Atoms vs Ions Worksheet: Understanding the Difference
Atoms vs Ions: Understanding the Difference
In chemistry, atoms and ions are two fundamental concepts that are often confused with each other. While they are related, they have distinct differences in terms of their structure, properties, and behavior. In this article, we will explore the difference between atoms and ions, and provide a comprehensive guide to understanding these concepts.
What are Atoms?
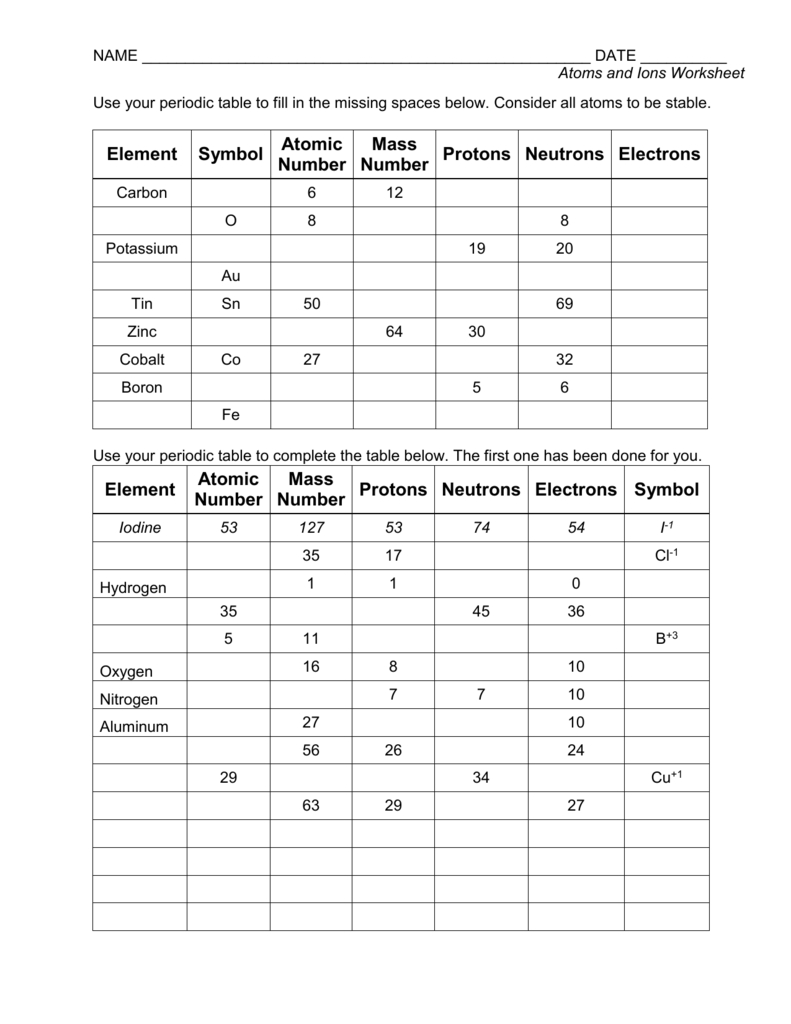
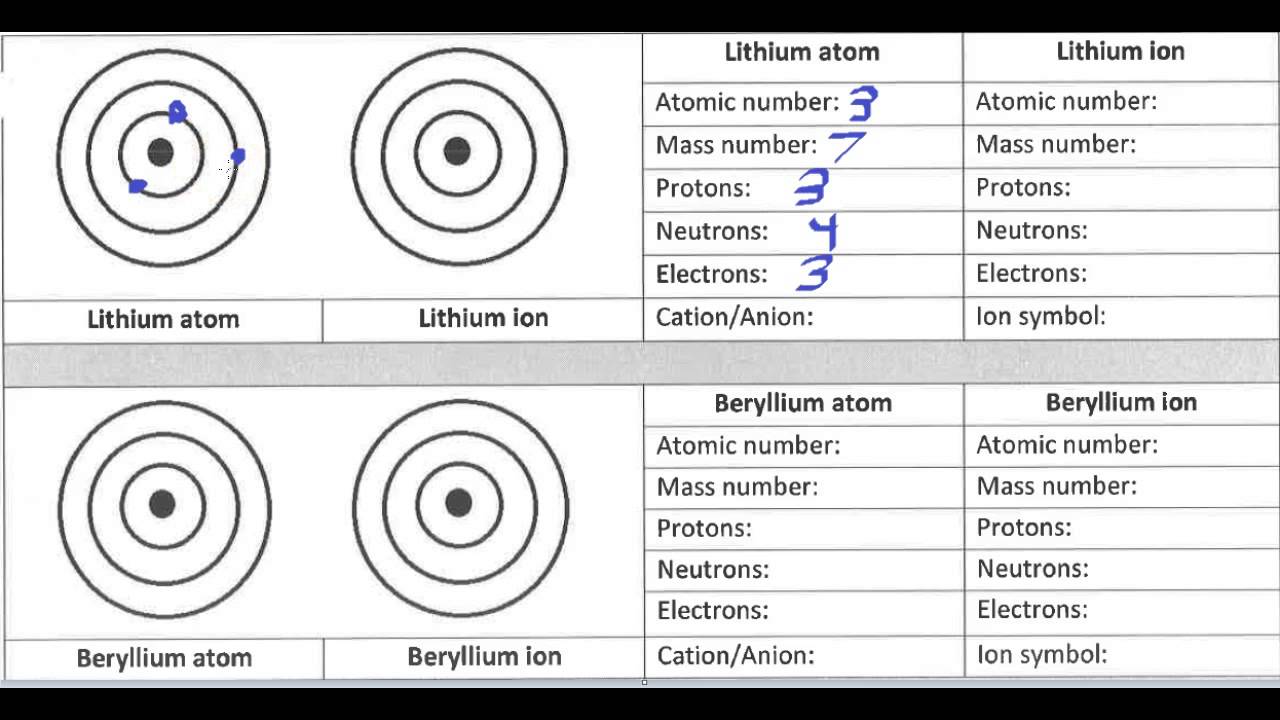
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
Atoms are neutral in charge, meaning they have an equal number of protons and electrons. This balance of charge is what makes atoms stable and allows them to exist independently.
What are Ions?
An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion, known as a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion, known as an anion.
Ions are formed when an atom reacts with other atoms or molecules, resulting in the transfer of electrons. This transfer of electrons can occur through various chemical reactions, such as acid-base reactions or redox reactions.
Key Differences between Atoms and Ions
Here are the main differences between atoms and ions:
- Charge: Atoms are neutral in charge, while ions have a net positive or negative charge.
- Number of Electrons: Atoms have a fixed number of electrons, while ions have a different number of electrons due to the gain or loss of electrons.
- Reactivity: Atoms are less reactive than ions, as ions have a stronger tendency to react with other atoms or molecules to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
- Formation: Atoms are formed through nuclear reactions, while ions are formed through chemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons.
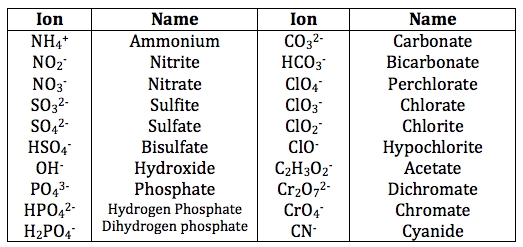
Examples of Atoms and Ions
Here are some examples of atoms and ions:
| Atom | Ion |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | Hydrogen ion (H+) |
| Oxygen (O) | Oxide ion (O2-) |
| Sodium (Na) | Sodium ion (Na+) |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Chloride ion (Cl-) |
🔹 Note: The above table shows examples of atoms and their corresponding ions. The ions are formed by the gain or loss of electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
Conclusion
In conclusion, atoms and ions are two distinct concepts in chemistry that have different properties and behaviors. Atoms are neutral in charge and have a fixed number of electrons, while ions have a net positive or negative charge and a different number of electrons. Understanding the difference between atoms and ions is crucial in chemistry, as it helps us to predict the behavior of elements and compounds in various chemical reactions.
What is the main difference between an atom and an ion?
+The main difference between an atom and an ion is the charge. Atoms are neutral in charge, while ions have a net positive or negative charge due to the gain or loss of electrons.
What is an example of a positively charged ion?
+An example of a positively charged ion is a sodium ion (Na+), which is formed when a sodium atom loses an electron.
What is the process called when an atom gains or loses electrons to form an ion?
+The process is called ionization, which involves the gain or loss of electrons to form a positively or negatively charged ion.
Related Terms:
- Atoms vs Ions Worksheet PDF
- Atoms vs ions worksheet answers
- Ions Worksheet with answers
- Isotope ion worksheet
- Ion Charges Worksheet