Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers Explained Simply
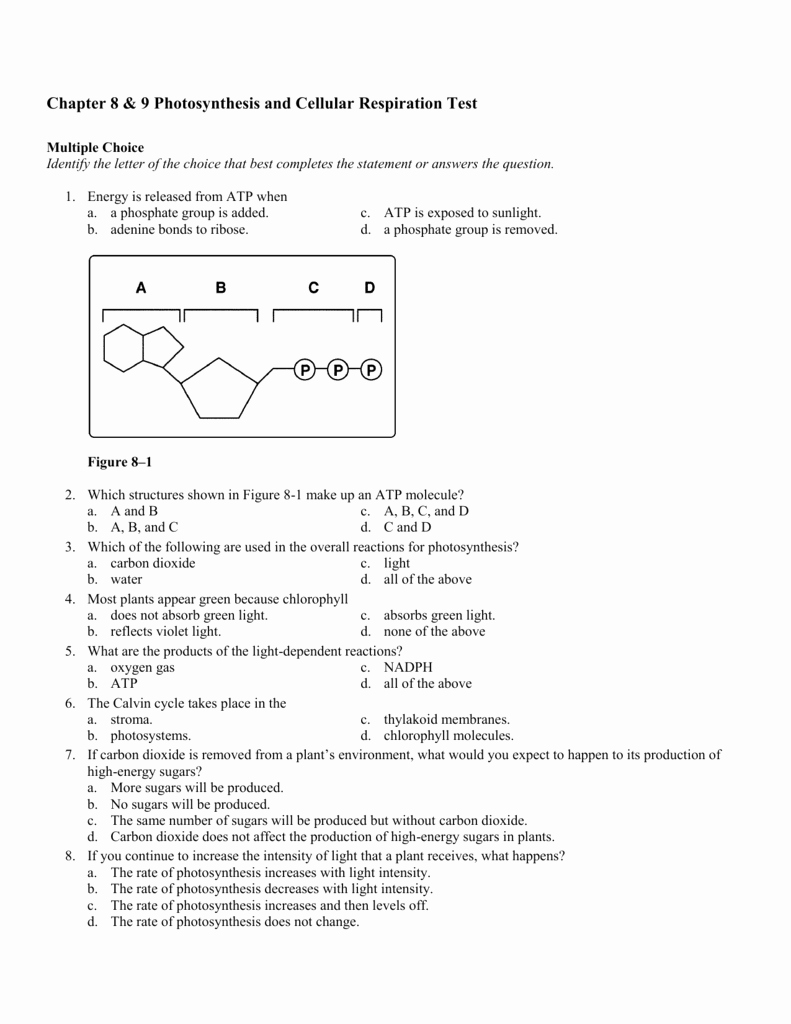
Understanding Cellular Respiration: A Simplified Explanation
Cellular respiration is a complex biochemical process that occurs in the cells of organisms to generate energy. It is a vital process that converts glucose into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). In this article, we will break down the cellular respiration worksheet answers and explain the process in simple terms.
What is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that takes place in the cells of organisms to produce energy. It involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce ATP, which is the primary energy currency of the cell. The process of cellular respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis: The First Stage of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration, which takes place in the cytosol of the cell. In this stage, glucose (a six-carbon sugar) is converted into pyruvate (a three-carbon molecule). The process of glycolysis involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that result in the production of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules.
Key Points to Remember:
- Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of the cell.
- Glucose is converted into pyruvate.
- Two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules are produced.
The Citric Acid Cycle: The Second Stage of Cellular Respiration
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is the second stage of cellular respiration. In this stage, pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, which then enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid cycle produces two ATP molecules, six NADH molecules, and two FADH2 molecules.
Key Points to Remember:
- The citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondria.
- Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA.
- Two ATP molecules, six NADH molecules, and two FADH2 molecules are produced.
Oxidative Phosphorylation: The Third Stage of Cellular Respiration
Oxidative phosphorylation is the third and final stage of cellular respiration. In this stage, the electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through a series of electron transport chains, resulting in the production of ATP molecules. The electron transport chains are located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Key Points to Remember:
- Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria.
- Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through electron transport chains.
- ATP molecules are produced.
Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
Now that we have explained the process of cellular respiration, let’s move on to the worksheet answers.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary energy currency of the cell? | ATP (adenosine triphosphate) |
| What is the first stage of cellular respiration? | Glycolysis |
| What is the end product of glycolysis? | Pyruvate |
| What is the second stage of cellular respiration? | The citric acid cycle |
| What is the end product of the citric acid cycle? | Acetyl-CoA |
| What is the third stage of cellular respiration? | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur? | Mitochondria |
📝 Note: The electron transport chains in oxidative phosphorylation produce the majority of ATP molecules in cellular respiration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cellular respiration is a complex biochemical process that occurs in the cells of organisms to generate energy. The process involves three stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. By understanding the key points of each stage, you can better appreciate the importance of cellular respiration in maintaining life.
Key Takeaways:
- Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that produces energy.
- Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation are the three stages of cellular respiration.
- ATP is the primary energy currency of the cell.
What is the primary purpose of cellular respiration?
+The primary purpose of cellular respiration is to generate energy for the cell in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What is the byproduct of glycolysis?
+Pyruvate is the byproduct of glycolysis.
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
+Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria.



