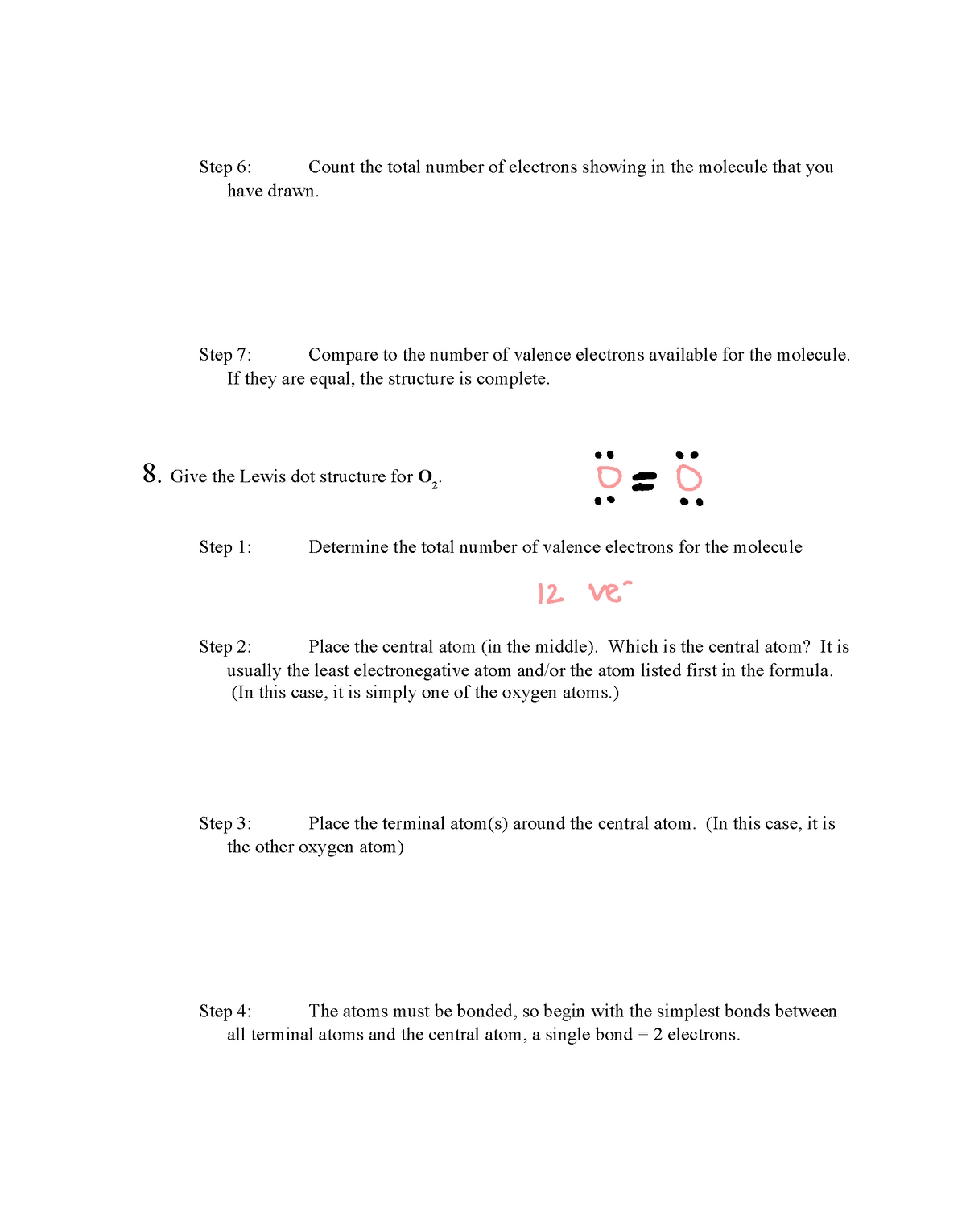
Mastering Lewis Dot Structures in Chemistry

Understanding the Basics of Lewis Dot Structures
Lewis dot structures are a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules. Developed by Gilbert N. Lewis, these structures are a crucial tool for understanding chemical bonding and the properties of molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lewis dot structures, exploring their basics, rules, and applications.
What are Lewis Dot Structures?
A Lewis dot structure, also known as a Lewis structure or electron dot structure, is a graphical representation of the valence electrons of an atom or molecule. It uses dots to represent electrons and lines to represent covalent bonds. Lewis dot structures help chemists visualize the distribution of electrons in a molecule, making it easier to understand chemical bonding and predict molecular properties.
Components of a Lewis Dot Structure
A Lewis dot structure consists of the following components:
- Atoms: Represented by their chemical symbols (e.g., H, C, O)
- Dots: Represent valence electrons, which are electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom
- Lines: Represent covalent bonds between atoms
Rules for Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
To draw accurate Lewis dot structures, follow these rules:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons: Add up the valence electrons of all atoms in the molecule.
- Draw the skeleton of the molecule: Connect the atoms with lines, representing covalent bonds.
- Distribute the electrons: Place dots around the atoms to represent valence electrons.
- Satisfy the octet rule: Ensure that each atom has eight electrons in its outermost energy level, except for hydrogen, which requires two electrons.
- Minimize formal charges: Arrange electrons to minimize formal charges on individual atoms.
💡 Note: Formal charges are calculated by subtracting the number of dots around an atom from the atom's valence electrons.
Examples of Lewis Dot Structures
Let’s draw Lewis dot structures for a few simple molecules:
- Water (H2O): Two hydrogen atoms bonded to a single oxygen atom
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): One carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms
- Methane (CH4): One carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms
| Molecule | Lewis Dot Structure |
|---|---|
| Water (H2O) | H - O - H |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | O = C = O |
| Methane (CH4) | H - C - H |
Applications of Lewis Dot Structures
Lewis dot structures have numerous applications in chemistry:
- Predicting molecular shape: Lewis dot structures help predict the shape of a molecule, which is crucial for understanding its properties and behavior.
- Identifying polarity: By analyzing the distribution of electrons, Lewis dot structures can help identify polar molecules.
- Understanding chemical reactivity: Lewis dot structures provide insights into the reactivity of molecules, helping chemists predict reaction mechanisms and outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Lewis Dot Structures
While Lewis dot structures are a powerful tool, they have limitations:
- Simplifications: Lewis dot structures simplify the complex world of molecular orbitals and electron density.
- Exceptions to the octet rule: Some molecules, like those with an odd number of electrons or those containing certain atoms, may not follow the octet rule.
- Ambiguity in electron distribution: In some cases, Lewis dot structures may not provide a clear picture of electron distribution.
Conclusion
Mastering Lewis dot structures is an essential skill for chemists, providing a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and molecular properties. By following the rules and guidelines outlined in this article, you can become proficient in drawing accurate Lewis dot structures and unlock the secrets of molecular chemistry.
What is the purpose of a Lewis dot structure?
+A Lewis dot structure represents the arrangement of electrons in an atom or molecule, helping chemists understand chemical bonding and predict molecular properties.
What is the octet rule in Lewis dot structures?
+The octet rule states that each atom in a molecule should have eight electrons in its outermost energy level, except for hydrogen, which requires two electrons.
What are some limitations of Lewis dot structures?
+Lewis dot structures simplify the complex world of molecular orbitals and electron density, and may not always provide a clear picture of electron distribution. Additionally, some molecules may not follow the octet rule.