6 Ways to Calculate Density with Ease

Understanding Density and Its Importance
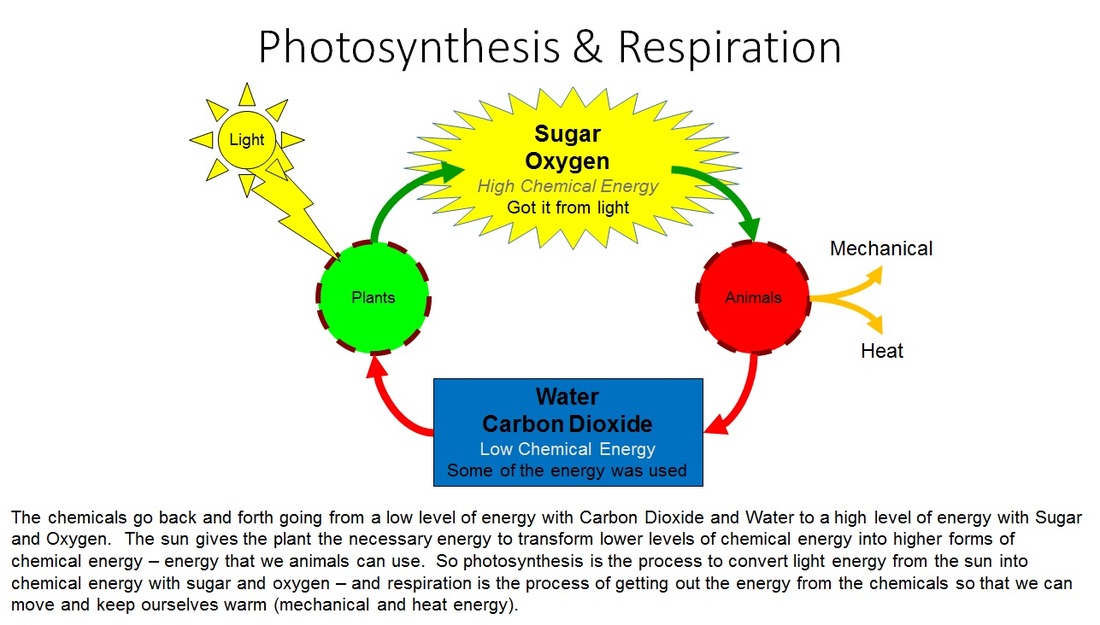
Density is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry that describes the amount of mass contained in a given volume of a substance. It is a measure of how tightly packed the molecules of a substance are. Density is an essential property that helps us distinguish between different substances and is crucial in various fields, including engineering, materials science, and biology.
Why Calculate Density?
Calculating density is essential in various applications, such as:
- Identifying the composition of a substance
- Determining the buoyancy of an object
- Calculating the weight of a substance
- Analyzing the properties of materials
- Understanding the behavior of fluids and gases
6 Ways to Calculate Density
There are several ways to calculate density, and the method used depends on the available data and the properties of the substance. Here are six common methods:
1. Mass and Volume Method
This is the most direct method of calculating density. It involves measuring the mass and volume of a substance and then dividing the mass by the volume.
Formula: Density = Mass / Volume
Example: A block of wood has a mass of 500 grams and a volume of 200 cubic centimeters. What is its density?
Density = 500 g / 200 cm³ = 2.5 g/cm³
📝 Note: This method requires accurate measurements of mass and volume.
2. Displacement Method
This method involves measuring the volume of a substance by displacing a known volume of water or another fluid.
Formula: Density = (Weight of substance in air - Weight of substance in fluid) / Volume of fluid displaced
Example: A rock has a weight of 200 grams in air and 150 grams when submerged in water. If the volume of water displaced is 100 cubic centimeters, what is the density of the rock?
Density = (200 g - 150 g) / 100 cm³ = 0.5 g/cm³
💧 Note: This method requires a fluid with a known density.
3. Hydrostatic Weighing Method
This method involves measuring the weight of a substance in air and then measuring its weight when submerged in a fluid of known density.
Formula: Density = Weight of substance in air / (Weight of substance in air - Weight of substance in fluid)
Example: A metal cylinder has a weight of 500 grams in air and 400 grams when submerged in water. If the density of water is 1 g/cm³, what is the density of the metal cylinder?
Density = 500 g / (500 g - 400 g) = 2.5 g/cm³
🔄 Note: This method requires a fluid with a known density.
4. Pycnometer Method
A pycnometer is a device used to measure the volume of a substance by measuring the volume of a fluid displaced by the substance.
Formula: Density = Mass of substance / (Volume of pycnometer - Volume of fluid displaced)
Example: A pycnometer has a volume of 200 cubic centimeters, and a substance displaces 50 cubic centimeters of fluid. If the mass of the substance is 300 grams, what is its density?
Density = 300 g / (200 cm³ - 50 cm³) = 2 g/cm³
🧮 Note: This method requires a pycnometer and a fluid with a known density.
5. Specific Gravity Method
Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water. This method involves measuring the specific gravity of a substance and then multiplying it by the density of water.
Formula: Density = Specific gravity × Density of water
Example: The specific gravity of a rock is 2.5. If the density of water is 1 g/cm³, what is the density of the rock?
Density = 2.5 × 1 g/cm³ = 2.5 g/cm³
💧 Note: This method requires the density of water.
6. Archimedes’ Principle Method
Archimedes’ Principle states that the buoyancy force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. This method involves measuring the weight of an object in air and then measuring its weight when submerged in a fluid.
Formula: Density = Weight of object in air / (Weight of object in air - Weight of object in fluid)
Example: A metal sphere has a weight of 200 grams in air and 150 grams when submerged in water. What is its density?
Density = 200 g / (200 g - 150 g) = 2 g/cm³
🔄 Note: This method requires a fluid with a known density.
As we’ve seen, there are several ways to calculate density, each with its own advantages and limitations. By choosing the right method and using accurate measurements, we can determine the density of a substance with ease.
To summarize, density is a fundamental property that is essential in various fields, and calculating it accurately is crucial. The six methods discussed above provide different ways to calculate density, and by understanding the principles behind each method, we can choose the best approach for our specific needs.
What is density?
+Density is a measure of how tightly packed the molecules of a substance are. It is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance.
Why is density important?
+Density is essential in various fields, including engineering, materials science, and biology. It helps us distinguish between different substances and understand their properties.
What are the different methods of calculating density?
+There are six common methods of calculating density: mass and volume method, displacement method, hydrostatic weighing method, pycnometer method, specific gravity method, and Archimedes’ Principle method.