Cells Alive Worksheet Answer Key for Biology Students
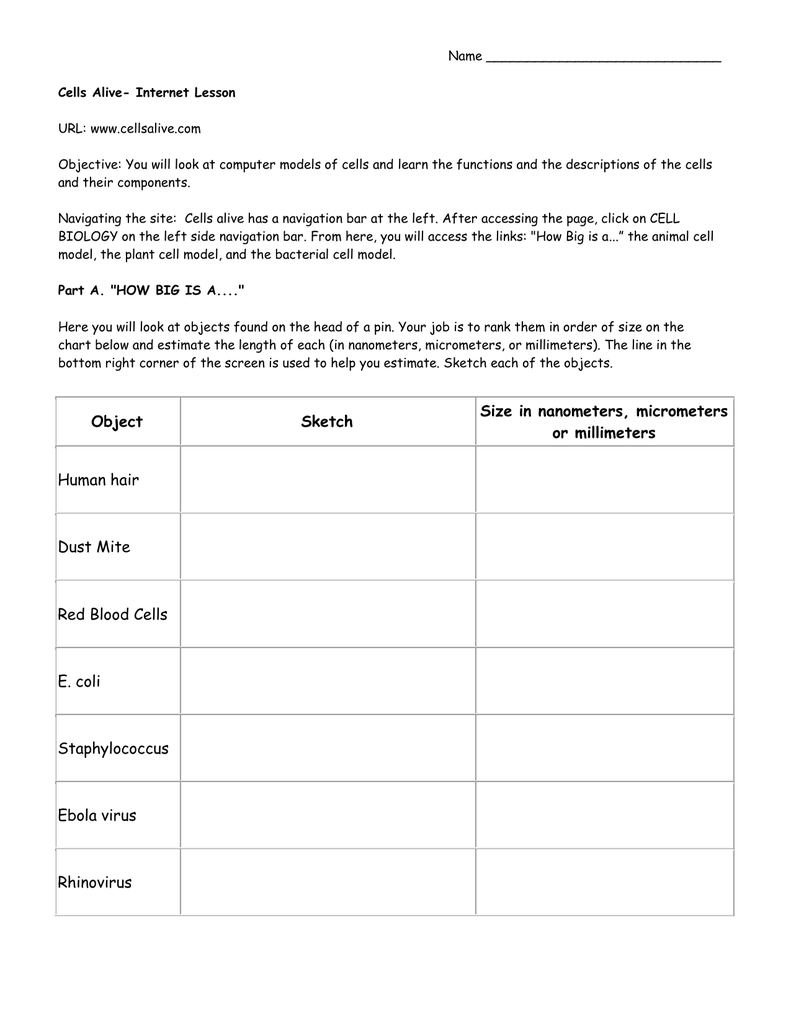
Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life
As biology students, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of cells, the basic units of life. Cells are the smallest functional units of life, and understanding their structure, function, and behavior is crucial for comprehending the complexities of life. In this post, we’ll explore the Cells Alive worksheet, providing an answer key to help you better understand cells and their functions.
Cell Structure and Function
Cells are the building blocks of life, and their structure and function are critical to understanding how living organisms work. The Cells Alive worksheet is designed to help you understand the different components of a cell and their functions.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that surrounds the cell. Its primary function is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
- Answer Key:
- What is the main function of the cell membrane? Regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
- What is the cell membrane composed of? Lipid and protein molecules.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane where many metabolic processes take place. It’s composed of water, salts, sugars, and various organelles.
- Answer Key:
- What is cytoplasm composed of? Water, salts, sugars, and various organelles.
- What is the primary function of cytoplasm? Many metabolic processes take place here.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell where DNA is stored. It’s surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary function of the nucleus? Stores DNA and controls cell growth and reproduction.
- What surrounds the nucleus? A double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
Cellular Organelles
Cells contain various organelles, each with unique functions. Understanding the roles of these organelles is essential for comprehending cellular processes.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, as they generate energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary function of mitochondria? Generate energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
- What is the process by which mitochondria produce energy? Cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The ER is a network of membranous tubules and sacs that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, folding, and transport.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary function of the ER? Protein synthesis, folding, and transport.
- What type of ER is involved in protein synthesis? Rough ER.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs that contain digestive enzymes and acidic substances. They break down and recycle cellular waste and foreign substances.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary function of lysosomes? Break down and recycle cellular waste and foreign substances.
- What is the pH level inside lysosomes? Acidic.
💡 Note: The Cells Alive worksheet may include additional questions and topics not covered in this answer key. Be sure to review the entire worksheet for a comprehensive understanding of cells and their functions.
Cellular Transport
Cells need to transport materials across their membranes to maintain homeostasis and facilitate various cellular processes.
Passive Transport
Passive transport involves the movement of materials from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the use of energy.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary characteristic of passive transport? Movement of materials from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without energy.
- What are the three types of passive transport? Diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport
Active transport involves the movement of materials against their concentration gradient, requiring energy.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary characteristic of active transport? Movement of materials against their concentration gradient, requiring energy.
- What type of transport is used to move ions across cell membranes? Active transport.
Cellular Processes
Cells undergo various processes to maintain homeostasis, grow, and reproduce.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plant cells convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary function of photosynthesis? Convert light energy into chemical energy.
- What type of cells perform photosynthesis? Plant cells.
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce themselves.
- Answer Key:
- What is the primary function of cell division? Reproduce cells.
- What are the two types of cell division? Mitosis and meiosis.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
+The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
+The primary function of mitochondria is to generate energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
What is the primary characteristic of passive transport?
+The primary characteristic of passive transport is the movement of materials from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without energy.
In conclusion, understanding cells and their functions is essential for comprehending the complexities of life. The Cells Alive worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of cellular structure, function, and processes. By reviewing the answer key and exploring the topics in-depth, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of cells and their roles in maintaining life.