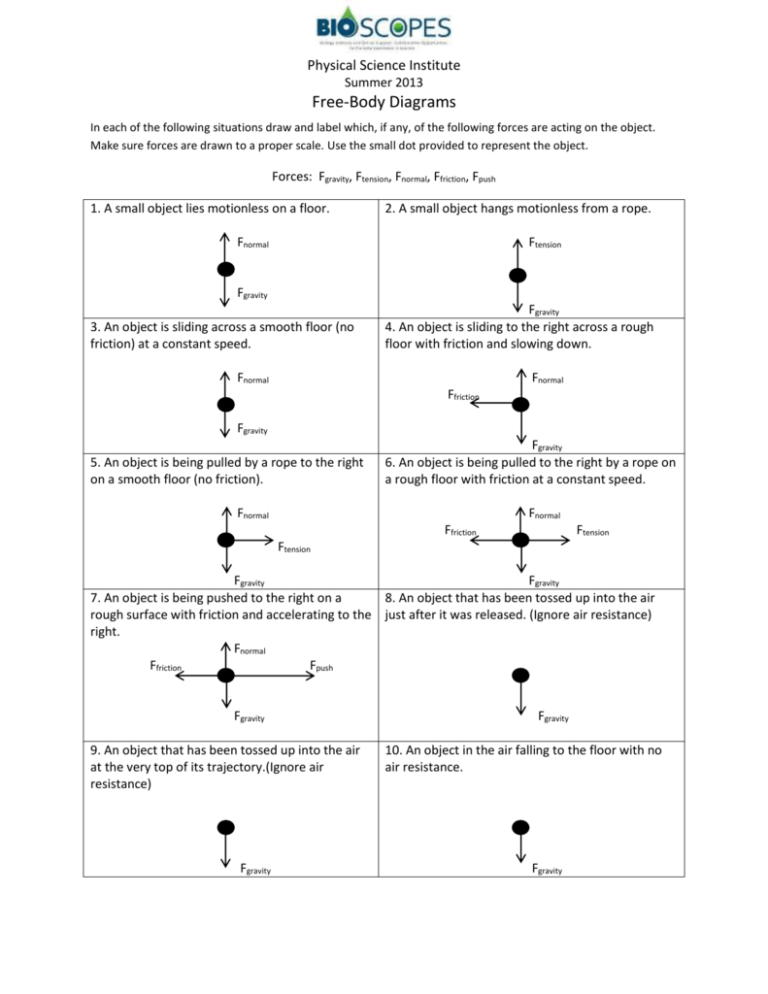
6 Key Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers Revealed
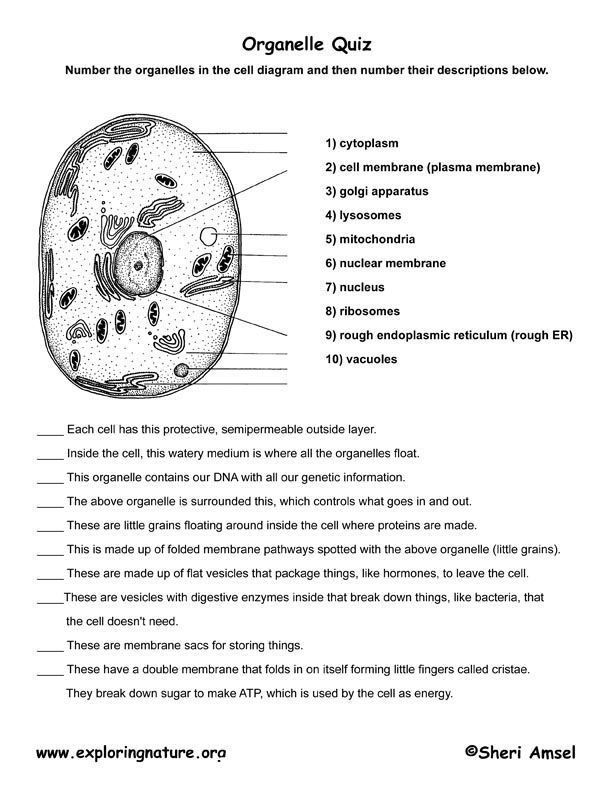
Unlocking the Secrets of Cell Organelles: A Comprehensive Guide
Cells are the building blocks of life, and within these tiny structures, various organelles work together to maintain cellular functions. Understanding the roles and functions of these organelles is crucial for grasping the intricacies of cellular biology. In this article, we will delve into the world of cell organelles, exploring six key organelles and their functions.
1. Nucleus: The Control Center
The nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell and serves as the control center. It contains the genetic material, or DNA, which carries the instructions for cellular growth, division, and function. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus.
🔍 Note: The nucleus is often referred to as the "brain" of the cell due to its role in controlling cellular activities.
2. Mitochondria: The Powerhouse
Mitochondria are organelles responsible for generating energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration. They convert glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria have two membranes: the outer membrane and the inner membrane, which is folded into cristae to increase the surface area for energy production.
💡 Note: Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell due to their role in generating energy.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Transport System
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that serves as a transport system for the cell. It is responsible for transporting proteins, lipids, and other molecules throughout the cell. The ER also plays a role in protein synthesis, folding, and quality control.
4. Golgi Apparatus: The Processing Center
The Golgi apparatus is a complex organelle responsible for processing and modifying proteins and lipids synthesized by the ER. It consists of a series of flattened sacs and tubules that work together to modify, sort, and package molecules for transport to other parts of the cell.
5. Lysosomes: The Digestive System
Lysosomes are organelles responsible for cellular digestion and recycling. They contain digestive enzymes that break down and recycle cellular waste, proteins, and lipids. Lysosomes also play a role in cellular defense, destroying pathogens and other foreign substances that enter the cell.
6. Ribosomes: The Protein Factories
Ribosomes are small organelles found throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. They are responsible for protein synthesis, reading messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences and assembling amino acids into proteins. Ribosomes are essential for cellular growth, division, and function.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Control center, contains genetic material |
| Mitochondria | Energy production, converts glucose into ATP |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Transport system, protein synthesis and transport |
| Golgi Apparatus | Processing center, modifies and packages proteins and lipids |
| Lysosomes | Digestive system, breaks down and recycles cellular waste |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis, reads mRNA sequences and assembles amino acids |
In conclusion, understanding the functions and roles of these six key cell organelles is essential for grasping the intricacies of cellular biology. Each organelle plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and function, and their dysregulation can lead to various diseases and disorders.
What is the main function of the nucleus?
+The main function of the nucleus is to serve as the control center of the cell, containing the genetic material and regulating cellular activities.
What is the role of mitochondria in the cell?
+Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy for the cell through cellular respiration, converting glucose into ATP.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
+The Golgi apparatus is responsible for processing and modifying proteins and lipids synthesized by the ER, sorting and packaging them for transport to other parts of the cell.