5 Ways the Plasma Membrane Defends the Cell
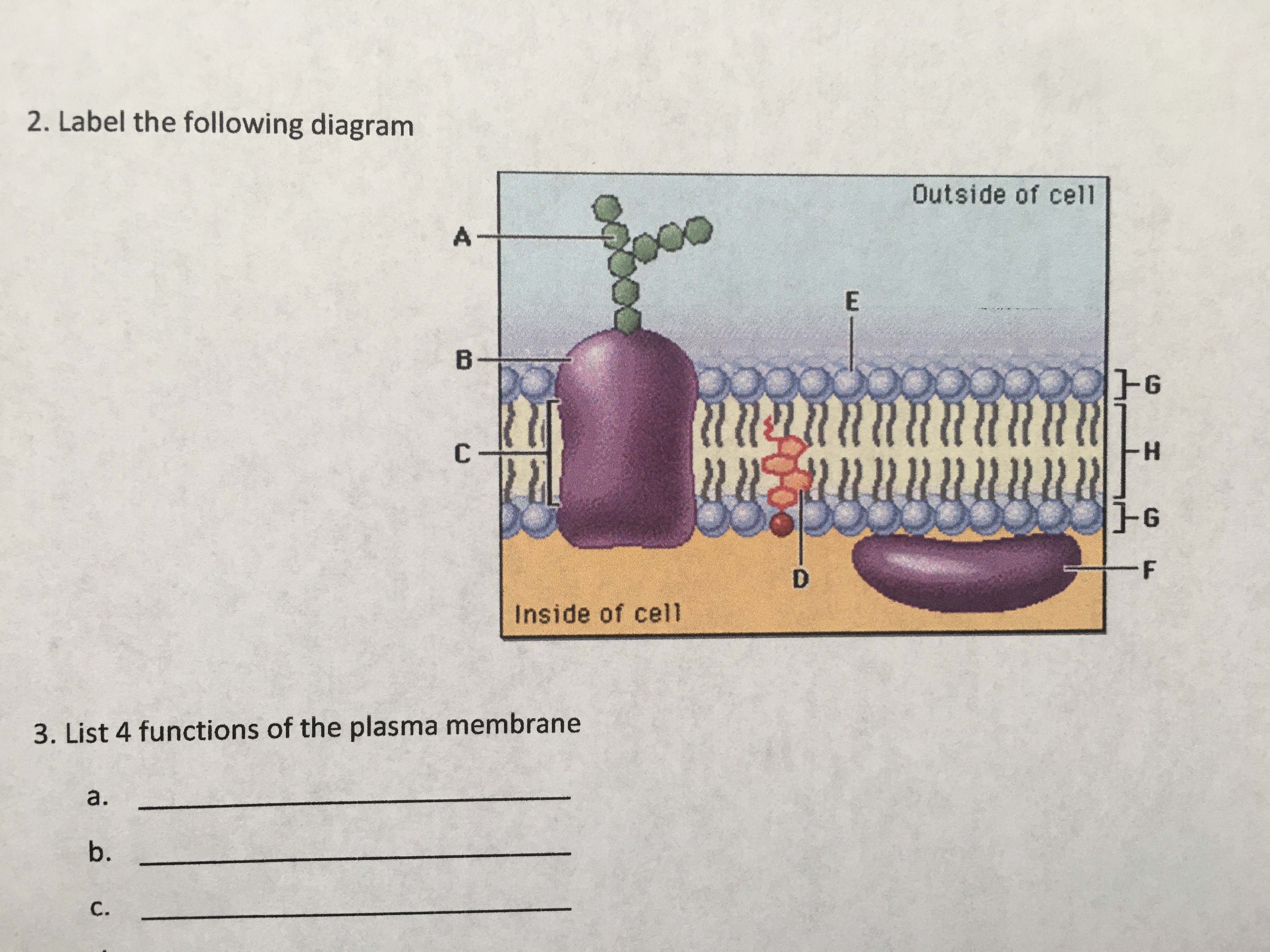
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that acts as the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is a crucial component of the cell, regulating what enters and leaves the cell, and maintaining the cell’s internal environment. One of the key functions of the plasma membrane is to defend the cell against external threats, such as pathogens, toxins, and mechanical damage. Here are 5 ways the plasma membrane defends the cell:
1. Selective Permeability
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, meaning that it allows certain molecules to pass through while keeping others out. This is achieved through the presence of specific proteins and lipids that control the movement of molecules across the membrane. For example, some proteins form channels that allow ions and small molecules to pass through, while others act as pumps to transport molecules against their concentration gradient. This selective permeability helps to prevent the entry of harmful substances into the cell.
2. Cell Signaling and Communication
The plasma membrane plays a crucial role in cell signaling and communication. It receives and responds to signals from the environment, such as hormones and neurotransmitters, and transmits signals to other cells. This helps the cell to respond to changes in its environment and to coordinate its activities with other cells. For example, when a hormone binds to a receptor on the plasma membrane, it triggers a signaling cascade that can lead to changes in gene expression, protein synthesis, or other cellular processes.
3. Phagocytosis and Endocytosis
The plasma membrane is involved in the process of phagocytosis, where the cell engulfs and ingests foreign particles or microorganisms. This helps to remove pathogens and other harmful substances from the environment. The plasma membrane also undergoes endocytosis, where it invaginates to form vesicles that internalize substances from the environment. This helps to regulate the amount of certain substances in the cell and to remove waste products.
4. Maintenance of Cell Shape and Integrity
The plasma membrane helps to maintain the shape and integrity of the cell by providing mechanical support and resisting external forces. It is semi-permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while maintaining the cell’s internal environment. The plasma membrane also helps to regulate the cell’s volume by controlling the movement of ions and water across the membrane. This helps to maintain the cell’s osmotic balance and prevent excessive shrinkage or swelling.
5. Recognition and Response to Pathogens
The plasma membrane plays a crucial role in recognizing and responding to pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses. It contains pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and trigger an immune response. For example, when a PRR recognizes a PAMP, it activates a signaling cascade that leads to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the activation of immune cells.
🚨 Note: The plasma membrane is a dynamic structure that is constantly being remodeled and reorganized in response to changes in the cell's environment. This helps to ensure that the cell remains protected and functional.
In conclusion, the plasma membrane plays a vital role in defending the cell against external threats. Its selective permeability, cell signaling and communication, phagocytosis and endocytosis, maintenance of cell shape and integrity, and recognition and response to pathogens all contribute to its defensive functions. Understanding how the plasma membrane defends the cell is essential for understanding how cells respond to their environment and maintain their internal homeostasis.
What is the main function of the plasma membrane?
+The main function of the plasma membrane is to regulate what enters and leaves the cell, and to maintain the cell’s internal environment.
How does the plasma membrane recognize pathogens?
+The plasma membrane recognizes pathogens through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
What is the role of phagocytosis in cell defense?
+Phagocytosis is the process by which the cell engulfs and ingests foreign particles or microorganisms, helping to remove pathogens and other harmful substances from the environment.