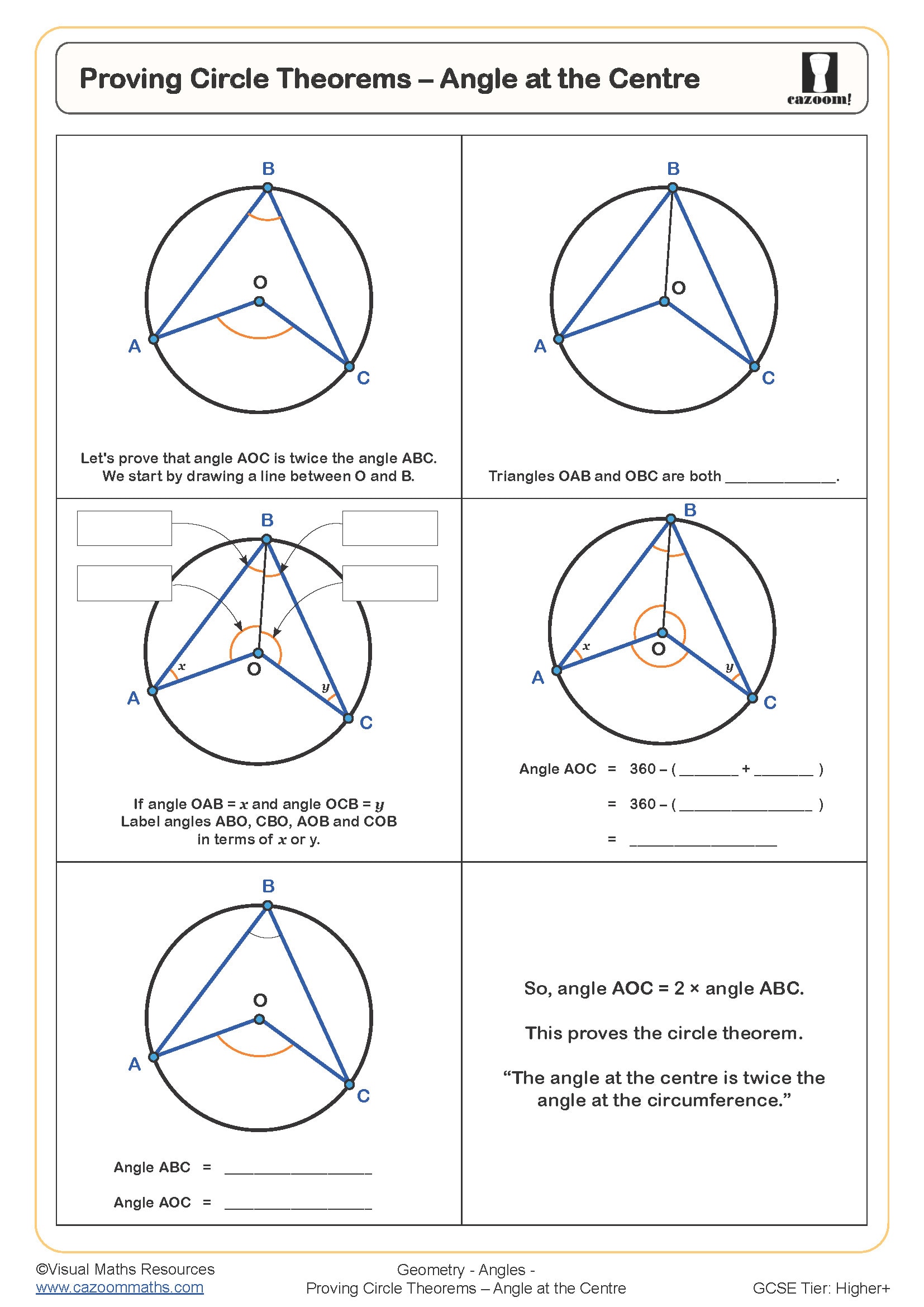
Mastering Circle Angles: A Comprehensive Guide
Circle angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, and understanding them is crucial for solving various problems in mathematics and real-world applications. In this article, we will delve into the world of circle angles, exploring their definitions, types, and properties. We will also provide a worksheet to help you practice and reinforce your knowledge.
What is a Circle Angle?
A circle angle, also known as a central angle, is an angle formed by two radii of a circle. The vertex of the angle is at the center of the circle, and the two sides are the radii. Circle angles are measured in degrees, and their sizes can vary from 0° to 360°.
Types of Circle Angles
There are several types of circle angles, including:
- Central angle: An angle formed by two radii of a circle, with its vertex at the center of the circle.
- Inscribed angle: An angle formed by two chords of a circle, with its vertex on the circle.
- Circumscribed angle: An angle formed by two tangents of a circle, with its vertex on the circle.
- Intercepted arc: An arc formed by two chords of a circle, with its endpoints on the circle.
Properties of Circle Angles
Circle angles have several important properties:
- Inspection property: The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.
- Intercepted arc property: The measure of an intercepted arc is equal to twice the measure of its corresponding central angle.
- Sum of central angles: The sum of the measures of the central angles of a circle is 360°.
Circle Angle Theorems
There are several theorems related to circle angles:
- Inscribed angle theorem: The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.
- Central angle theorem: The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc.
- Tangent-secant theorem: The measure of an angle formed by a tangent and a secant is equal to half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Circle Angle Worksheet
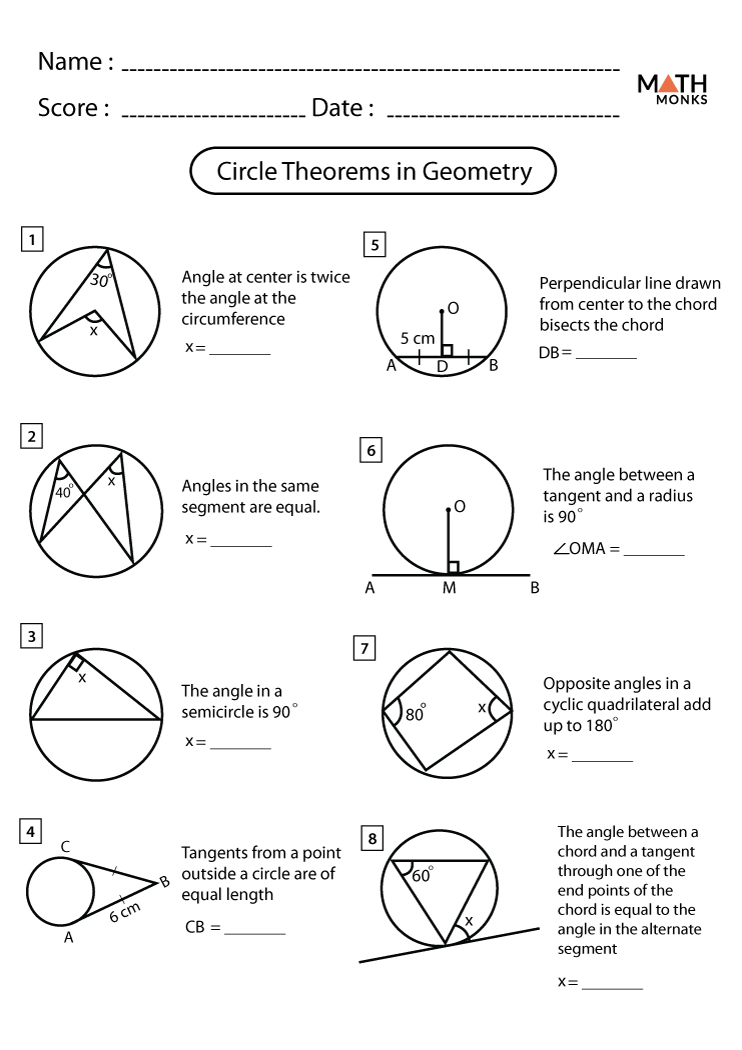
Practice your knowledge of circle angles with the following worksheet:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| 1. In a circle, a central angle measures 60°. What is the measure of its intercepted arc? | 120° |
| 2. In a circle, an inscribed angle measures 45°. What is the measure of its intercepted arc? | 90° |
| 3. In a circle, a tangent and a secant form an angle measuring 30°. What is the measure of the intercepted arc? | 60° |
| 4. In a circle, the sum of the measures of two central angles is 150°. What is the measure of the third central angle? | 210° |
| 5. In a circle, an inscribed angle intercepts an arc measuring 120°. What is the measure of the inscribed angle? | 60° |
📝 Note: Make sure to check your answers with a protractor or calculator to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Mastering circle angles is essential for success in geometry and mathematics. By understanding the definitions, types, and properties of circle angles, you can solve various problems and apply your knowledge to real-world situations. Remember to practice regularly and use online resources or worksheets to reinforce your learning.
What is the difference between a central angle and an inscribed angle?
+A central angle is an angle formed by two radii of a circle, with its vertex at the center of the circle. An inscribed angle is an angle formed by two chords of a circle, with its vertex on the circle.
What is the sum of the measures of the central angles of a circle?
+The sum of the measures of the central angles of a circle is 360°.
How do I find the measure of an inscribed angle?
+The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.