5 Ways to Master Cell Structure and Function
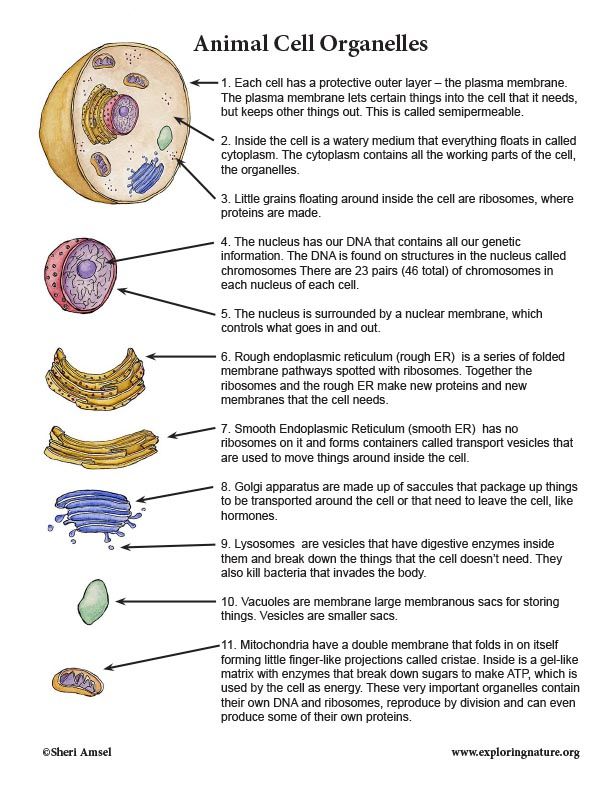
Understanding the Basics of Cell Structure and Function
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. Every living thing, from plants to animals, is composed of one or more cells. Cells are incredibly diverse, with different types of cells performing various functions in the body. However, all cells share certain common characteristics, such as having a cell membrane, genetic material, and the ability to reproduce. Mastering cell structure and function is essential for understanding the intricacies of life and the human body.
1. Learn the Cell Membrane and Its Functions
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that surrounds the cell. It acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while keeping others out. Understanding the cell membrane and its functions is crucial for mastering cell structure and function.
- Functions of the Cell Membrane:
- Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell
- Provides mechanical support and protection to the cell
- Acts as a site for cell signaling and communication
- Controls the cell’s interactions with its environment
📝 Note: The cell membrane is a dynamic structure that is constantly changing and adapting to the cell's needs.
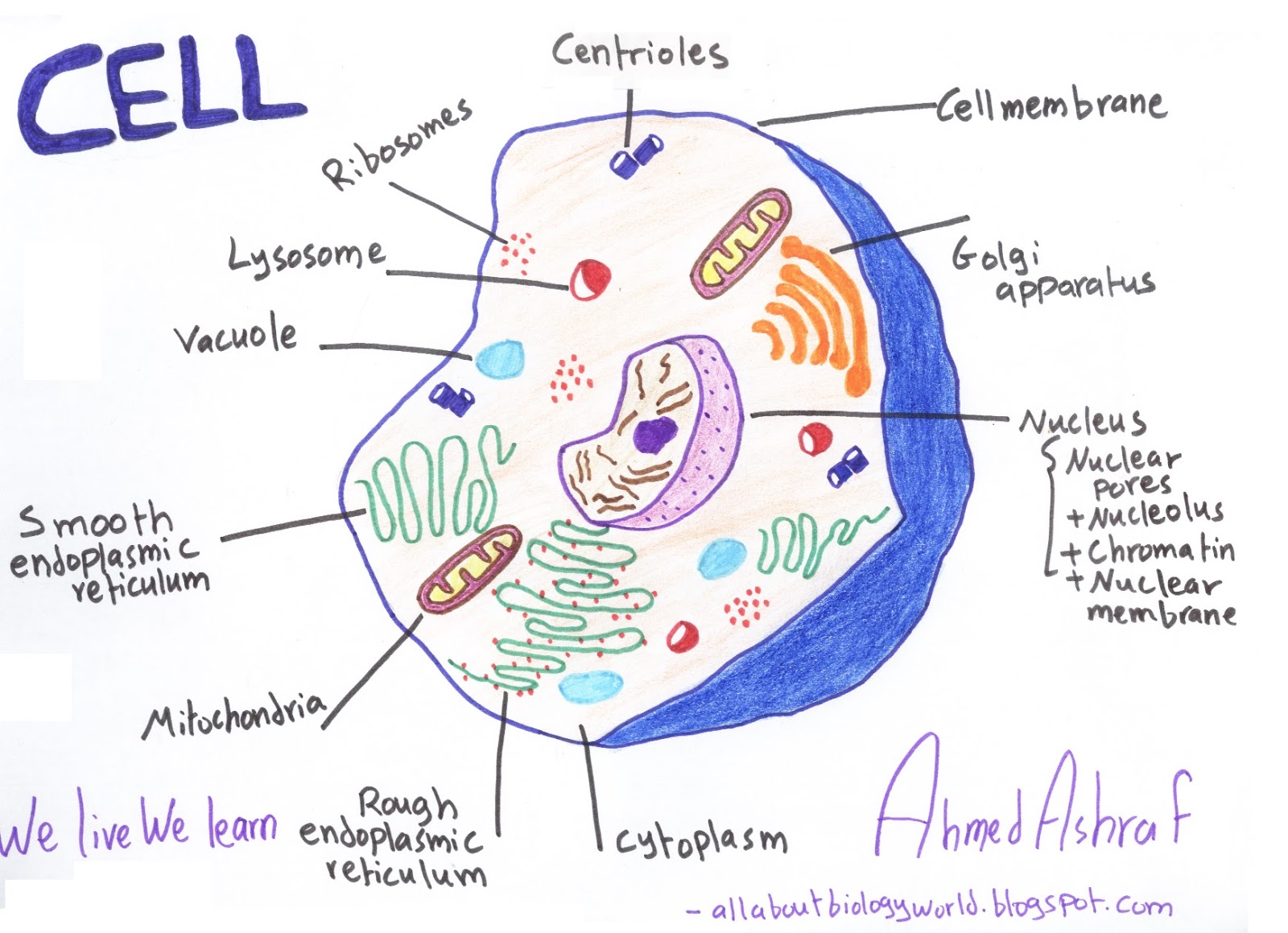
2. Understand the Different Cell Organelles
Cell organelles are specialized structures within the cell that perform specific functions. Each organelle has a unique role to play in the cell’s overall functioning. Some of the most important cell organelles include:
- Mitochondria: Known as the powerhouses of the cell, mitochondria generate energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
- Nucleus: The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material and controls cell growth and division.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is involved in protein synthesis, folding, and transport.
- Lysosomes: Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down and recycle cellular waste and foreign substances.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Mitochondria | Energy production |
| Nucleus | Genetic control |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Protein synthesis and transport |
| Lysosomes | Digestion and recycling |
3. Study Cell Division and Reproduction
Cell division is the process by which a cell splits into two daughter cells. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in the production of two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells and results in the production of four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Mitosis:
- Occurs in somatic cells
- Results in the production of two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell
- Meiosis:
- Occurs in reproductive cells
- Results in the production of four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell
📝 Note: Cell division is a critical process that occurs in all living organisms, from bacteria to humans.
4. Explore Cell Signaling and Communication
Cell signaling and communication are essential for the proper functioning of cells and tissues. Cells communicate with each other through various signaling pathways, including:
- Hormone Signaling: Hormones are chemical signals produced by endocrine glands that regulate various cellular processes.
- Neurotransmitter Signaling: Neurotransmitters are chemical signals produced by neurons that regulate various cellular processes.
- Cell-Cell Signaling: Cells communicate with each other through direct contact or through the release of signaling molecules.
5. Practice with Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Practicing with real-life examples and case studies is an effective way to master cell structure and function. By analyzing how cells function in different organisms and under different conditions, you can gain a deeper understanding of the intricacies of cell biology.
- Examples:
- Study how cells respond to environmental stressors, such as temperature and pH changes.
- Analyze how cells communicate with each other in different tissues and organs.
- Examine how cells adapt to different environments, such as high-altitude and deep-sea environments.
In conclusion, mastering cell structure and function requires a deep understanding of the cell membrane, cell organelles, cell division, cell signaling, and communication. By practicing with real-life examples and case studies, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the intricacies of cell biology.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
+The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
What are the three main types of cell division?
+The three main types of cell division are mitosis, meiosis, and binary fission.
What is the main function of mitochondria?
+The main function of mitochondria is to generate energy for the cell through cellular respiration.



