5 Bohr Model Worksheet Answers You Need
Understanding the Bohr Model: A Comprehensive Guide
The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that explains the structure of atoms. This model revolutionized our understanding of atomic structure and paved the way for the development of quantum mechanics. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of the Bohr model, its limitations, and provide answers to five essential worksheet questions.
The Bohr Model: A Simplified Explanation
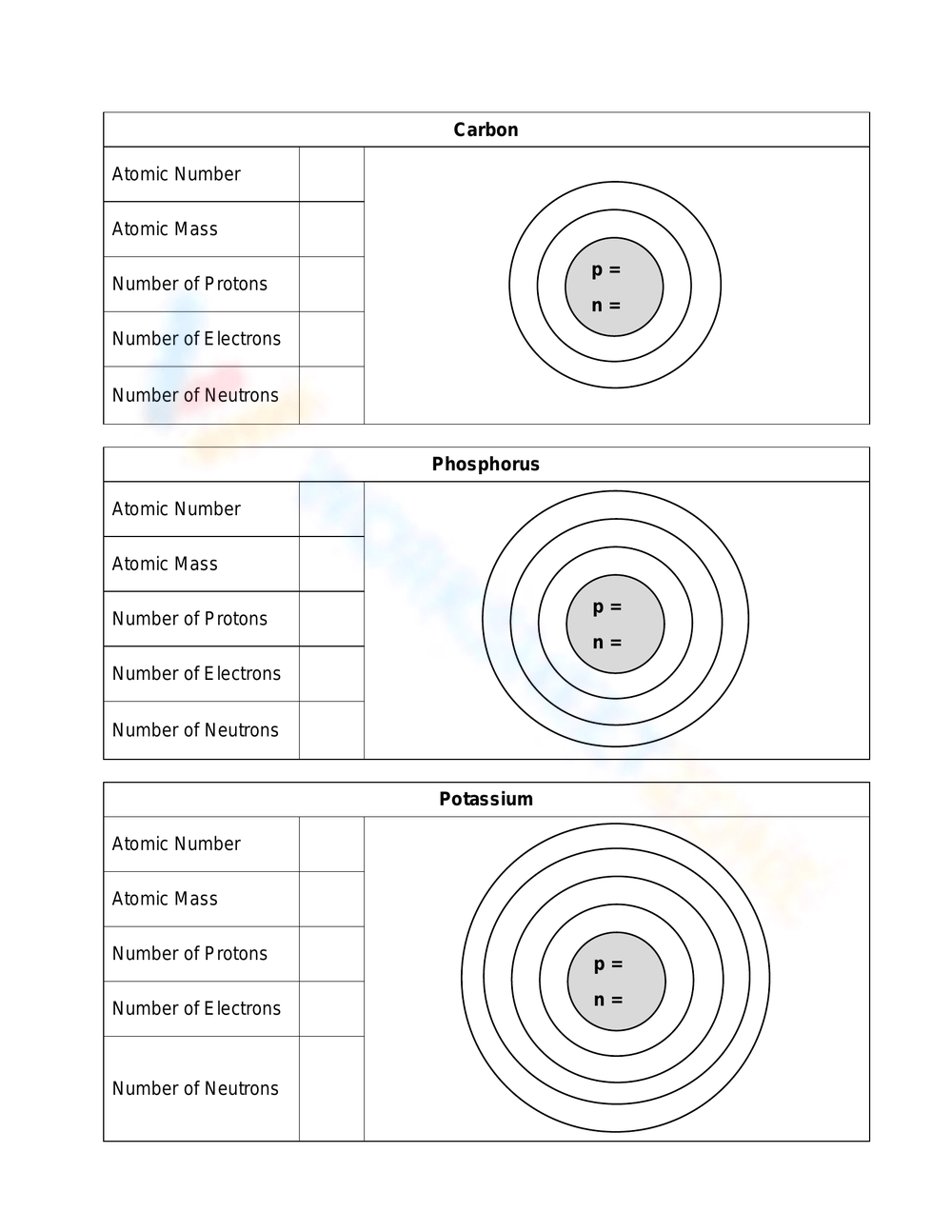
The Bohr model describes an atom as a small, heavy nucleus surrounded by electrons in orbit around it. The key features of the Bohr model are:
- The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons, and it is located at the center of the atom.
- Electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus.
- Each energy level has a fixed capacity, and electrons in the same energy level have the same energy.
- Electrons jump from one energy level to another by emitting or absorbing energy in the form of photons.
Key Components of the Bohr Model
- Nucleus: The central part of the atom, composed of protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
- Energy Levels: Specific regions around the nucleus where electrons are found.
- Orbitals: Mathematical descriptions of the regions where electrons are likely to be found.
Limitations of the Bohr Model
While the Bohr model was a significant improvement over earlier atomic models, it has several limitations:
- It does not account for the electron’s spin or the Zeeman effect.
- It does not explain the fine structure of spectral lines.
- It assumes that electrons occupy specific energy levels, which is not always the case.
5 Bohr Model Worksheet Answers You Need
Here are answers to five essential worksheet questions on the Bohr model:
Question 1: What is the main difference between the Bohr model and the Rutherford model?
Answer: The Bohr model introduces energy levels or shells, which are not present in the Rutherford model. In the Bohr model, electrons occupy specific energy levels, whereas in the Rutherford model, electrons are assumed to orbit the nucleus at random distances.
Question 2: What is the significance of the energy level in the Bohr model?
Answer: The energy level in the Bohr model represents the specific region around the nucleus where an electron is found. Each energy level has a fixed capacity, and electrons in the same energy level have the same energy.
Question 3: What happens when an electron jumps from one energy level to another?
Answer: When an electron jumps from one energy level to another, it emits or absorbs energy in the form of photons. This energy is equal to the difference between the two energy levels.
Question 4: What is the relationship between the number of protons in the nucleus and the number of electrons in an atom?
Answer: In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. This is because each proton has a positive charge, and each electron has a negative charge, and the charges balance each other out.
Question 5: What is the main limitation of the Bohr model?
Answer: The main limitation of the Bohr model is that it does not account for the electron’s spin or the Zeeman effect. Additionally, it assumes that electrons occupy specific energy levels, which is not always the case.
📝 Note: These answers provide a basic understanding of the Bohr model and its limitations. It is essential to delve deeper into the subject to gain a comprehensive understanding of atomic structure.
In Conclusion...
In conclusion, the Bohr model is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that explains the structure of atoms. While it has several limitations, it paved the way for the development of quantum mechanics and remains an essential topic in modern physics and chemistry. By understanding the key aspects of the Bohr model, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the subject and develop a strong foundation for further learning.
What is the main difference between the Bohr model and the Rutherford model?
+The main difference between the Bohr model and the Rutherford model is the introduction of energy levels or shells in the Bohr model. In the Bohr model, electrons occupy specific energy levels, whereas in the Rutherford model, electrons are assumed to orbit the nucleus at random distances.
What is the significance of the energy level in the Bohr model?
+The energy level in the Bohr model represents the specific region around the nucleus where an electron is found. Each energy level has a fixed capacity, and electrons in the same energy level have the same energy.
What happens when an electron jumps from one energy level to another?
+When an electron jumps from one energy level to another, it emits or absorbs energy in the form of photons. This energy is equal to the difference between the two energy levels.