Cladogram Practice Worksheet Answers
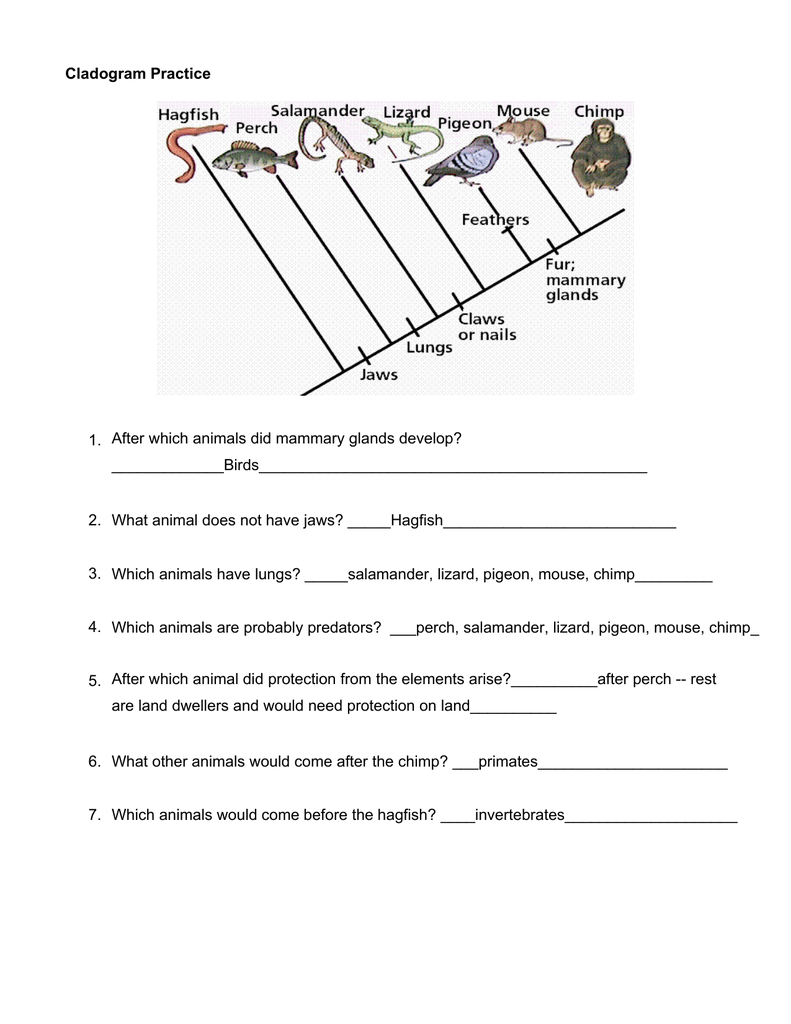
Understanding Cladograms: A Practice Worksheet Guide
Cladograms are a crucial tool in biology, used to visualize the evolutionary relationships between different species. They provide a way to organize and display the characteristics of various organisms, making it easier to identify their shared ancestry and understand the process of evolution. In this practice worksheet, we’ll go through the steps to read and interpret cladograms, providing answers to common questions and exercises.
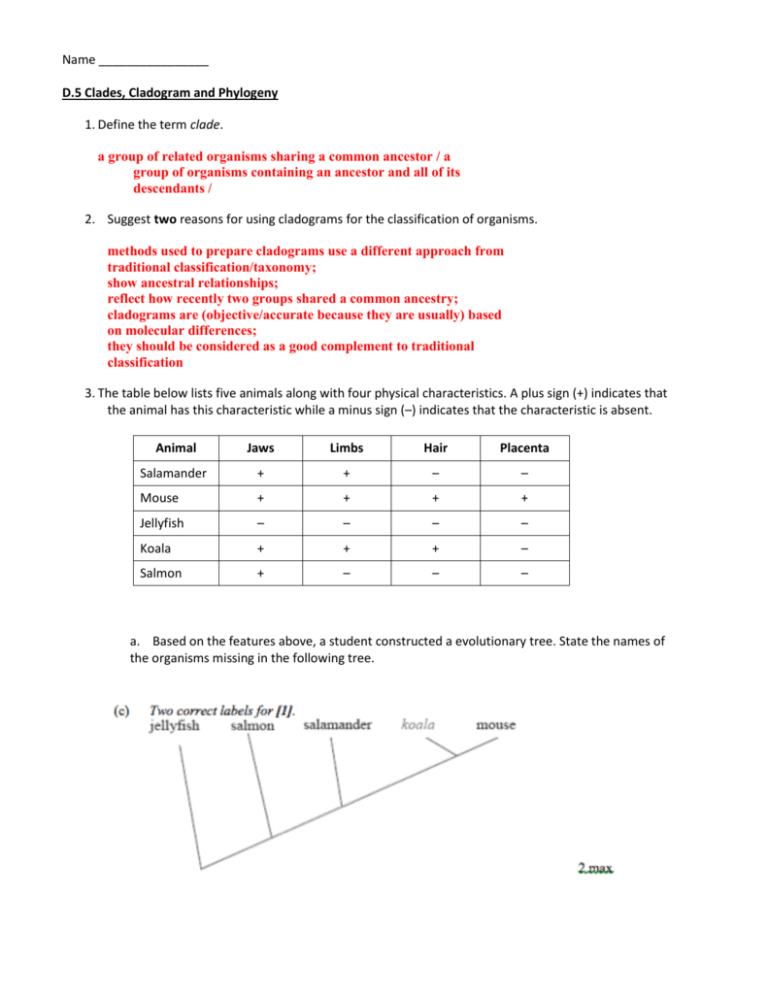
What is a Cladogram?
A cladogram is a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships between different species based on their shared characteristics. It’s a tree-like structure, with branches representing the relationships between organisms. The cladogram is read from the bottom up, with the most recent common ancestor at the base of the tree.
How to Read a Cladogram
Reading a cladogram involves understanding the relationships between the different branches and nodes. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Start at the base of the tree, which represents the most recent common ancestor.
- Move up the tree, and each node represents a common ancestor of the species above it.
- The branches represent the relationships between the species. A branch that splits into two or more smaller branches indicates a common ancestor of those species.
- The tips of the branches represent the individual species.
Practice Exercise 1: Identifying Shared Ancestors
Use the following cladogram to answer the questions:
| Human | Chimpanzee | Gorilla | Orangutan | |
| Node A | ||||
| Node B | ||||
| Common Ancestor |
Questions:
- Which node represents the most recent common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees?
- Which species shares a common ancestor with gorillas at Node B?
- What is the relationship between the orangutan and the other three species?
Answers:
- Node A represents the most recent common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees.
- The chimpanzee shares a common ancestor with gorillas at Node B.
- The orangutan is not as closely related to the other three species, as it branches off from the common ancestor earlier in the tree.
🔍 Note: Node A represents the most recent common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees, indicating that they share a more recent common ancestor than the other species.
Practice Exercise 2: Interpreting Branch Lengths
Use the following cladogram to answer the questions:
| Species A | Species B | Species C | |
| Node X | |||
| Node Y | |||
| Common Ancestor |
Questions:
- Which species is most closely related to Species A?
- What does the length of the branch between Node X and Node Y indicate?
- How does the relationship between Species B and Species C compare to their relationships with Species A?
Answers:
- Species B is most closely related to Species A, as they share a more recent common ancestor.
- The length of the branch between Node X and Node Y indicates the time elapsed between the two nodes. A longer branch indicates more time has passed since the common ancestor.
- Species B and Species C are more distantly related to each other than they are to Species A, as they branch off from the common ancestor at different nodes.
🔍 Note: The length of the branches in a cladogram can indicate the amount of time that has passed since the common ancestor. However, this is not always the case, and branch lengths can be arbitrary.
Conclusion
Cladograms are a powerful tool for understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species. By reading and interpreting cladograms, we can gain insights into the shared ancestry and evolutionary history of various organisms. In this practice worksheet, we’ve covered the basics of cladogram interpretation and provided answers to common questions. Remember to always start at the base of the tree and work your way up, and don’t hesitate to ask questions if you’re unsure about any aspect of cladogram interpretation.
What is the purpose of a cladogram?
+A cladogram is used to visualize the evolutionary relationships between different species based on their shared characteristics.
How do I read a cladogram?
+Start at the base of the tree, which represents the most recent common ancestor. Move up the tree, and each node represents a common ancestor of the species above it. The branches represent the relationships between the species.
What does the length of a branch in a cladogram indicate?
+The length of a branch in a cladogram can indicate the amount of time that has passed since the common ancestor. However, this is not always the case, and branch lengths can be arbitrary.
Related Terms:
- Cladogram Worksheet with answers PDF
- Cladogram Worksheet pdf
- Phylogenetic tree worksheet with answers
- Cladogram Practice answer key
- Cladogram Practice problems
- Making Cladograms Worksheet Answers