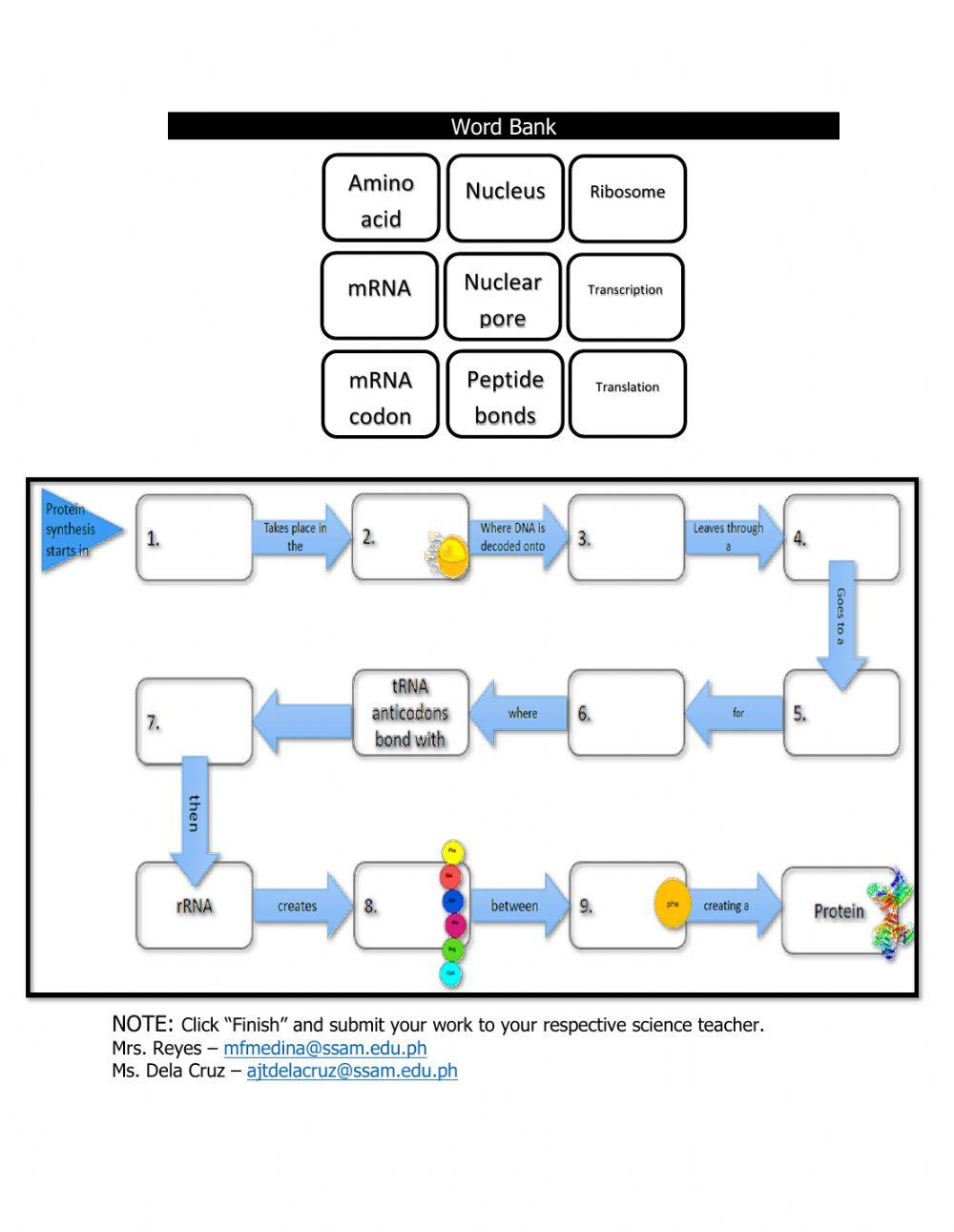
6 Ways to Learn Rocks and Soil with Bill Nye

Introduction to Learning about Rocks and Soil
Are you ready to dig into the fascinating world of geology with Bill Nye the Science Guy? Learning about rocks and soil can be a fun and educational experience, especially with the right approaches and resources. In this post, we’ll explore six engaging ways to learn about rocks and soil, perfect for students, teachers, and anyone curious about the natural world.
1. Hands-on Experimentation
Get your hands dirty with Bill Nye’s favorite approach to learning: experimentation! With a few simple materials, you can conduct experiments that demonstrate fundamental concepts in geology. For example:
- Soil Erosion: Create a model of a landscape using clay or sand and observe how water can erode the soil. This demonstrates the importance of soil conservation and the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Rock Cycle: Simulate the rock cycle by heating, cooling, and pressurizing different materials to demonstrate the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- Soil Composition: Mix different materials like sand, silt, and clay to create a variety of soil textures and observe how they affect plant growth.
These experiments not only make learning fun but also help you understand complex geological processes.
2. Virtual Field Trips
Embark on virtual field trips with Bill Nye to explore some of the most fascinating geological formations around the world. These online excursions can be just as engaging as real-life field trips, without the travel costs!
- Google Expeditions: Join Bill Nye on a virtual tour of the Grand Canyon, exploring the Colorado River’s impact on the landscape and the formation of this natural wonder.
- National Park Service: Explore the geology of Yellowstone National Park, including its unique hot springs, geysers, and diverse rock formations.
- GeoGebra: Use this interactive platform to visualize and explore geological structures, such as folds, faults, and volcanoes, in 3D.
Virtual field trips offer an immersive learning experience, allowing you to explore and interact with geological wonders from the comfort of your own space.
3. Interactive Games and Simulations
Make learning about rocks and soil a game with interactive simulations and activities. These can be played individually or in a classroom setting.
- Rock Cycle Simulation: Play a simulation game where you can manipulate variables like temperature, pressure, and time to observe the formation of different rock types.
- Soil Formation: Participate in a puzzle game where you assemble the correct sequence of events that lead to soil formation.
- Geology Jeopardy: Test your knowledge of rocks and soil with a Jeopardy-style game, complete with questions and challenges.
These interactive games and simulations make learning about geology an enjoyable and engaging experience.
4. Real-World Applications
Connect the dots between geology and everyday life by exploring real-world applications of rocks and soil.
- Agriculture: Learn how soil type and composition affect crop growth and agricultural practices.
- Construction: Understand how the properties of rocks and soil impact building design, foundation stability, and construction materials.
- Environmental Conservation: Discover how geology informs our understanding of climate change, natural disasters, and environmental conservation efforts.
By exploring real-world applications, you’ll see the relevance and importance of geology in our daily lives.
5. Collaborative Projects
Work with others on collaborative projects that foster teamwork, creativity, and critical thinking.
- Soil Quality Testing: Conduct a group project to test and analyze the quality of different soil samples, exploring factors like pH, nutrient content, and texture.
- Rock Identification: Collaborate with classmates to identify and classify rock samples, using techniques like observation, measurement, and research.
- Geology-themed Art: Create art pieces inspired by geological formations, processes, or features, promoting creativity and artistic expression.
Collaborative projects help develop essential skills like communication, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
6. Watching Educational Videos
Watch educational videos featuring Bill Nye and other experts to gain a deeper understanding of rocks and soil.
- Bill Nye the Science Guy: Watch episodes from the classic TV series, covering topics like plate tectonics, rock formation, and soil erosion.
- Crash Course Geology: Engage with this YouTube series, which offers an in-depth look at geological concepts, from the basics to advanced topics.
- Geology documentaries: Explore documentaries that showcase the natural beauty and complexity of geological formations, such as the BBC’s “Planet Earth” series.
Educational videos provide an entertaining and informative way to learn about rocks and soil, making complex concepts more accessible and engaging.
📚 Note: Supplement your learning with textbooks, online resources, and expert advice to ensure a comprehensive understanding of rocks and soil.
By incorporating these six approaches into your learning routine, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a rock-solid expert on rocks and soil, just like Bill Nye!
Without a deep understanding of geology, we risk neglecting the very foundation of our planet. By embracing these engaging learning methods, you’ll not only expand your knowledge but also develop a new appreciation for the fascinating world of rocks and soil.
What is the rock cycle?
+The rock cycle is the process by which rocks are formed, transformed, and destroyed. It involves the continuous movement of rocks between the Earth’s crust, mantle, and atmosphere.
Why is soil important for plant growth?
+Soil provides essential nutrients, water, and support for plant growth. Its composition and texture affect the availability of these resources, making it crucial for agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
What are some common types of rocks?
+The three main types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from magma, sedimentary rocks from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks from transformed existing rocks.