Cell Cycle Answers Worksheet
Understanding the Cell Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
The cell cycle is a crucial process in biology that describes the stages a cell goes through from its birth to its division. It’s a fundamental concept in cell biology, and understanding it can help you grasp various biological processes. In this worksheet, we’ll explore the cell cycle, its stages, and key concepts related to it.
What is the Cell Cycle?
The cell cycle, also known as the cell division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell, leading to its division and duplication. It’s a highly regulated process that ensures the proper replication and segregation of genetic material. The cell cycle consists of three main stages: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
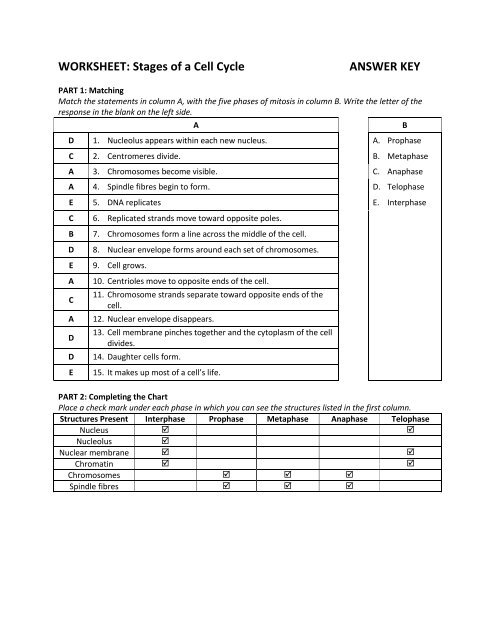
Stages of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is divided into several stages, each with distinct characteristics and functions.
Interphase
Interphase is the longest stage of the cell cycle, during which the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division. It’s further divided into three sub-stages:
- Gap 1 (G1): The cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
- Synthesis (S): The cell replicates its DNA.
- Gap 2 (G2): The cell prepares for cell division.
Mitosis
Mitosis is the stage where the replicated DNA is divided equally between two daughter cells. It’s a complex process that involves several steps:
- Prophase: Chromatin condenses, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate.
- Telophase: Nuclear envelope reforms.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the final stage of the cell cycle, where the cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
Key Concepts Related to the Cell Cycle
- Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs): Proteins that regulate the cell cycle by binding to cyclins.
- Cyclins: Proteins that bind to CDKs to regulate the cell cycle.
- Checkpoints: Mechanisms that ensure the proper progression of the cell cycle.
- Apoptosis: Programmed cell death, which can occur if the cell cycle is disrupted.
Cell Cycle Regulation
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by various mechanisms to ensure proper progression and prevent errors. Some key regulators include:
- p53: A tumor suppressor protein that can halt the cell cycle if DNA damage is detected.
- Rb: A tumor suppressor protein that regulates the G1-S transition.
- Cyclin-CDK complexes: Regulate the cell cycle by phosphorylating key proteins.
Cell Cycle Abnormalities
Abnormalities in the cell cycle can lead to various diseases, including cancer. Some common abnormalities include:
- Uncontrolled cell growth: Can lead to cancer.
- Genetic mutations: Can occur if the cell cycle is disrupted.
- Apoptosis resistance: Can lead to cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell cycle is a complex process that’s essential for life. Understanding its stages, regulation, and key concepts can provide valuable insights into various biological processes. By recognizing the importance of the cell cycle, we can better appreciate the intricacies of life and the consequences of disruptions to this process.
What is the main function of the cell cycle?
+The main function of the cell cycle is to ensure the proper replication and segregation of genetic material, leading to the division and duplication of cells.
What are the three main stages of the cell cycle?
+The three main stages of the cell cycle are interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
What is the role of p53 in the cell cycle?
+p53 is a tumor suppressor protein that can halt the cell cycle if DNA damage is detected.