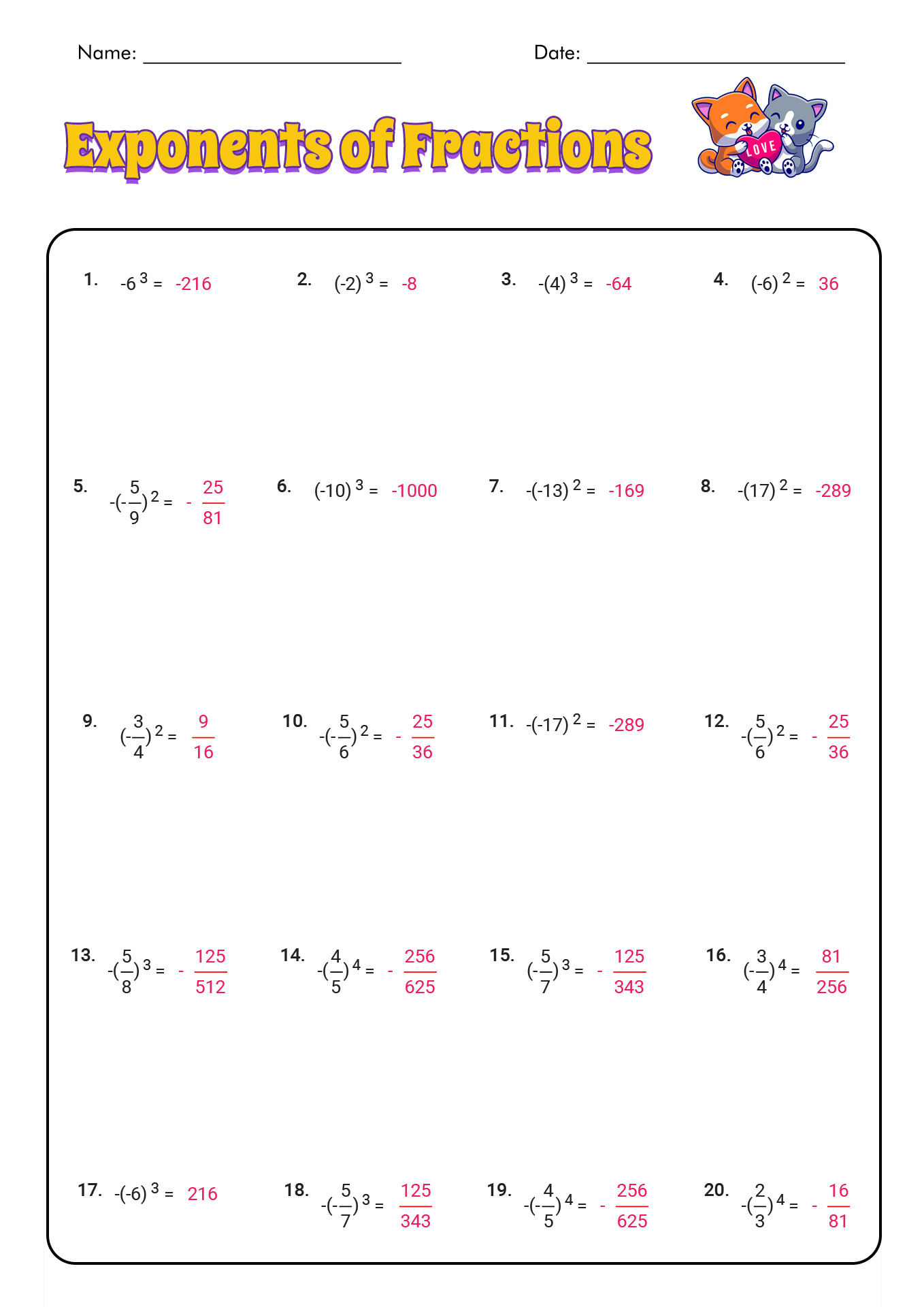
6 Tips to Master Mendel and Heredity Worksheet Answers

Understanding Mendel and Heredity: A Comprehensive Guide
The study of heredity and genetics is a fundamental aspect of biology, and it all began with the pioneering work of Gregor Mendel. Mendel’s laws of inheritance, which describe how traits are passed down from one generation to the next, are still widely used today. However, many students struggle to understand the complex concepts and apply them to worksheet answers. In this guide, we will provide six tips to help you master Mendel and heredity, making it easier to tackle those worksheet answers.
Tip 1: Understand the Basics of Mendelian Genetics
Before diving into the complexities of heredity, it’s essential to understand the basics of Mendelian genetics. Mendel’s laws describe the inheritance of traits in a predictable manner. The three main laws are:
- The Law of Segregation: Each pair of alleles (different forms of a gene) separates from each other during gamete formation.
- The Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles for different genes are sorted independently of each other during gamete formation.
- The Law of Dominance: One allele can be dominant over another allele, resulting in the dominant allele being expressed.
Key Terms to Remember:
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism.
- Phenotype: The physical expression of an organism’s genotype.
- Dominant: An allele that will be expressed if an organism has one or two copies of the allele.
- Recessive: An allele that will only be expressed if an organism has two copies of the allele.
Tip 2: Learn to Identify Genotype and Phenotype
To answer worksheet questions, you need to be able to identify an organism’s genotype and phenotype. This involves understanding the relationship between the genotype and phenotype.
- Genotype to Phenotype: If an organism has a dominant allele (B), it will be expressed (B). If an organism has two recessive alleles (bb), the recessive trait will be expressed.
- Phenotype to Genotype: If an organism expresses a dominant trait (B), it can have either BB or Bb genotype. If an organism expresses a recessive trait (b), it must have the bb genotype.
Example:

| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| BB | B (dominant) |
| Bb | B (dominant) |
| bb | b (recessive) |
Tip 3: Understand Punnett Squares
Punnett squares are a graphical representation of the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. They are a powerful tool for predicting the probability of certain traits being expressed.
- Punnett Square Steps:
- Determine the genotype of the parents.
- Determine the possible gametes (sperm or egg cells) for each parent.
- Create a grid with the possible gametes from each parent.
- Fill in the grid with the possible genotypes of the offspring.
Example:
Suppose we have two parents with the genotype Bb and bb. We want to determine the probability of their offspring expressing the dominant trait (B).
| B | b | |
|---|---|---|
| B | BB | Bb |
| b | Bb | bb |
The Punnett square shows that there is a 50% chance of the offspring expressing the dominant trait (B).
Tip 4: Practice, Practice, Practice
The best way to master Mendel and heredity is to practice, practice, practice! Work through as many examples and worksheet answers as you can. This will help you become more comfortable with the concepts and develop your problem-solving skills.
Example:
What is the probability of a child inheriting the dominant allele (B) from a parent with the genotype Bb?
A) 25% B) 50% C) 75% D) 100%
Answer: B) 50%
Tip 5: Use Real-World Examples
Using real-world examples can help make the concepts more tangible and interesting. For example, you can use the genetics of eye color or hair color to illustrate the principles of Mendelian inheritance.
Example:
Brown eye color (B) is dominant, while blue eye color (b) is recessive. What is the probability of a child inheriting blue eyes if both parents have brown eyes and are carriers of the recessive allele (Bb)?
A) 25% B) 50% C) 75% D) 100%
Answer: A) 25%
Tip 6: Review and Reinforce
Finally, review and reinforce your understanding of Mendel and heredity by revisiting the concepts regularly. This will help solidify your knowledge and build your confidence in tackling worksheet answers.
Key Concepts to Review:
- Mendel’s laws of inheritance
- Genotype and phenotype
- Punnett squares
- Dominant and recessive alleles
By following these six tips, you’ll be well on your way to mastering Mendel and heredity and becoming proficient in answering worksheet questions.
What is the main difference between genotype and phenotype?
+The genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism, while the phenotype is the physical expression of the genotype.
What is a Punnett square used for?
+A Punnett square is used to predict the probability of certain traits being expressed in offspring.
What is the law of independent assortment?
+The law of independent assortment states that alleles for different genes are sorted independently of each other during gamete formation.
In conclusion, mastering Mendel and heredity requires a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts, including genotype and phenotype, dominant and recessive alleles, and Punnett squares. By following these six tips and practicing regularly, you’ll become proficient in answering worksheet questions and develop a deeper understanding of the principles of Mendelian inheritance.
Related Terms:
- Gregor Mendel
- Gregor Mendel news
- Gregor Mendel images
- Gregor Mendel videos