Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Made Easy for Genetics Students

Understanding Dihybrid Crosses: A Comprehensive Guide
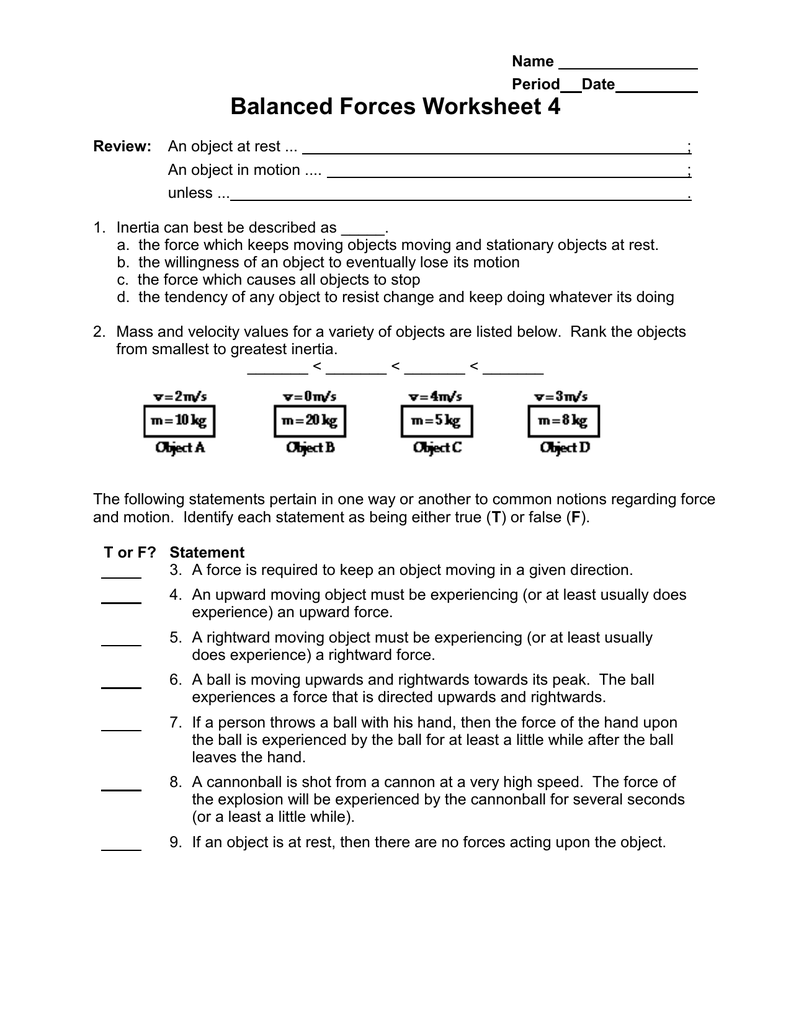
As a genetics student, understanding dihybrid crosses is a crucial part of your learning journey. A dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves two different traits, each with two alleles. This type of cross is essential in understanding the principles of Mendelian inheritance and how genes interact with each other. In this post, we will break down the concept of dihybrid crosses, provide a step-by-step guide on how to solve dihybrid cross problems, and offer tips to make solving these problems easier.
What is a Dihybrid Cross?
A dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves two different traits, each with two alleles. For example, let’s say we are studying the traits of flower color and plant height. The flower color trait has two alleles: red ® and white ®. The plant height trait also has two alleles: tall (T) and short (t). A dihybrid cross would involve crossing two parents that are heterozygous for both traits, resulting in offspring with different combinations of the alleles.
Step-by-Step Guide to Solving Dihybrid Cross Problems
Solving dihybrid cross problems can be challenging, but with a step-by-step approach, it becomes more manageable. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you solve dihybrid cross problems:
- Identify the traits and alleles involved: Start by identifying the two traits and their corresponding alleles. Make sure you understand the genotype and phenotype of each parent.
- Determine the genotype of the parents: Determine the genotype of each parent, including the alleles they carry for each trait.
- Predict the possible genotypes of the offspring: Use a Punnett square or a genetic grid to predict the possible genotypes of the offspring. Make sure to include all possible combinations of alleles.
- Determine the phenotype of the offspring: Determine the phenotype of each offspring based on their genotype. Use the rules of Mendelian inheritance to determine the phenotype.
- Calculate the probability of each phenotype: Calculate the probability of each phenotype by counting the number of offspring with each phenotype and dividing it by the total number of offspring.
📝 Note: When solving dihybrid cross problems, make sure to include all possible combinations of alleles and use the rules of Mendelian inheritance to determine the phenotype.
Using Punnett Squares to Solve Dihybrid Cross Problems
Punnett squares are a useful tool for solving dihybrid cross problems. A Punnett square is a grid that shows all possible combinations of alleles. To use a Punnett square, follow these steps:
- Draw a grid: Draw a grid with the alleles of one parent on one axis and the alleles of the other parent on the other axis.
- Fill in the grid: Fill in the grid with the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Determine the phenotype: Determine the phenotype of each offspring based on their genotype.
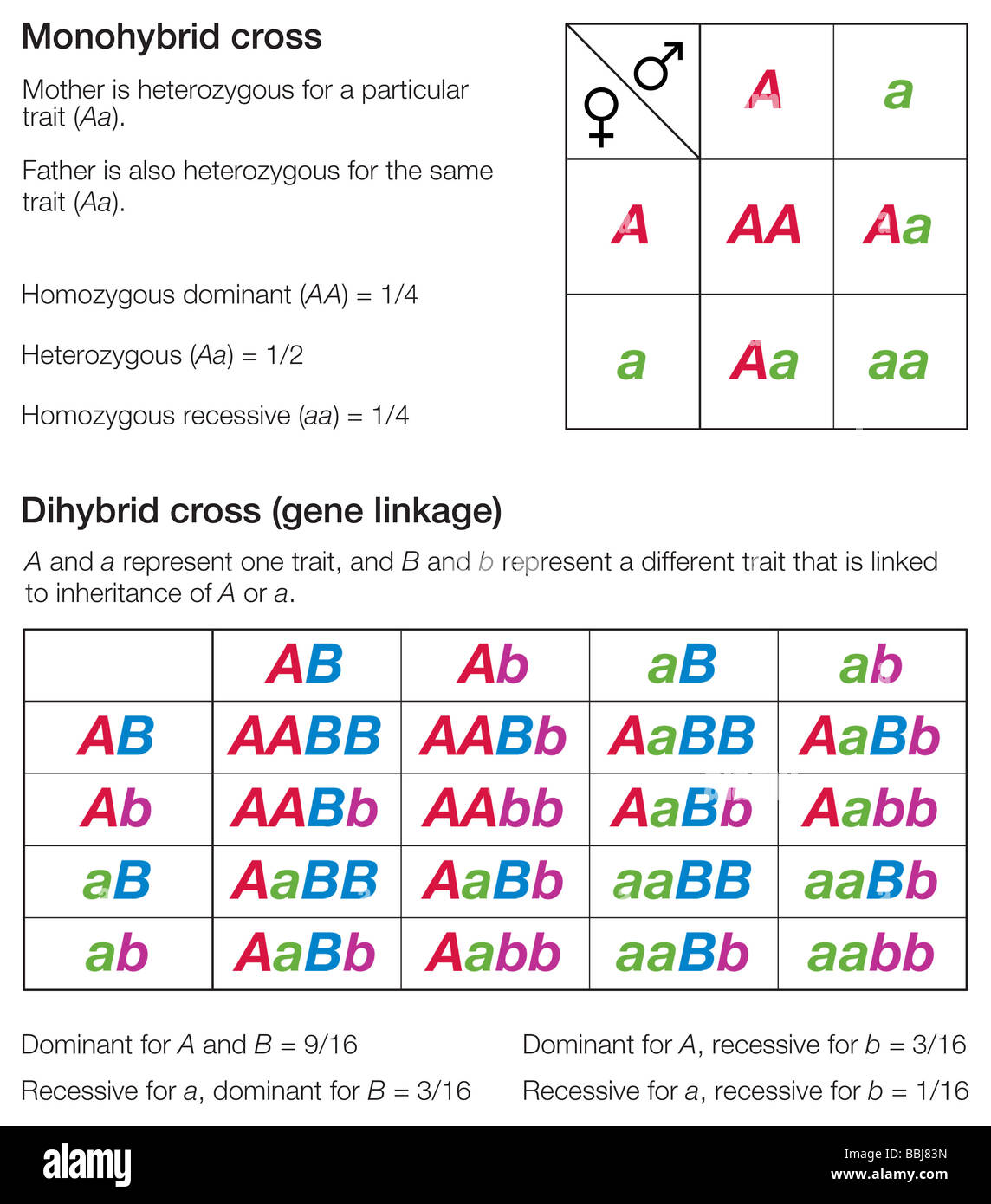
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| RR or Rr | Red |
| rr | White |
| TT or Tt | Tall |
| tt | Short |
Tips for Solving Dihybrid Cross Problems
Here are some tips to help you solve dihybrid cross problems:
- Start with the basics: Make sure you understand the traits and alleles involved, as well as the genotype and phenotype of each parent.
- Use a Punnett square: Punnett squares are a useful tool for solving dihybrid cross problems. They help you visualize the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Determine the phenotype: Use the rules of Mendelian inheritance to determine the phenotype of each offspring.
- Calculate the probability: Calculate the probability of each phenotype by counting the number of offspring with each phenotype and dividing it by the total number of offspring.
📝 Note: When solving dihybrid cross problems, make sure to include all possible combinations of alleles and use the rules of Mendelian inheritance to determine the phenotype.
By following these steps and tips, you’ll be able to solve dihybrid cross problems with ease. Remember to practice, practice, practice, and you’ll become a pro at solving these types of problems.
In conclusion, dihybrid crosses are an essential part of genetics, and understanding how to solve these problems is crucial for any genetics student. By following the step-by-step guide and using Punnett squares, you’ll be able to solve dihybrid cross problems with ease. Remember to practice and use the tips provided to help you along the way.
What is a dihybrid cross?
+A dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves two different traits, each with two alleles.
How do I solve dihybrid cross problems?
+To solve dihybrid cross problems, follow the step-by-step guide provided in this post, including identifying the traits and alleles involved, determining the genotype of the parents, predicting the possible genotypes of the offspring, determining the phenotype of the offspring, and calculating the probability of each phenotype.
What is a Punnett square?
+A Punnett square is a grid that shows all possible combinations of alleles. It’s a useful tool for solving dihybrid cross problems.