5 Ways to Master Boyle's Law Problems

Understanding Boyle's Law
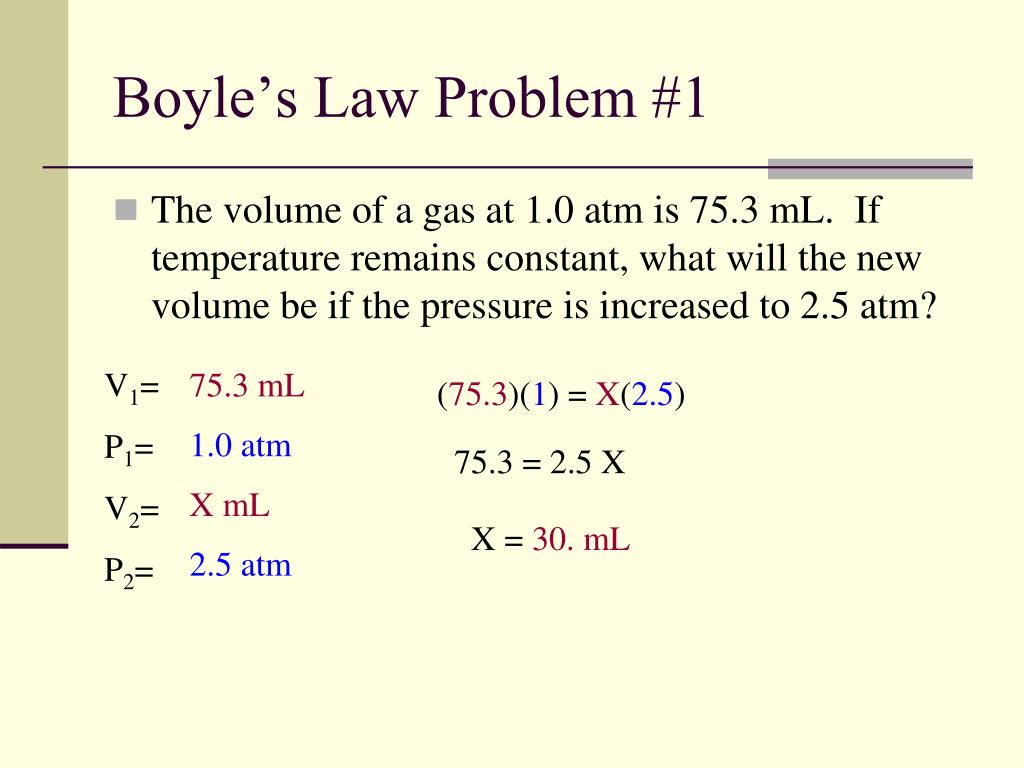
Boyle’s Law is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas. The law states that, at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure. Mathematically, this can be expressed as P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 are the final pressure and volume. Mastering Boyle’s Law problems is essential for students of chemistry and physics, as it is a crucial concept in understanding various natural phenomena and industrial processes.
5 Ways to Master Boyle's Law Problems
1. Understand the Concept
To master Boyle’s Law problems, it is essential to understand the underlying concept. Boyle’s Law is based on the idea that, at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume. This means that, if the pressure of a gas is increased, its volume will decrease, and vice versa. Understanding this concept is crucial in solving Boyle’s Law problems.
2. Practice with Simple Problems
Practice is key to mastering Boyle’s Law problems. Start with simple problems, such as finding the initial or final pressure or volume of a gas, given the other variables. For example:
- A gas has an initial pressure of 2 atm and an initial volume of 5 L. If the pressure is increased to 3 atm, what is the final volume?
- A gas has an initial volume of 10 L and an initial pressure of 1 atm. If the volume is decreased to 5 L, what is the final pressure?
Solving these simple problems will help you understand the concept and build your confidence.
3. Use the Formula
The formula P1V1 = P2V2 is essential in solving Boyle’s Law problems. Make sure you understand how to use the formula to solve problems. For example:
- A gas has an initial pressure of 3 atm and an initial volume of 8 L. If the pressure is decreased to 2 atm, what is the final volume?
- A gas has an initial volume of 12 L and an initial pressure of 2 atm. If the volume is increased to 15 L, what is the final pressure?
Using the formula will help you solve problems quickly and accurately.
4. Use Tables and Graphs
Tables and graphs can be useful tools in solving Boyle’s Law problems. A table can be used to organize data and identify patterns, while a graph can be used to visualize the relationship between pressure and volume. For example:
| Pressure (atm) | Volume (L) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 3.33 |
| 4 | 2.5 |
Using a table like this can help you identify patterns and solve problems quickly.
5. Practice with Complex Problems
Once you have mastered simple problems, it’s time to move on to more complex problems. These problems may involve multiple steps or require you to think critically. For example:
- A gas has an initial pressure of 2 atm and an initial volume of 10 L. If the pressure is increased to 3 atm and then decreased to 2 atm, what is the final volume?
- A gas has an initial volume of 15 L and an initial pressure of 1 atm. If the volume is decreased to 10 L and then increased to 12 L, what is the final pressure?
Solving these complex problems will help you develop your critical thinking skills and master Boyle’s Law problems.
💡 Note: Make sure you understand the concept of Boyle's Law and practice with simple problems before moving on to more complex problems.
In conclusion, mastering Boyle’s Law problems requires a combination of understanding the concept, practicing with simple problems, using the formula, using tables and graphs, and practicing with complex problems. By following these steps, you can develop your skills and become proficient in solving Boyle’s Law problems.
What is Boyle’s Law?
+Boyle’s Law is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas. The law states that, at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure.
What is the formula for Boyle’s Law?
+The formula for Boyle’s Law is P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 are the final pressure and volume.
How can I practice solving Boyle’s Law problems?
+You can practice solving Boyle’s Law problems by starting with simple problems and gradually moving on to more complex problems. You can also use online resources, such as worksheets and practice problems, to help you practice.