Cells Alive Bacterial Cell Worksheet

Understanding Bacterial Cells: A Comprehensive Guide
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that are ubiquitous in our environment, playing a vital role in various ecosystems. Despite their small size, bacterial cells are complex structures that have fascinated scientists for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the world of bacterial cells, exploring their structure, function, and characteristics.
Bacterial Cell Structure
A typical bacterial cell consists of several key components:
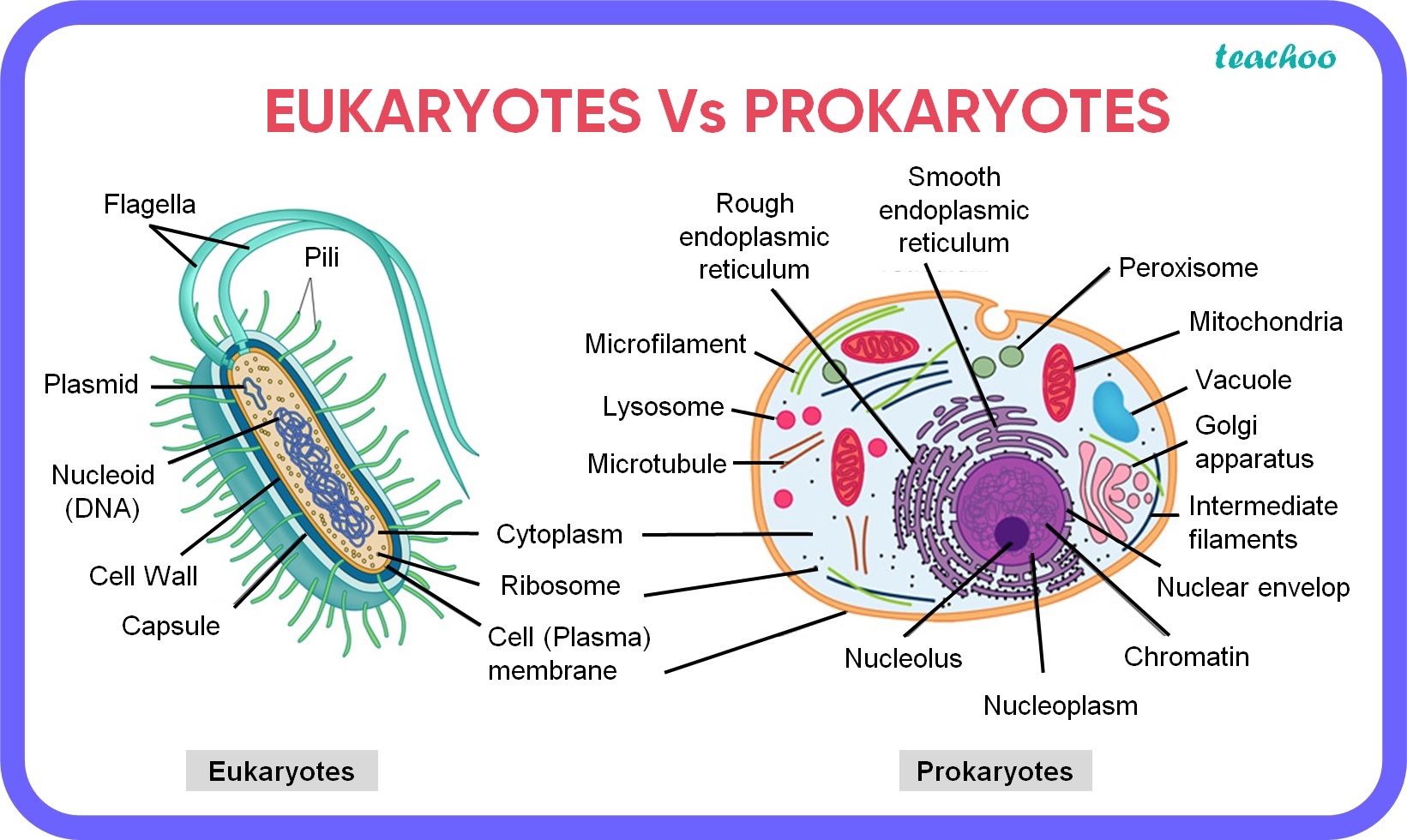
- Cell Wall: The cell wall provides structural support and maintains the cell’s shape. It is composed of peptidoglycan (also known as murein), which is a polysaccharide molecule cross-linked with short peptides.
- Plasma Membrane: The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out. It is semi-permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell where metabolic processes take place. It contains various organelles, proteins, and other molecules necessary for cell growth and maintenance.
- Nucleoid: The nucleoid is the region where the bacterial cell’s genetic material (DNA) is located. Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacterial cells do not have a true nucleus.
- Pili: Pili are hair-like structures on the surface of bacterial cells that aid in attachment, DNA transfer, and other cellular processes.
- Flagella: Flagella are whip-like structures that enable bacterial cells to move through their environment.
Bacterial Cell Function
Bacterial cells perform various functions essential for their survival and growth:
- Metabolism: Bacteria carry out metabolic processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and fermentation to generate energy and produce essential compounds.
- DNA Replication: Bacterial cells replicate their DNA to ensure genetic continuity and prepare for cell division.
- Protein Synthesis: Bacteria synthesize proteins necessary for cell growth, maintenance, and response to environmental stimuli.
- Cell Division: Bacterial cells divide by a process called binary fission, where the cell splits into two identical daughter cells.
Characteristics of Bacterial Cells
Bacterial cells exhibit several distinct characteristics:
- Small Size: Bacterial cells are typically 0.5-5.0 micrometers in length, making them invisible to the naked eye.
- Rapid Growth: Bacteria can grow and divide rapidly, with some species doubling in number in as little as 20 minutes.
- Metabolic Diversity: Bacteria exhibit a wide range of metabolic capabilities, allowing them to thrive in diverse environments.
- Resistance to Environmental Stress: Bacteria have developed various strategies to withstand environmental stressors, such as antibiotics, temperature fluctuations, and radiation.
Types of Bacterial Cells
Bacteria can be classified into several types based on their morphology, metabolism, and other characteristics:
- Spherical Bacteria: Also known as cocci, these bacteria are spherical in shape and include species such as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Rod-Shaped Bacteria: These bacteria are rod-shaped and include species such as Escherichia coli (E. coli).
- Spiral Bacteria: These bacteria have a spiral shape and include species such as Helicobacter pylori.
- Photosynthetic Bacteria: These bacteria, such as cyanobacteria, are capable of photosynthesis and produce their own food.
🔍 Note: Bacterial cells are incredibly diverse, with thousands of species exhibiting unique characteristics and capabilities.
Importance of Bacterial Cells
Bacterial cells play a vital role in various aspects of our lives:
- Ecological Balance: Bacteria contribute to the balance of ecosystems, decomposing organic matter, and recycling nutrients.
- Food Production: Bacteria are used in food production, such as in the fermentation of yogurt, cheese, and bread.
- Human Health: Bacteria are essential for human health, aiding in digestion, immunity, and disease prevention.
- Biotechnology: Bacteria are used in biotechnology applications, such as in the production of antibiotics, vaccines, and other pharmaceuticals.
Cells Alive Bacterial Cell Worksheet
To reinforce your understanding of bacterial cells, complete the following worksheet:

| Bacterial Cell Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Provides structural support and maintains cell shape |
| Plasma Membrane | Regulates movement of materials in and out of the cell |
| Cytoplasm | Jelly-like substance where metabolic processes take place |
| Nucleoid | Region where bacterial cell’s genetic material (DNA) is located |
| Pili | Hair-like structures on the surface of bacterial cells |
| Flagella | Whip-like structures that enable bacterial cells to move |
Match the following bacterial cell functions with their descriptions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Generate energy and produce essential compounds |
| DNA Replication | Replicate genetic material to ensure genetic continuity |
| Protein Synthesis | Synthesize proteins necessary for cell growth and maintenance |
| Cell Division | Divide into two identical daughter cells |
Identify the characteristics of bacterial cells:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Small Size | Typically 0.5-5.0 micrometers in length |
| Rapid Growth | Can grow and divide rapidly |
| Metabolic Diversity | Exhibit a wide range of metabolic capabilities |
| Resistance to Environmental Stress | Can withstand environmental stressors |
In Conclusion
Bacterial cells are fascinating organisms that have adapted to thrive in diverse environments. Understanding their structure, function, and characteristics is essential for appreciating their importance in our lives. By completing the worksheet and exploring the world of bacterial cells, you have taken the first step in unlocking the secrets of these incredible microorganisms.
What is the primary function of the cell wall in bacterial cells?
+The primary function of the cell wall in bacterial cells is to provide structural support and maintain the cell’s shape.
What is the difference between pili and flagella?
+Pili are hair-like structures on the surface of bacterial cells that aid in attachment, DNA transfer, and other cellular processes, while flagella are whip-like structures that enable bacterial cells to move through their environment.
What is the importance of bacterial cells in human health?
+Bacterial cells are essential for human health, aiding in digestion, immunity, and disease prevention.