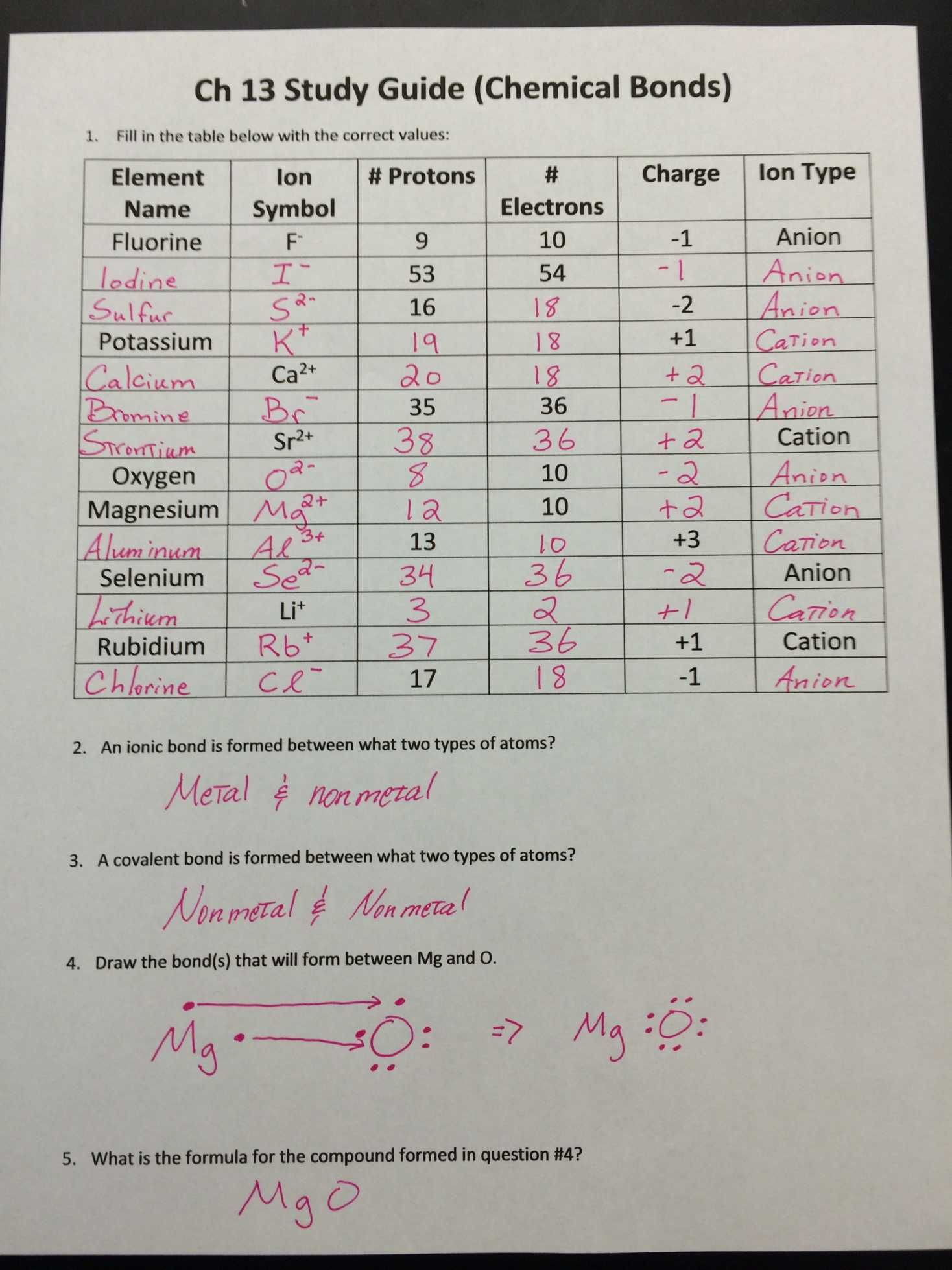
Atoms Worksheet Answers
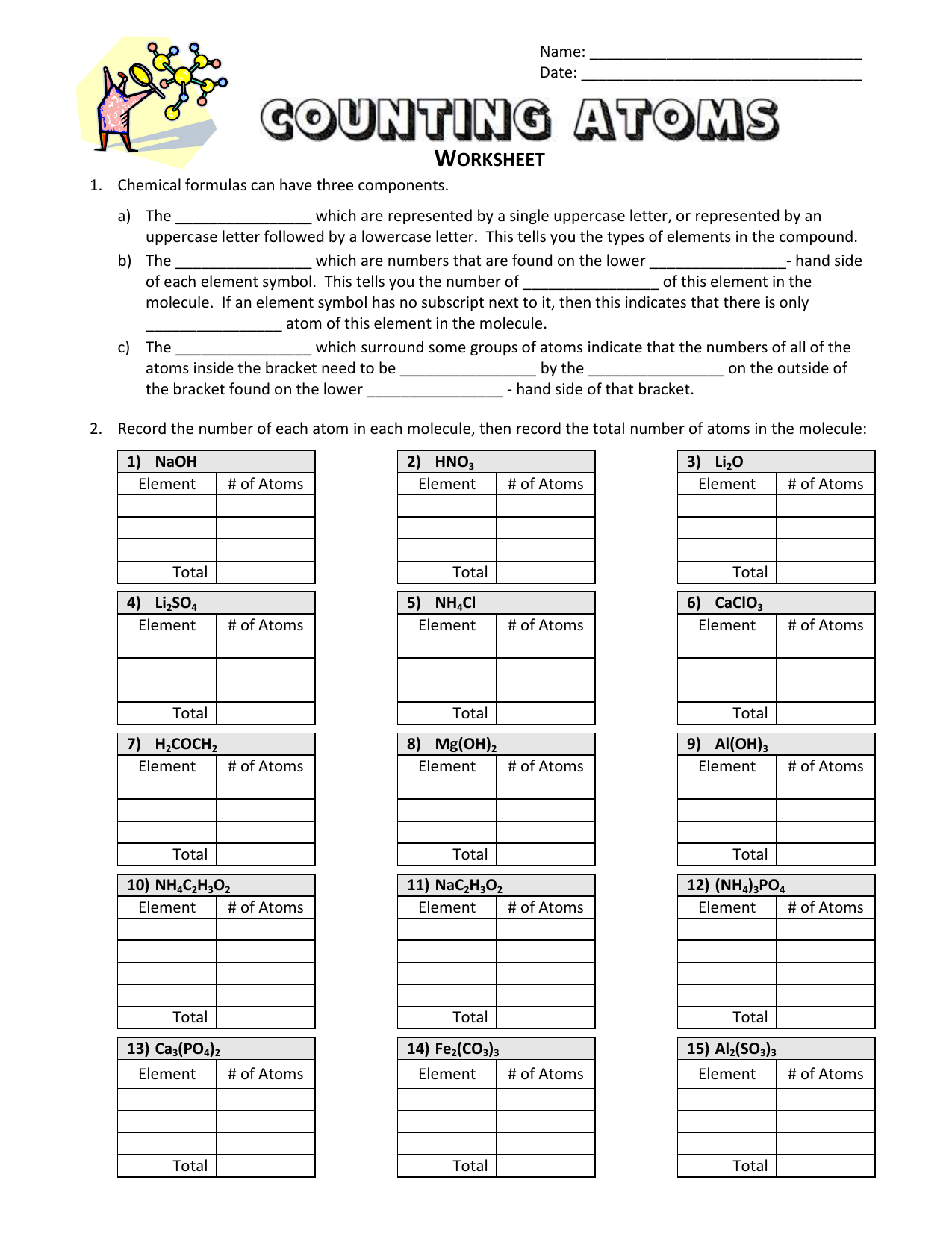
Understanding Atoms: A Comprehensive Guide
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, and understanding their structure and properties is crucial for various fields of science, including physics, chemistry, and biology. In this article, we will delve into the world of atoms, exploring their components, types, and characteristics.
What is an Atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element that retains the properties of that element. It consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that are found in the nucleus along with protons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
Structure of an Atom
The structure of an atom can be likened to a solar system, with the nucleus at the center and the electrons orbiting around it. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus determine the mass of the atom, while the electrons determine its chemical properties.
| Particle | Charge | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | Positive | Nucleus | Determines atomic number |
| Neutron | Neutral | Nucleus | Contributes to mass |
| Electron | Negative | Orbiting nucleus | Determines chemical properties |
Types of Atoms
Atoms can be classified into different types based on their atomic number (number of protons), mass number (total number of protons and neutrons), and electron configuration.
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
- Isobars: Atoms of different elements with the same number of nucleons (protons and neutrons).
- Ion: An atom that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
Atomic Models
Over the years, several atomic models have been proposed to explain the structure and behavior of atoms. Some of the most notable models include:
- Rutherford Model: Proposed by Ernest Rutherford, this model describes the atom as a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
- Bohr Model: Developed by Niels Bohr, this model introduces energy levels and electron shells to explain atomic behavior.
- Quantum Mechanical Model: A modern model that uses quantum mechanics to describe the behavior of electrons in atoms.
🔍 Note: The quantum mechanical model is a complex and abstract concept that is still being refined and expanded upon by scientists.
Atomic Bonding
Atoms can bond with each other to form molecules through various types of chemical bonds. The main types of chemical bonds are:
- Ionic Bonds: Formed when electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
- Covalent Bonds: Formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- Metallic Bonds: Found in metals, these bonds involve the delocalization of electrons among a lattice of metal ions.
Atomic Applications
The study of atoms has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Energy Production: Nuclear power plants generate electricity by harnessing the energy released from atomic reactions.
- Materials Science: Understanding the properties of atoms is crucial for the development of new materials with unique properties.
- Medicine: Radioisotopes are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
In summary, atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, and understanding their structure and properties is essential for various scientific fields. By exploring the components, types, and characteristics of atoms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate world of atomic science.
What is the smallest unit of a chemical element?
+
An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element that retains the properties of that element.
What are the three main parts of an atom?
+
The three main parts of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
+
An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element, while a molecule is a group of atoms bonded together.
Related Terms:
- Periodic table practice worksheet
- Isotope practice worksheet