Autosomal Pedigrees Worksheet Made Easy
Understanding Autosomal Pedigrees: A Comprehensive Guide
Autosomal pedigrees are a crucial tool in genetics, used to study the inheritance of traits and identify patterns of inheritance. In this guide, we will delve into the world of autosomal pedigrees, exploring what they are, how to read and create them, and their significance in genetics.
What are Autosomal Pedigrees?
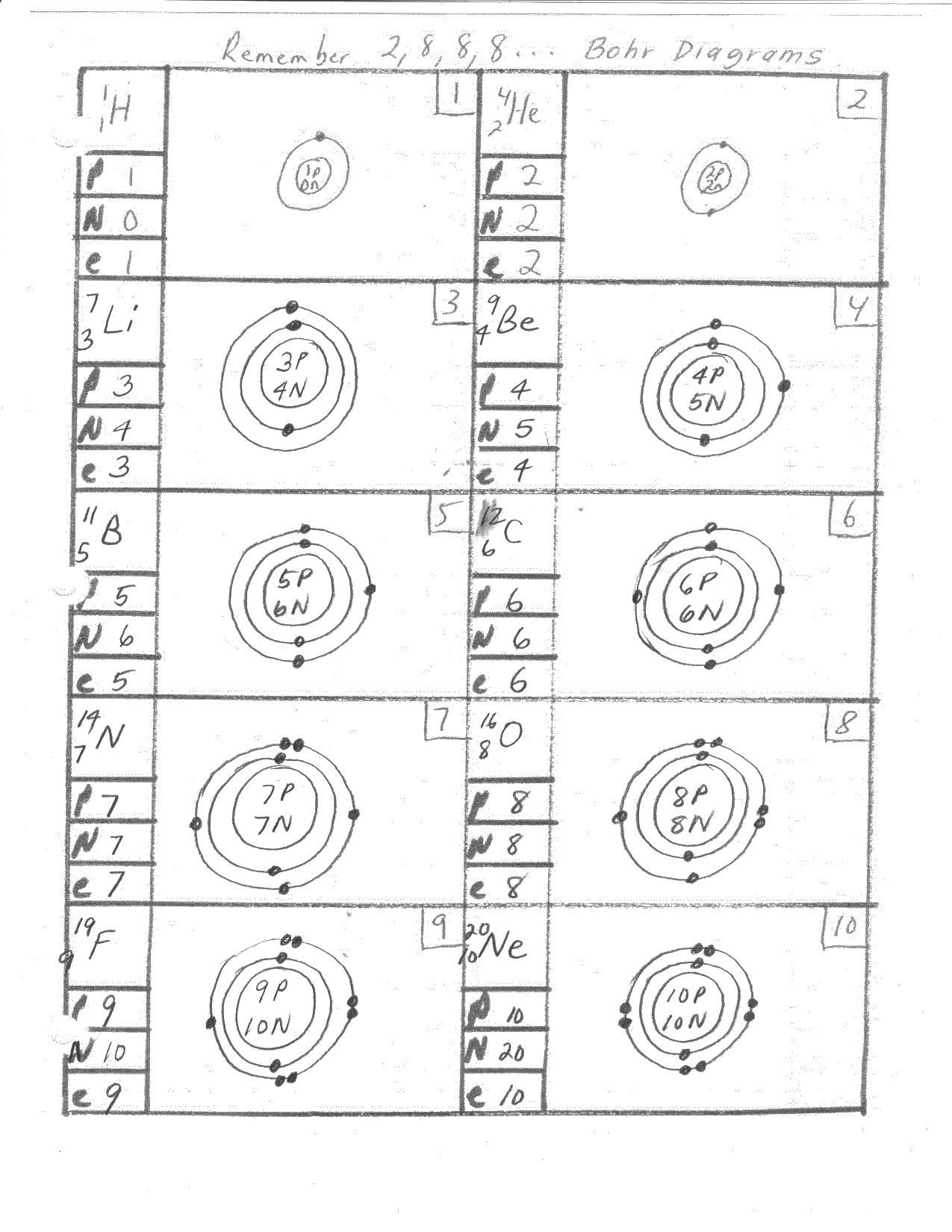
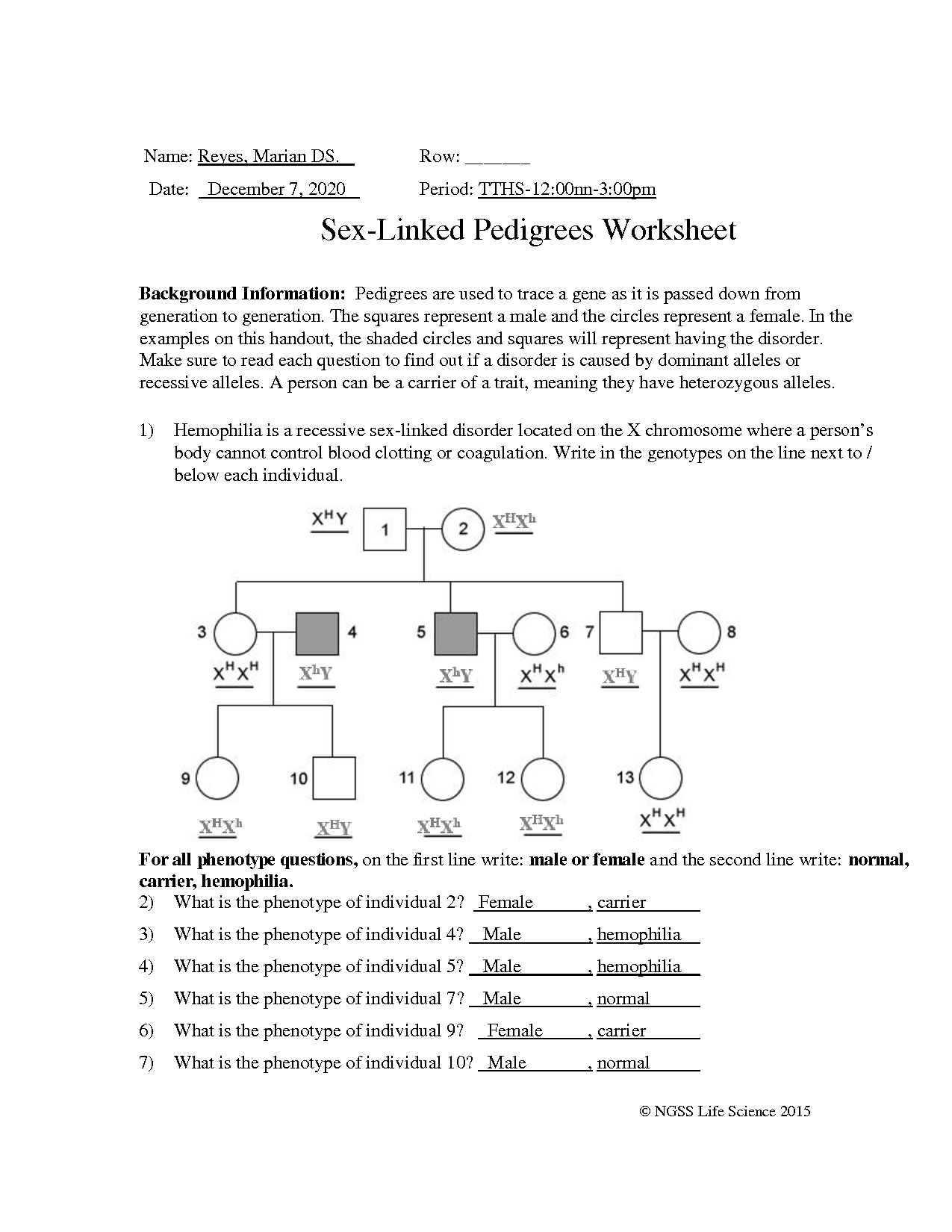
Autosomal pedigrees are diagrams that show the relationships between family members and the inheritance of traits. The term “autosomal” refers to the fact that these pedigrees involve the inheritance of traits that are not sex-linked, meaning they are not located on the X or Y chromosomes. Autosomal traits are inherited in an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive pattern.
Reading an Autosomal Pedigree
Reading an autosomal pedigree can seem daunting at first, but it’s actually quite straightforward. Here are the key elements to look out for:
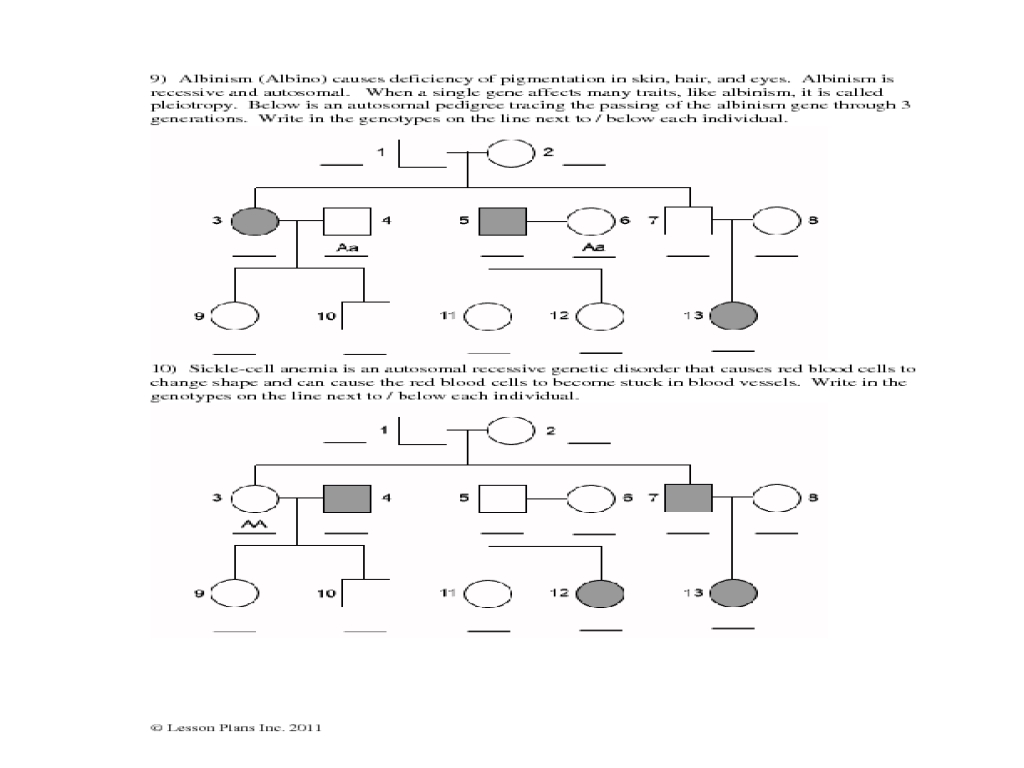
- Symbols: Circles represent females, while squares represent males. A diagonal line through a symbol indicates that the individual is deceased.
- Lines: A horizontal line connects parents to their offspring, while a vertical line connects siblings.
- Traits: Affected individuals are indicated by a shaded or filled-in symbol, while unaffected individuals have an empty symbol.
👉 Note: The symbols and lines used in an autosomal pedigree can vary depending on the specific diagram, but the principles remain the same.
Creating an Autosomal Pedigree
Creating an autosomal pedigree involves gathering information about a family’s medical history and relationships. Here are the steps to follow:
- Gather information: Collect data on the family’s medical history, including any genetic disorders or traits.
- Determine the relationships: Identify the relationships between family members, including parents, siblings, and offspring.
- Draw the pedigree: Use the symbols and lines to create the pedigree diagram.
- Indicate affected individuals: Shade or fill in the symbols of affected individuals.
Types of Autosomal Inheritance
Autosomal traits can be inherited in one of two patterns: autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive.
- Autosomal Dominant: A single copy of the dominant allele is enough to express the trait. Affected individuals can be heterozygous (having one copy of the dominant allele and one copy of the recessive allele) or homozygous (having two copies of the dominant allele).
- Autosomal Recessive: Two copies of the recessive allele are needed to express the trait. Affected individuals are homozygous recessive.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| DD or Dd | Affected (autosomal dominant) |
| dd | Unaffected (autosomal recessive) |
Significance of Autosomal Pedigrees
Autosomal pedigrees are essential in genetics, as they help:
- Identify patterns of inheritance: By analyzing the pedigree, researchers can identify the pattern of inheritance and determine whether a trait is autosomal dominant or recessive.
- Predict risk: Autosomal pedigrees can be used to predict the risk of a trait being passed on to offspring.
- Develop treatment plans: By understanding the genetic basis of a trait, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment plans.
👉 Note: Autosomal pedigrees are not limited to genetic disorders; they can also be used to study the inheritance of any trait.
In conclusion, autosomal pedigrees are a powerful tool in genetics, allowing researchers to study the inheritance of traits and identify patterns of inheritance. By understanding how to read and create autosomal pedigrees, you’ll be able to unlock the secrets of genetics and gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of inheritance.
What is the difference between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance?
+Autosomal dominant inheritance requires only one copy of the dominant allele to express the trait, while autosomal recessive inheritance requires two copies of the recessive allele.
How do I determine the genotype of an individual in an autosomal pedigree?
+To determine the genotype, you need to analyze the pedigree and look for patterns of inheritance. You can also use Punnett squares to predict the genotype of offspring.
Can autosomal pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of any trait?
+Yes, autosomal pedigrees can be used to study the inheritance of any trait, not just genetic disorders.